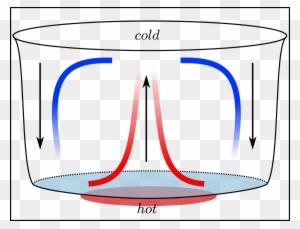
38 diagram of convection currents
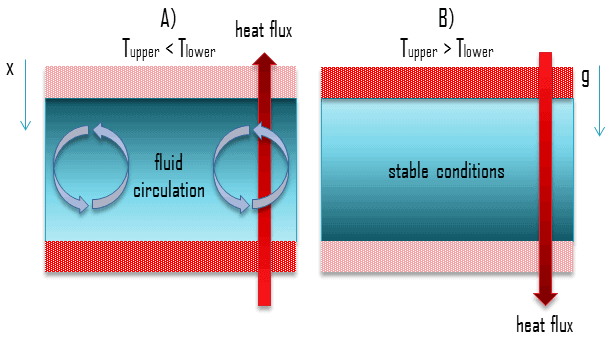
The T-Q diagram reveals two important truths regarding heat transfer: (1) T-lines for counter-current flows do not cross! It is impossible. (2) T-lines should not approach each other too closely: As they approach, the area required for heat transfer goes to infinity. The point of closest approach is called pinch point. Heat Exchangers: The T-Q ... Start studying Convection Currents. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
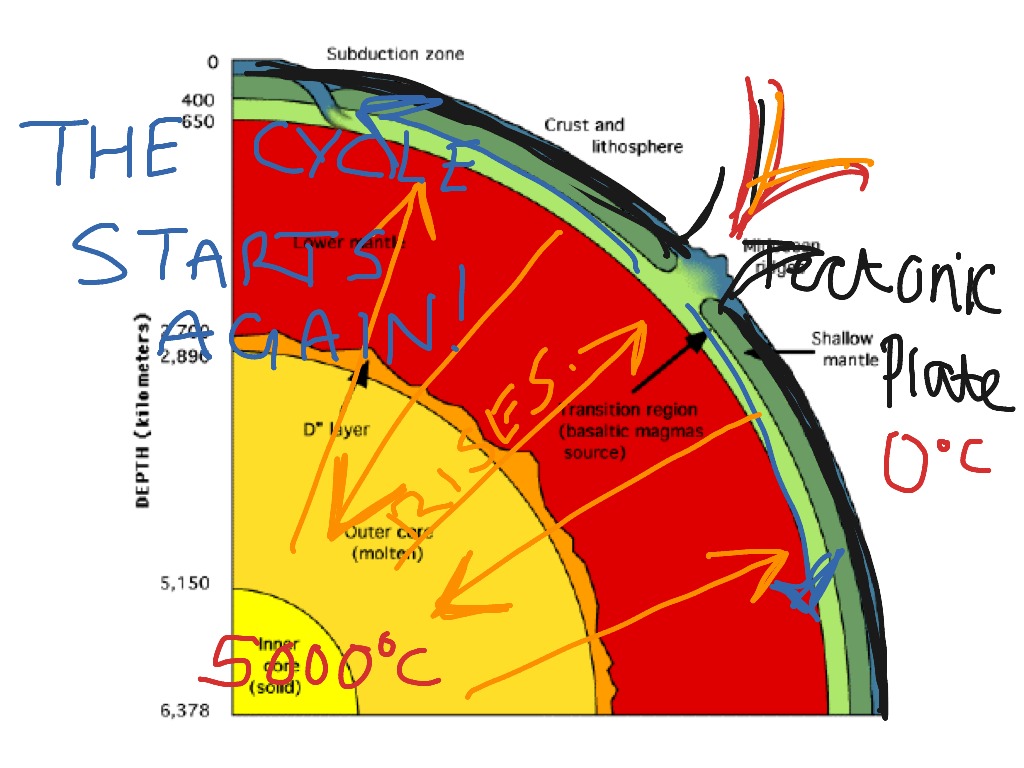
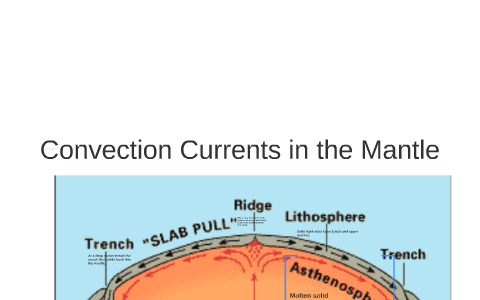
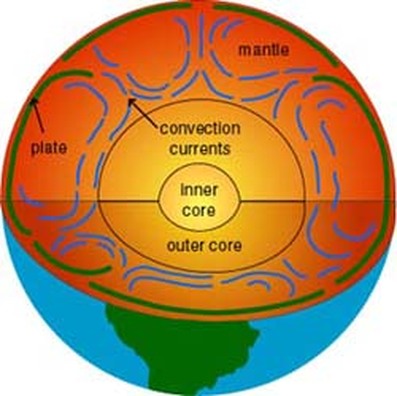
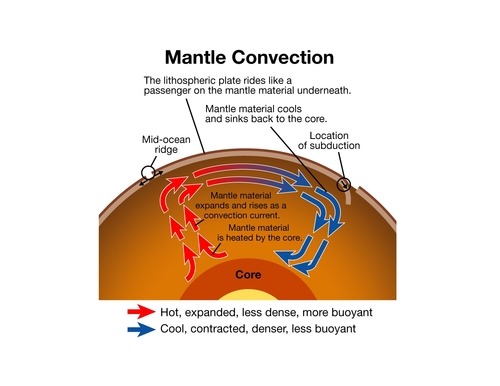
The Earth's crust is broken up into pieces called plates. The crust moves because of movements deep inside the earth. Heat rising and falling inside the mantle creates convection currents ...

Diagram of convection currents
convection currents. electromagnetic radiation. energy transfer by conduction. Tags: Question 5 . SURVEY . 30 seconds . Q. What is an insulator? ... Q. Use the diagram of a convection current to answer the question that follows. Which arrow represents the hottest air in this convection current? answer choices . 1. 2. 3. 4. Convection currents, that occur within the molten rock in the mantle, act like a conveyor belt for the plates. Tectonic plates move in different directions. A convection current refers to the movement of a liquid or gas during energy transfer. The liquid or gas moves upwards from the heat source (as it expands) and then downwards when the liquid or gas cools (as it contracts). Radiation is the transfer of energy where objects do not have to be physically touching.
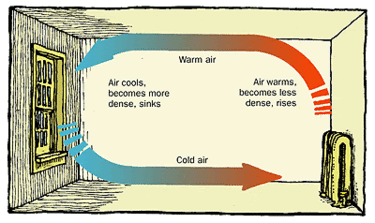
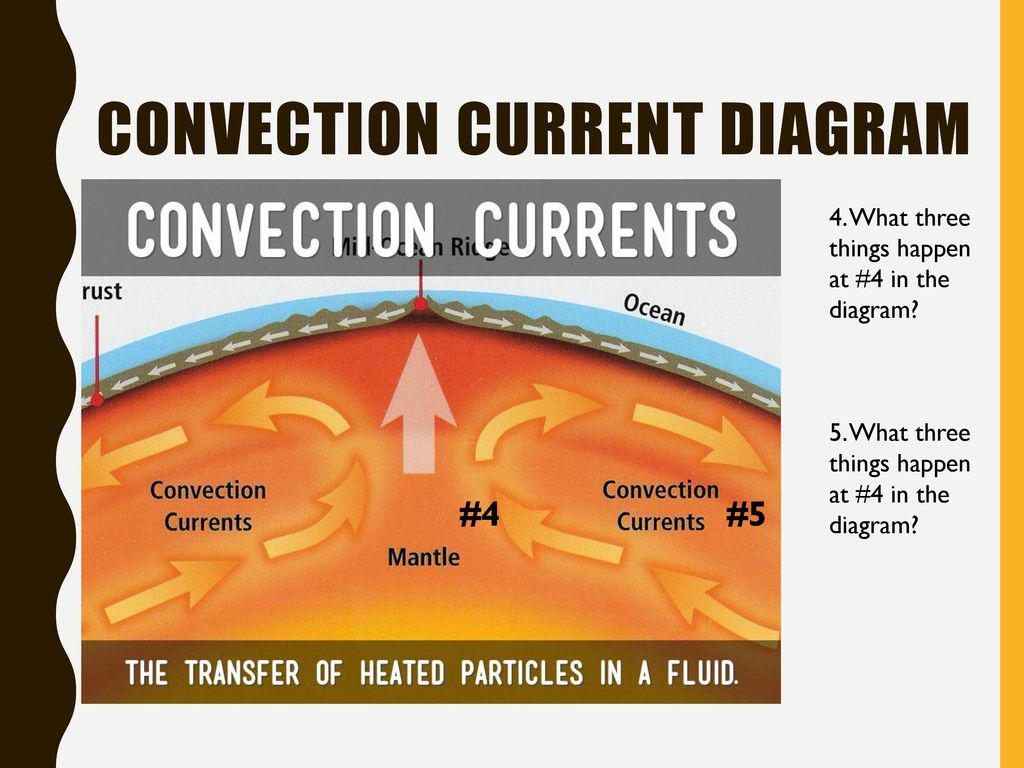
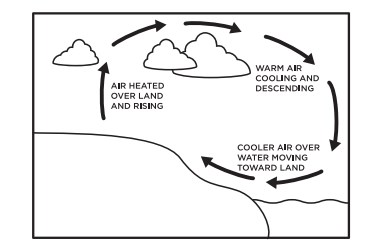
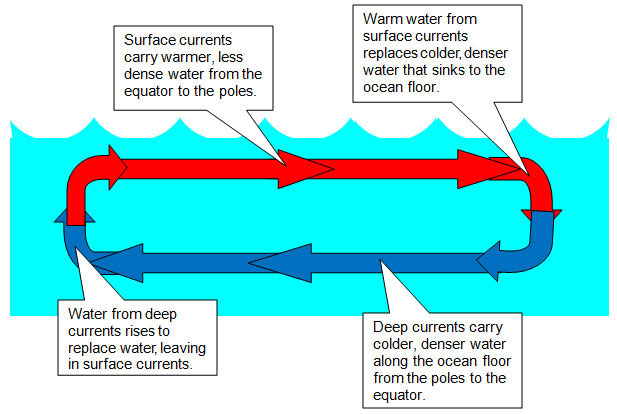
Diagram of convection currents. Convection currents are present in the air – A good example of convection current is the warm air that rises towards the ceiling in your house. The process happens as the warm air is said to be less dense than that of the colder air. Another good example of convection current is wind. The wind is mainly caused when the reflected radiation of ... Convection Currents, and these are very important for studying weather. 3. Radiation: Heat transfer by IR radiation. How heat is transferred through space; also works well in gases. Example: the heat from the sun. > A hot object will give off IR radiation; the hotter it is, the more intense the radiation (e.g., a bonfire vs. a match). We can ... Results 1 - 24 of 612 — Browse convection currents diagrams resources on Teachers Pay Teachers, a marketplace trusted by millions of teachers for original ... Mantle convection is the very slow creeping motion of Earth's solid silicate mantle caused by convection currents carrying heat from the interior to the ...
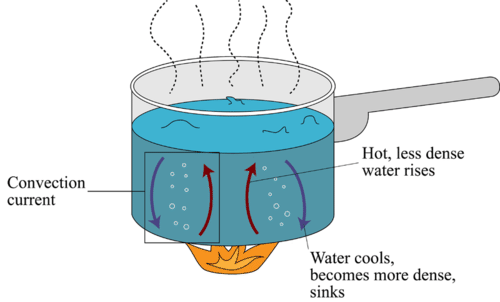
Diagram of a convection current Lucy Calkins, Earth Science, Heat Transfer, Diagram,. Visit. Save. From. ck12.org. Heat Transfer in the Atmosphere ( Read ) ... Theory that the Earth's crust is divided into tectonic plates which move around due to convection currents in the mantle. Convection currents The movement caused within a fluid by hotter and therefore less dense material to rise, and colder, denser material to sink under the influence of gravity. CONVECTION (teacher answers) I. Define: a) convection Convection is the transfer of heat energy which occurs when heated liquid or gas particles travel from one place to another. b) convection current Convection current is the circular pattern created when heat energy is transferred between particles. 2. Convection Currents are the reasons that the plates move. Label the parts of the diagram showing Convection in the Mantle. √ Steps to Convection in the ...4 pages
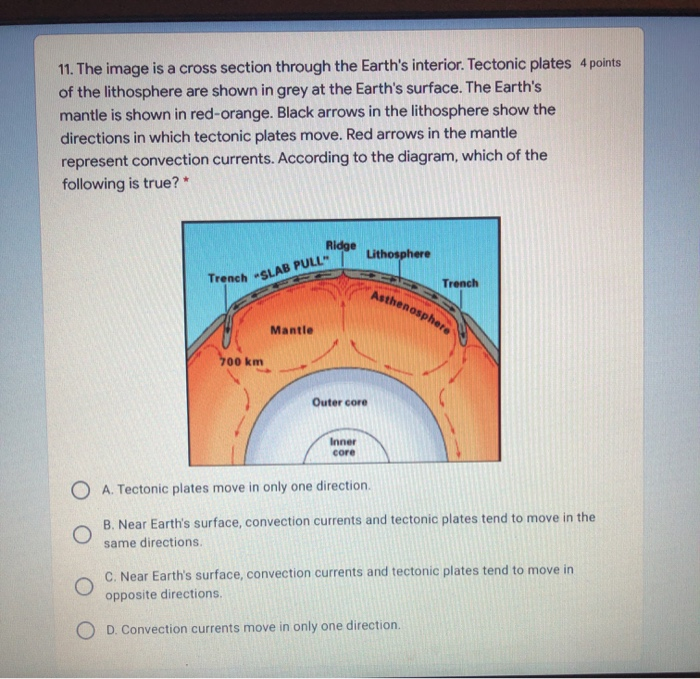
2:22Video of The roles that convection currents and other forces play in the movement of Earth's tectonic plates.8 Nov 2019 Diagram 2 shows the water level after one glass ball is added. ... A Convection currents occur because, when cooled, liquids contract and become more dense. B Convection currents occur because, when warmed, liquids expand and become more dense. C Convection currents only occur in liquids. A convection current refers to the movement of a liquid or gas during energy transfer. The liquid or gas moves upwards from the heat source (as it expands) and then downwards when the liquid or gas cools (as it contracts). Radiation is the transfer of energy where objects do not have to be physically touching. Convection currents, that occur within the molten rock in the mantle, act like a conveyor belt for the plates. Tectonic plates move in different directions.
convection currents. electromagnetic radiation. energy transfer by conduction. Tags: Question 5 . SURVEY . 30 seconds . Q. What is an insulator? ... Q. Use the diagram of a convection current to answer the question that follows. Which arrow represents the hottest air in this convection current? answer choices . 1. 2. 3. 4.





















0 Response to "38 diagram of convection currents"
Post a Comment