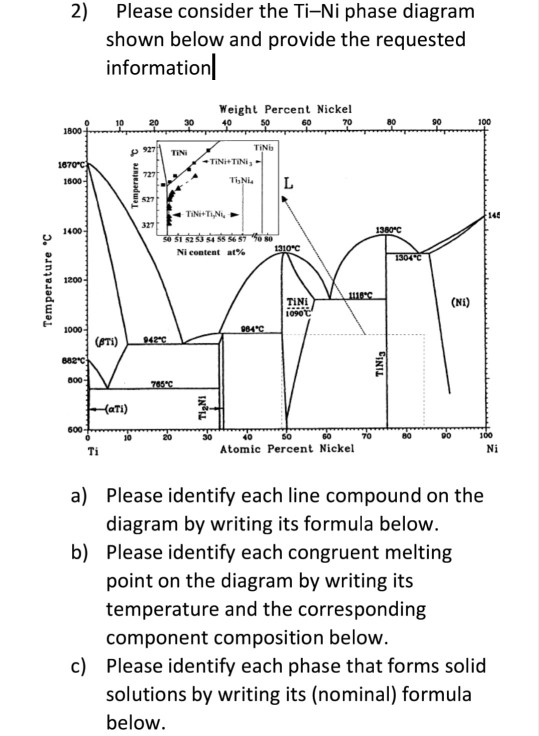
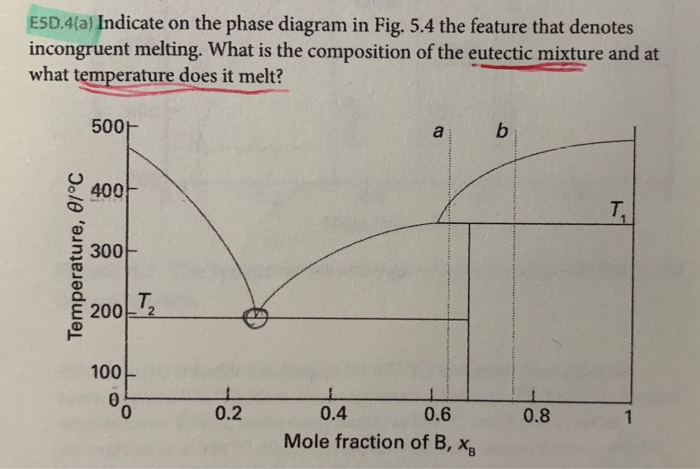
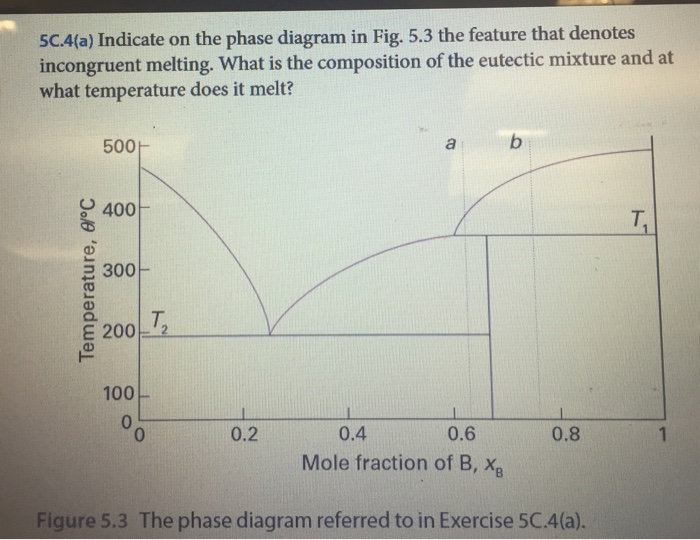
38 incongruent melting phase diagram
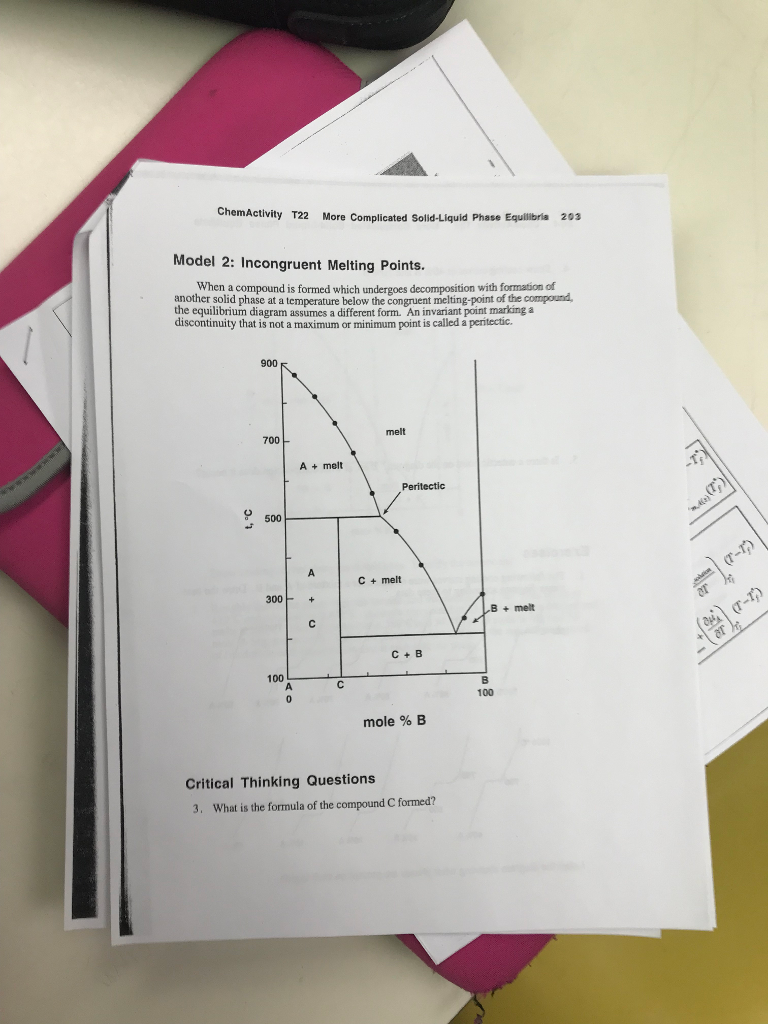
Incongruent melting occurs when a solid substance does not melt uniformly, so that the chemical composition of the resulting liquid is not the same as that of the original solid. During incongruent melting a new solid of different composition forms. In addition, phase diagrams provide valuable information about melting, casting, crystallization, and other phenomena. Phase transformations in which there are no compositional alternations are said to be congruent transformations, and during incongruent transformations at least one of the phases will...
ch3 part1 v2 - ltachai/335/phase_ congruent melting b. incongruent melting c. dissociation. Invariant Univariant Bivariant. SiO2(a) Equilibrium diagram(b) Metastable phases. Two-Component Phase DiagramBinary system: A B. P = 1 atm.
Incongruent melting phase diagram
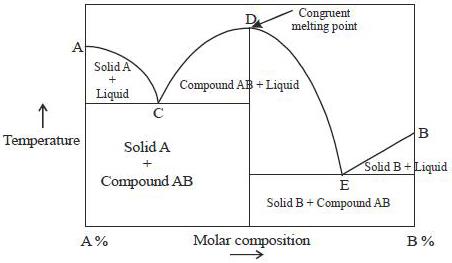
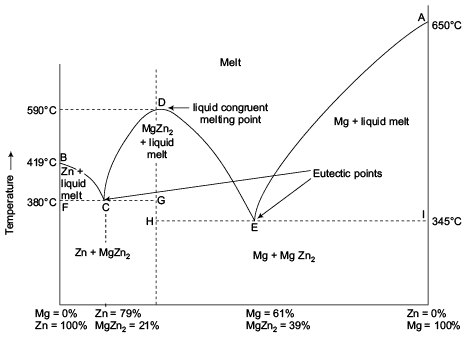
Liquid-Solid Phase Diagrams Eutectics Reacting Systems Incongruent Melting. Temperature compositions diagrams show the boundaries of compositions of phases at equilibrium at different temperatures at a given pressure (typically 1 atm) - liquid phase in lower part of diagram. Is the melting congruent? YVO3: incongruent melting when doped with Calcium TbMn2O5: decomposes in TbMnO3 and Mn3O4 BiFeO3: Bi2Fe4O9 and Bi25FeO40 stable phases. Observation of the phase diagram. Incongruent Melting • Binary Systems • The end components in this binary phase diagram also melt congruently. • The intermediate compound in this diagram (XY2) however is incongruently melting. • Incongruent melting is the temperature at which one solid phase transforms to another solid phase...
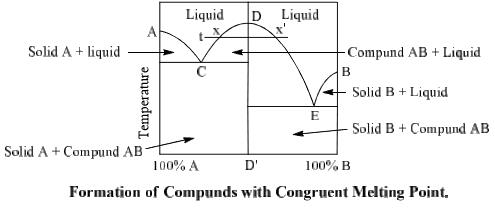
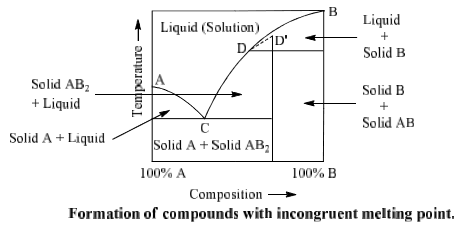
Incongruent melting phase diagram. End of incongruent melting process. Represented by letter C on binary phase diagram. Eutectic mixture. The beginning of incongruent melting is represented by this point on binary phase diagram. IV. Point representing melting point of pure compound A. Incongruent melting occurs when a substance does not melt uniformly and decomposes into another substance. Phase diagram — In physical chemistry, mineralogy, and materials science, a phase diagram is a type of graph used to show the equilibrium conditions between the thermodynamically... Incongruent melting point is called meritectic or peritectic temperature. In this process three phases i.e. two solids and one liquid are present so it is nonvariant system. The phase diagram has four maxima corresponding to the formation of four hydrates. Point C (37°C). E(32.5°C) and I(78.5°C)... Incongruent melting occurs when a solid substance does not melt uniformly, so that the chemical composition of the resulting liquid is not the same as that of A phase diagram in physical chemistry, engineering, mineralogy, and materials science is a type of chart used to show conditions at which...
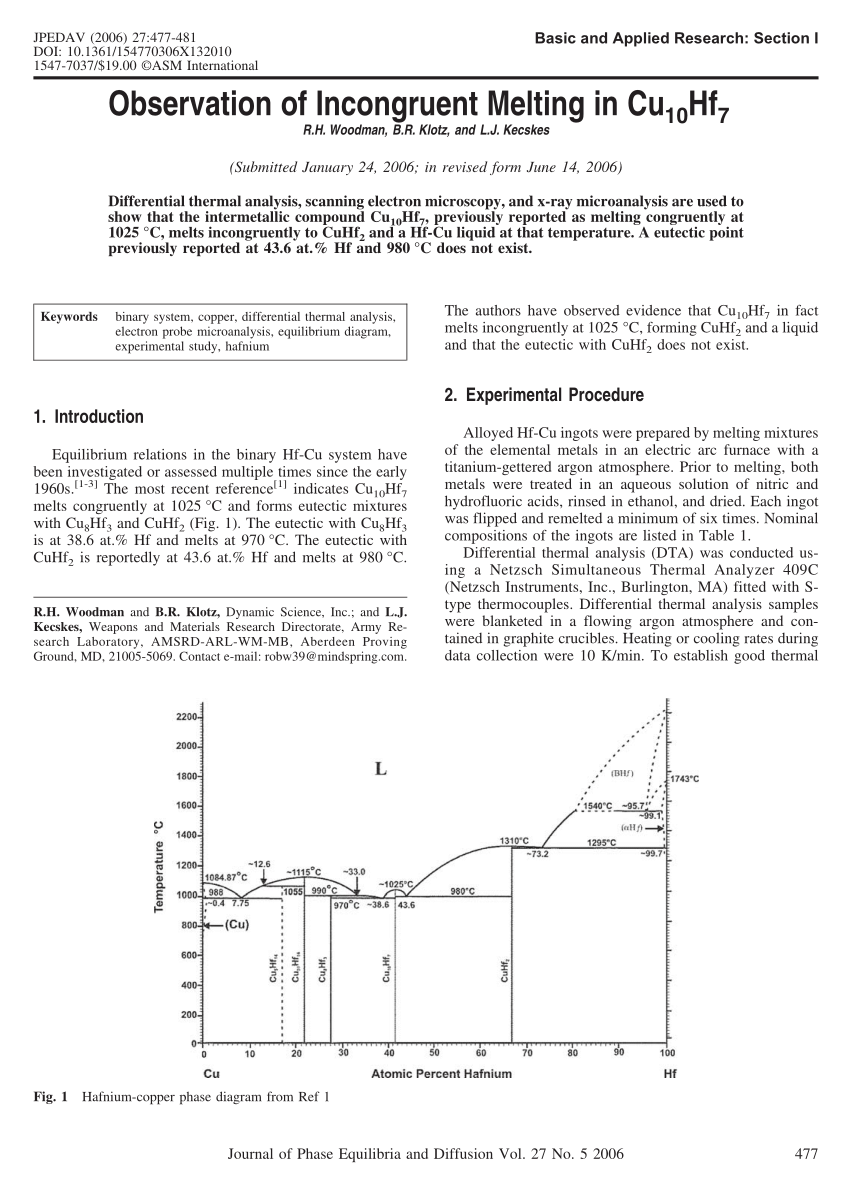
3.33 Schematic drawing of phase diagram around GaAs composition. TJ denotes the incongruent melting temperature for stoichiometric GaAs and denotes the congruent melting temperature. The congruent melting composition is assumed to be in the As excess region. incongruent melting, liquefaction of a solid accompanied by decomposition or by reaction with the melt to produce another solid and a liquid that differs in composition from the original solid. For example, enstatite, a magnesium silicate (MgSiO3), melts incongruently at low pressures to form. Unary phase diagrams will not let us get very far towards being able to understanding melting and crystallization because most rocks contain two or more In Figure 22 a binary phase diagram is given in which there are three incongruent melting compounds of intermediate composition - C, D, and E. Incongruent Melting. Steven Dutch, Professor Emeritus, Natural and Applied Sciences, Universityof Wisconsin - Green Bay. Thus we can expect the phase diagram to look as at left. We expect a field where solid enstatite and forsterite occur, and another field where solid enstatite and quartz occur.
Use simple phase diagrams - graphic device to illustrate equilibria between different phases. Graphical portrayal of the stability ranges of minerals and melts as functions of bulk composition, temperature, and pressure. Fractional crystallization - in incongruent melting diagram. The phase equilibrium diagram is a useful tool to visualize phase behavior. Phase equilibrium is a theoretical condition where the liquids and vapors have reached certain pressure and temperature conditions at which they can separate. Figure 3.3 illustrates several operating points on a generic... I understand that congruent melting means that the solid and liquid phases have the same composition, and that in incongruent melting, the third intermediate compound decomposes upon melting. However, I am having trouble relating this to the phase diagrams that supposedly depict congruent and incongruent melting. For [congruent](https://slideplayer.com/slide/13310126/80/images/14/Compounds+formation+with+congruent+melting+point..jpg) melting: does the liquid phase then contain all three compoun... The phase diagram for the (pseudo-) binary SrO-CuO system is shown in figure 6.7 for air atmosphere at ambient pressure [169]. In analogy to CuO the melting of Sr 2 CuO 3 , SrCuO 2 and Sr 14 Cu 24 O 41 is also incongruent in respect to the oxygen content, i.e. the equilibrium melt is oxygen poorer...
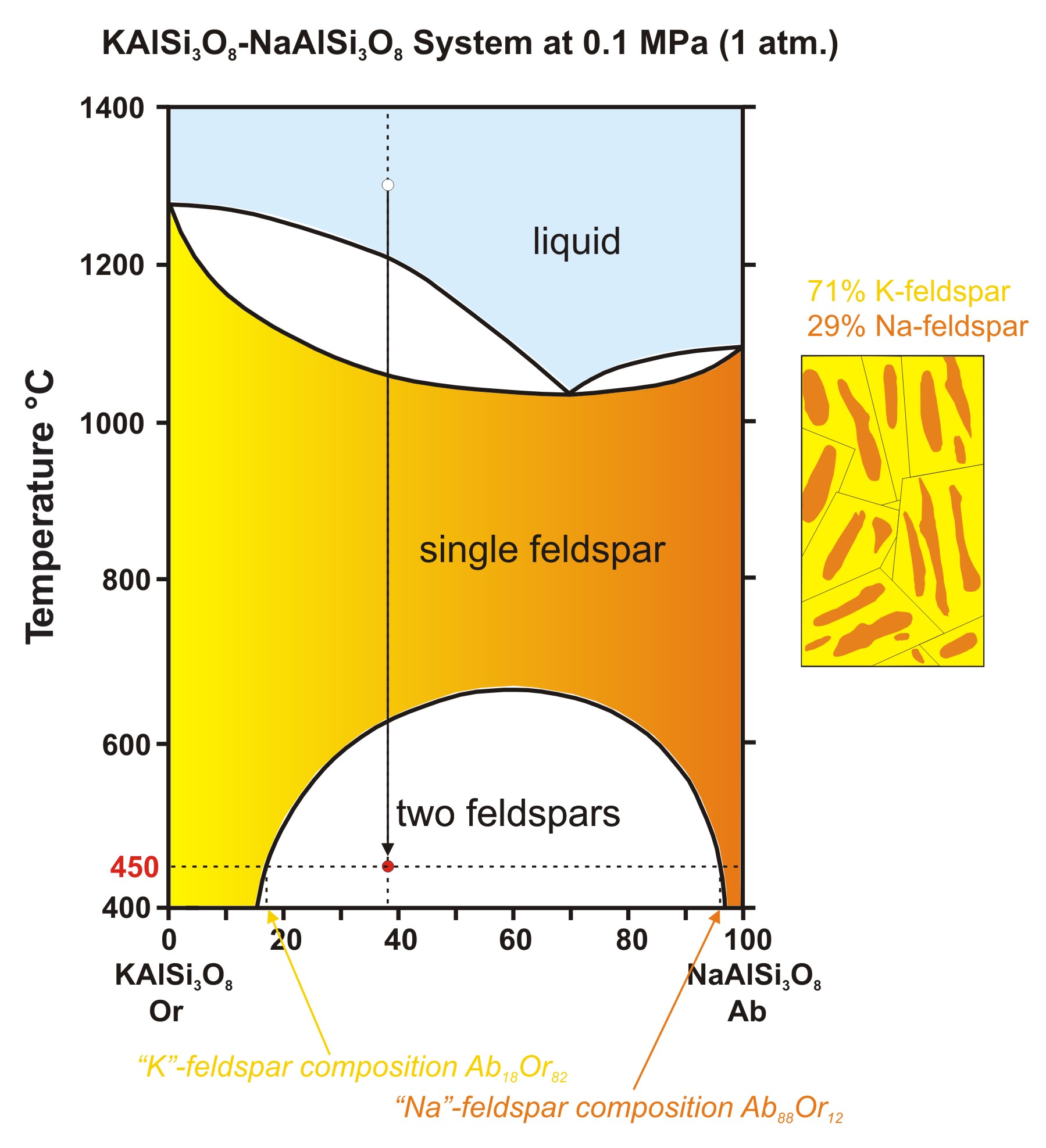
Incongruent melting occurs when a solid substance does not melt uniformly. During melting a new solid (of different composition) forms. For example, melting of orthoclase (KAlSi3O8) produces leucite (KAlSi2O6) in addition to a melt. The melt produced is rich in silica (SiO2)...
Incongruent melting - melting wherein a phase melts to a liquid with a composition different from the solid and produces a solid of different a phase diagram that has an intermediate compound that melts incongruently. a phase diagram that shows complete solid solution between two endmembers.
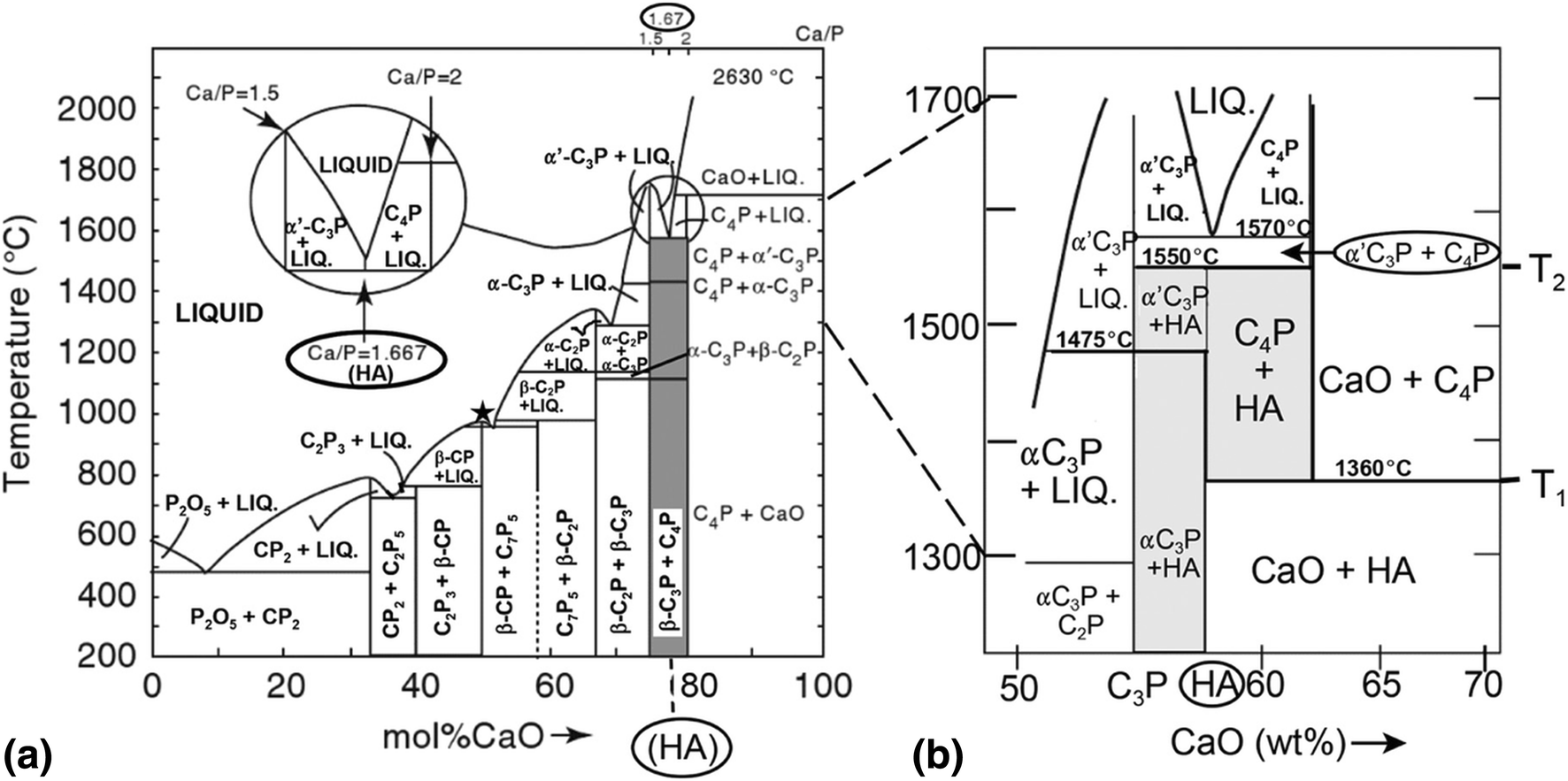
Properly constructed phase diagrams display the phase relations at thermodynamic equilibrium state of matter. That makes them unique for a given material system. That is, the single phase SiC crystal decomposes into a liquid and graphite, also called incongruent melting.
Phase diagrams with congruently melting compound8:56. By the nature of melting, intermediate phases can be divided into congruent and incongruent melting phases.
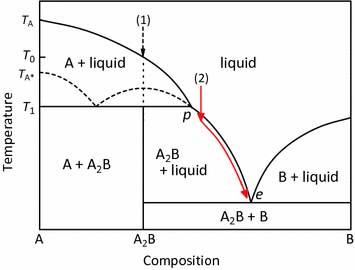
Incongruent Melting. • Binary Systems - The end components in this binary phase diagram also melt congruently. - Incongruent melting is the temperature at which one solid phase transforms to another solid phase and a liquid phase both of different chemical compositions than the original...
Phase Equilibria And Phase Rule Part 2 Thermodynamics Physical Chemistry Csir Net Government Jobs Notes Edurev
Isobaric T-X phase diagram of the system Fo-Silica at 0.1 MPa. After Bowen and Anderson (1914) and Grieg (1927). Different phases have different compressibilities Thus P will change Gibbs Free Energy differentially ● Raises melting point ● Shift eutectic position (and thus X of first melt, etc.)
Some phase diagrams (those for 1-component diagrams) depict relationships involving multiple phases having the same composition (for example, the relationships between the vapor, liquid and solid forms of H2O). Some involve incongruent melting; most do not.

Consider The Following Phase Diagram Of A Reacting System A Identify The Phases Present In Each Homeworklib
Incongruent melting occurs when a solid substance does not melt uniformly. A phase diagram tells us what phases are present at a particular combination of state variables. In order to orient ourselves in this diagram, we look first of all at the homogeneous phases.
Incongruent melting - melting wherein a phase melts to a liquid with a composition different from the solid and produces a solid of different composition to the original solid. For the case of incongruent melting, we will use the system forsterite (Mg2SiO4) - silica (SiO2), which has an intermediate...
TOPICS IN CHEMISTRY-DM Part Six of Phase Equilibrium Following topics are discussed. Two Component System Phase Diagram. Cooling Curve of pure compound Cooling Curve of Mixture Simple Eutectic Mixture Congruent Melting Point Incongruent Melting point peritectic reaction.
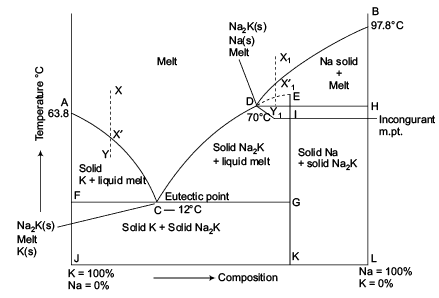
The important part of the phase diagram are the compositions of equal amounts of A and B (x = 0.5), pure A and pure B. Solid deposited along the cooling isopleth "a" is compound C. solid. phases, with. Incongruent Melting. Sometimes component C is not stable as a liquid (e.g., alloy Na2K).
q Incongruent melting: A crystalline phase melts into a solid phase (peritectic phase) and a liquid phase of different composition; primary phase region q Growth by cooling the stoichiometric melt: congruent melting substances q Growth by cooling melt solution (flux). (3) Ternary phase diagrams.
Incongruent Melting • Binary Systems • The end components in this binary phase diagram also melt congruently. • The intermediate compound in this diagram (XY2) however is incongruently melting. • Incongruent melting is the temperature at which one solid phase transforms to another solid phase...
Is the melting congruent? YVO3: incongruent melting when doped with Calcium TbMn2O5: decomposes in TbMnO3 and Mn3O4 BiFeO3: Bi2Fe4O9 and Bi25FeO40 stable phases. Observation of the phase diagram.
Liquid-Solid Phase Diagrams Eutectics Reacting Systems Incongruent Melting. Temperature compositions diagrams show the boundaries of compositions of phases at equilibrium at different temperatures at a given pressure (typically 1 atm) - liquid phase in lower part of diagram.
Phase Diagram That Shown Below Represents The Congruent Melting Point Which Of The Following Statementsare Not Correct A There Will Be Three Freezing Point Curves B Congruent Melting Point Always Liesabove The Melting Point Of
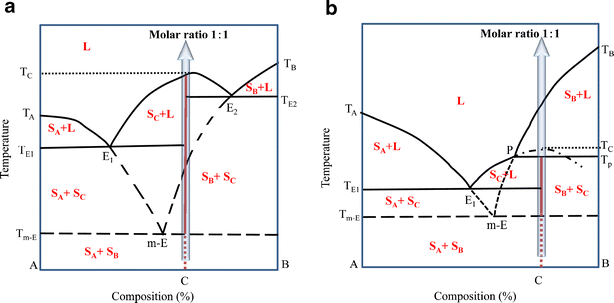
Figure 1 Detection Of Cocrystal Formation Based On Binary Phase Diagrams Using Thermal Analysis Springerlink

Figure 1 From Coformer Screening Using Thermal Analysis Based On Binary Phase Diagrams Semantic Scholar











0 Response to "38 incongruent melting phase diagram"
Post a Comment