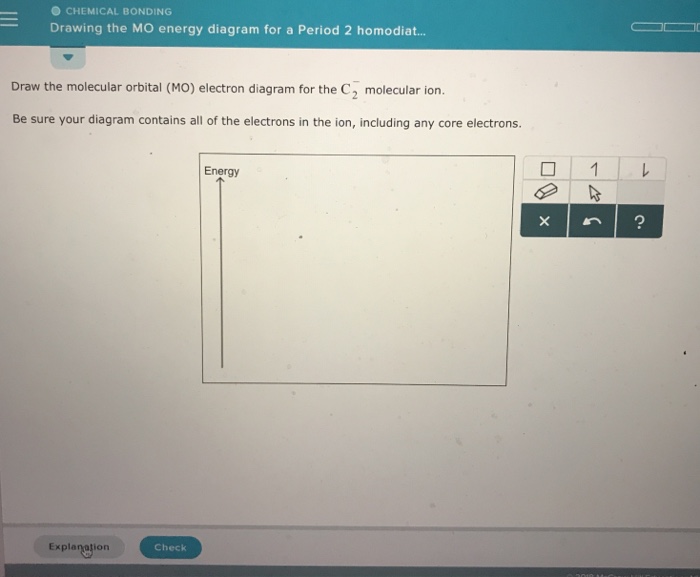
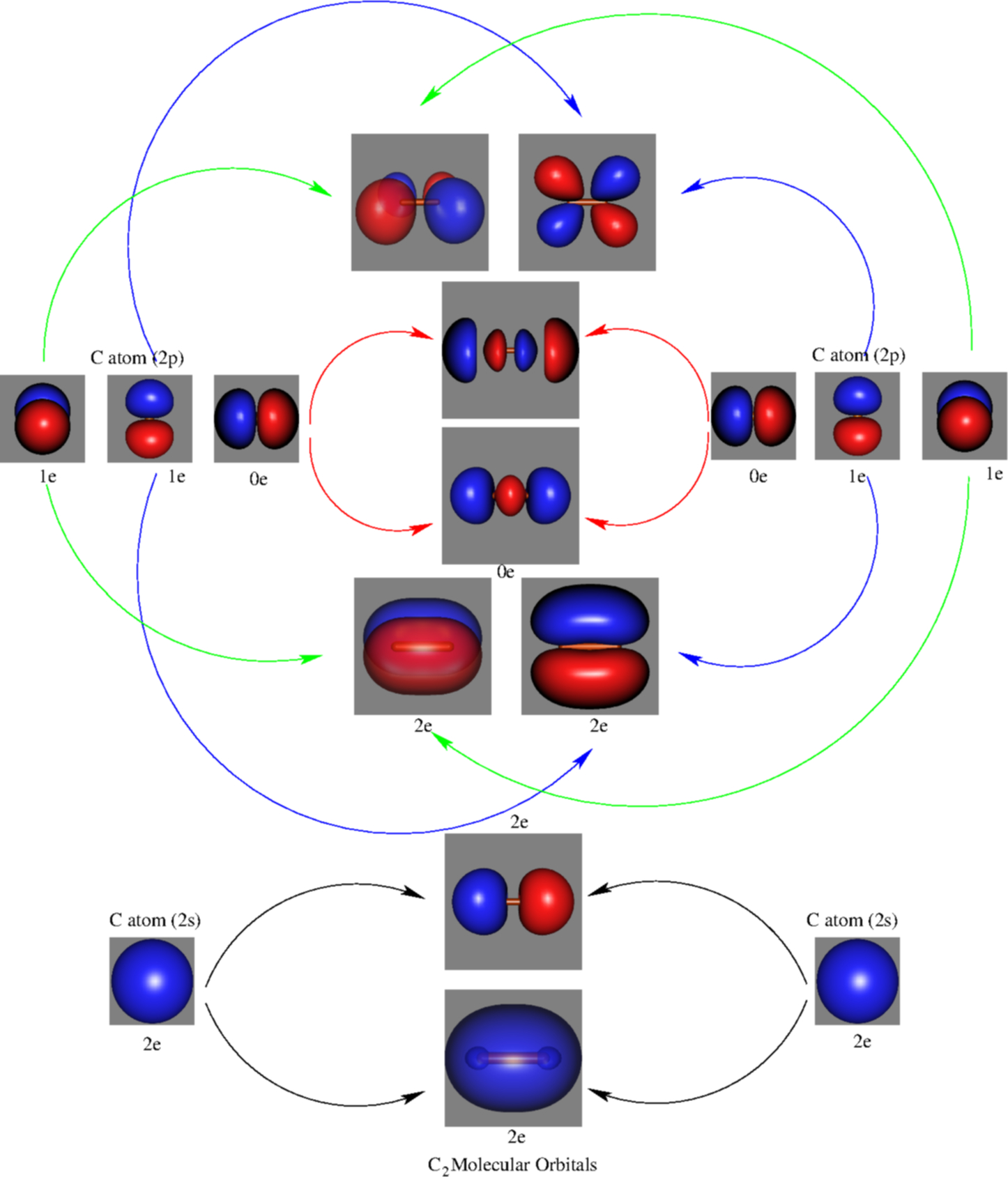
41 molecular orbital diagram c2
17.10.2018 · This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be2+, . electrons would be in a bonding orbital, we would predict the Li2 molecule to be . Explain why the relative energy levels diagrams for Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 are different The molecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical explanation. Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. … When two carbons atoms bond, the pi(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals.C2(2-) has a bond order of 3, so i...
First let us know what molecular orbital diagram is: A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. Now carbon monoxide’s MO ...
Molecular orbital diagram c2
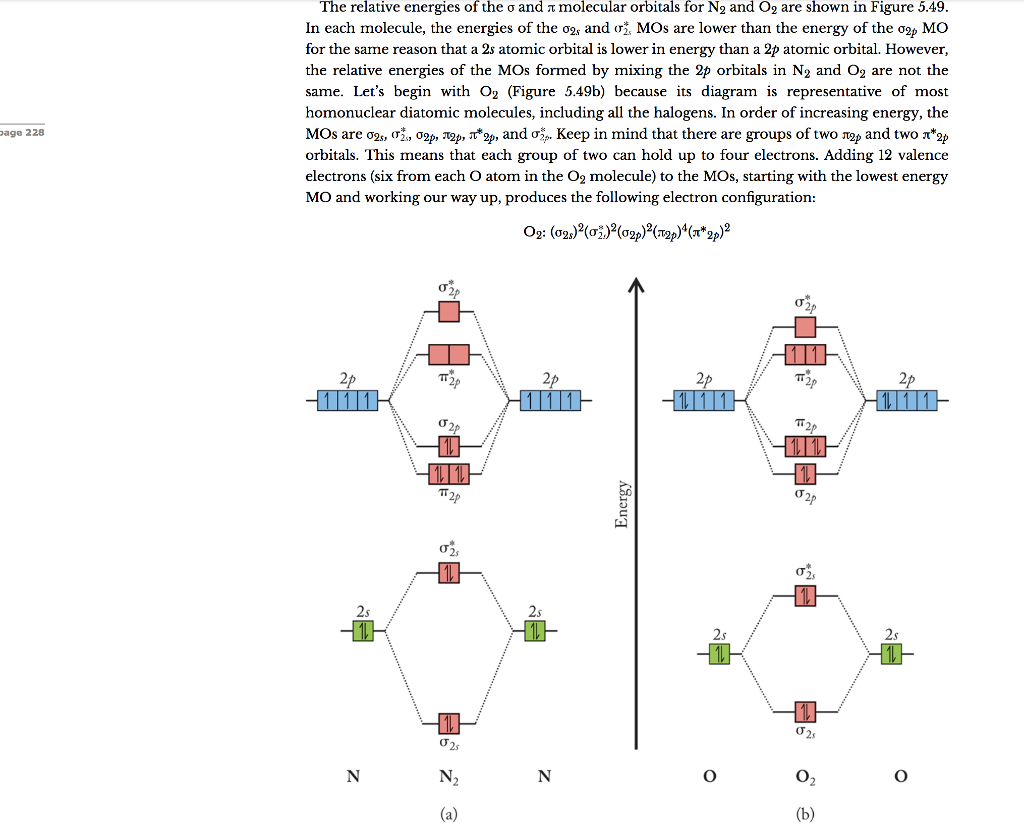
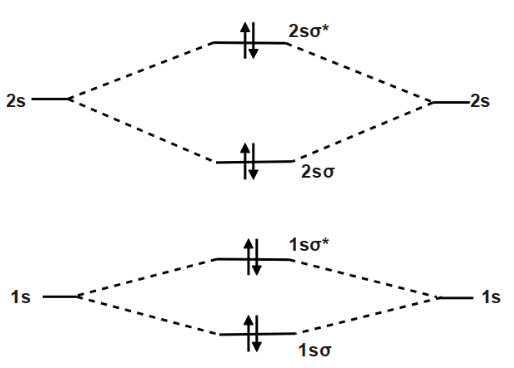
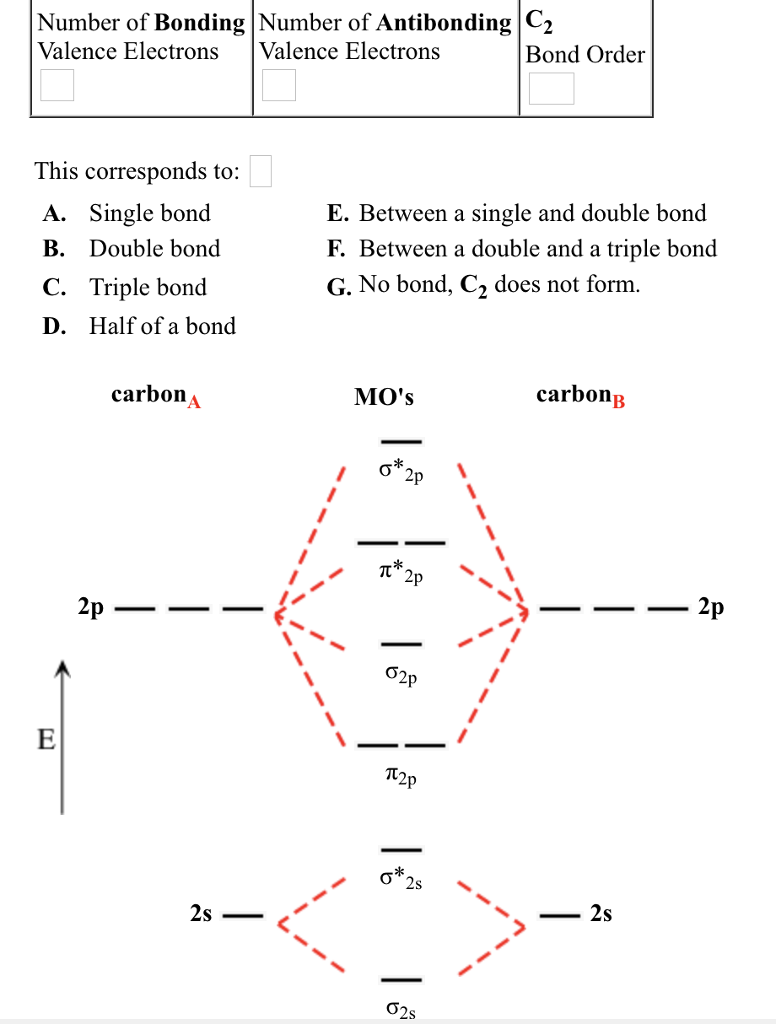
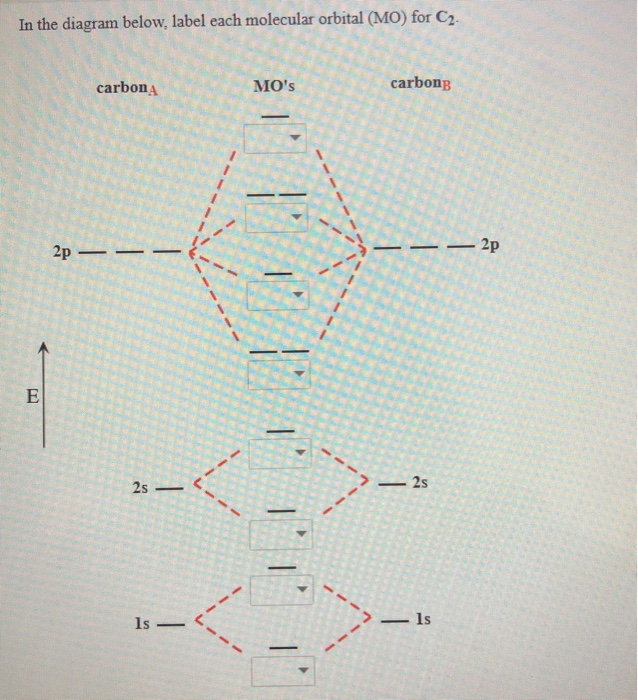
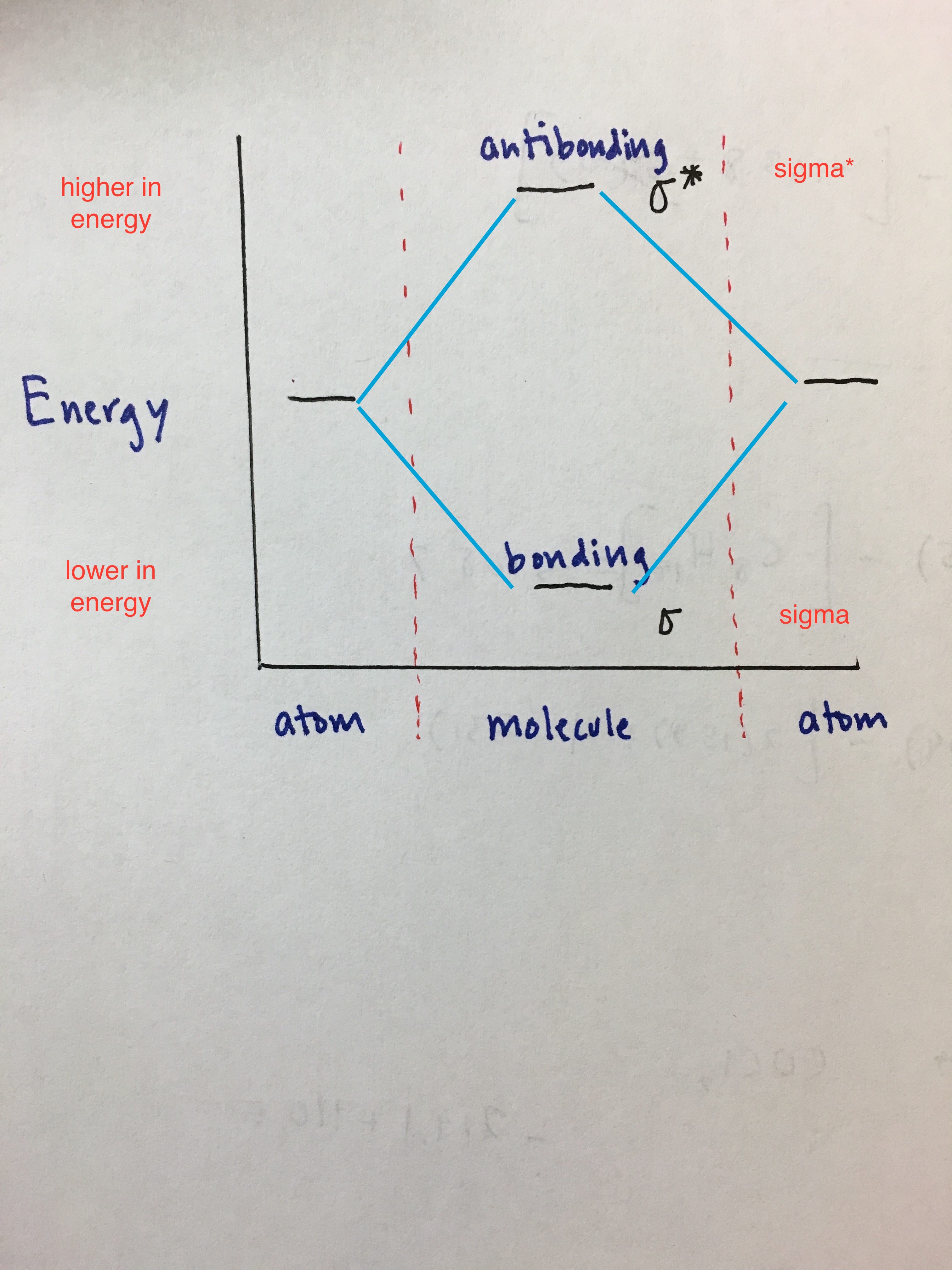
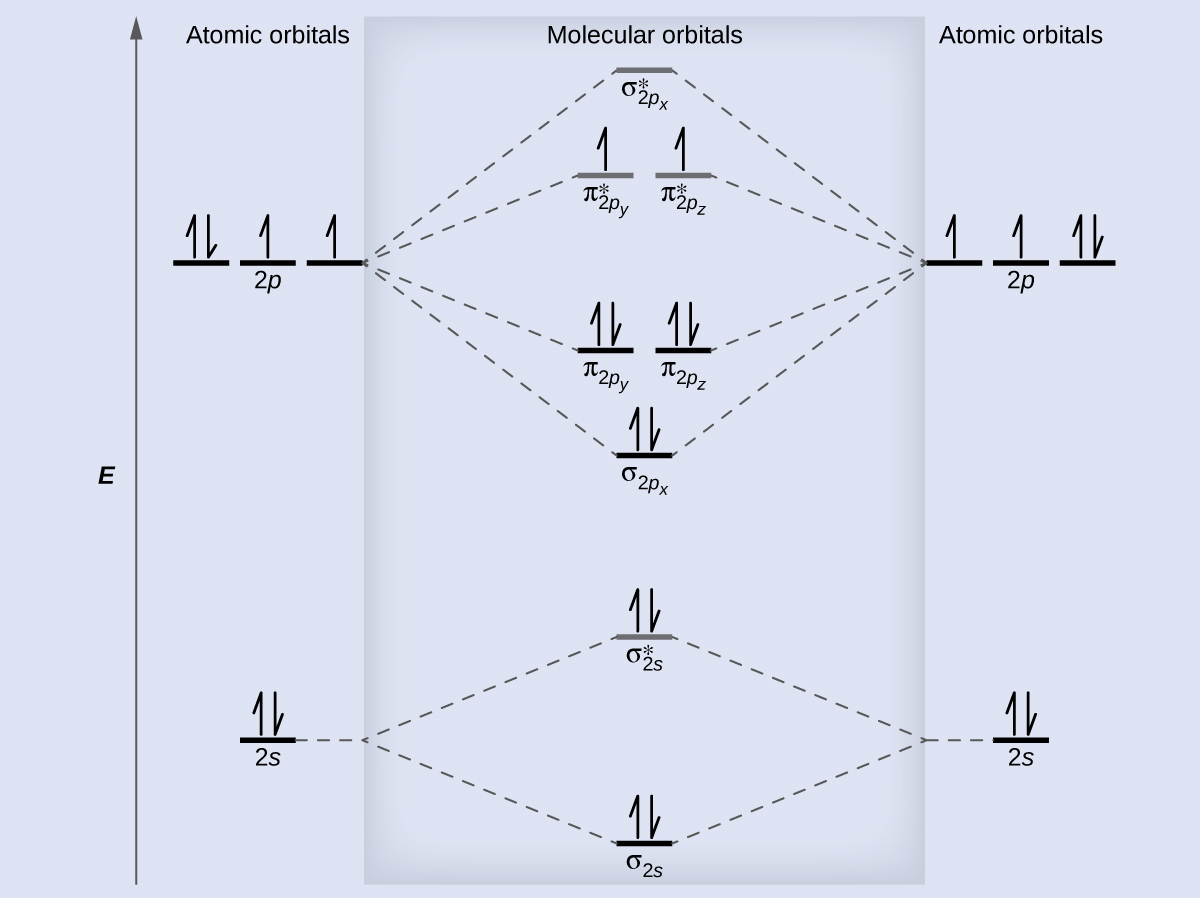
Place the following molecular orbitals in order of decreasing energy for species of B2, C2, and N2. start with the highest energy orbital. σ₂p* π₂p* σ₂p π₂p. Match each term with the appropriate electron arrangement paramagnetic diamagnetic. A molecular species with one or more unpaired electrons in an MO is _____ and will be attracted to a magnetic field, whereas a species with … d. the molecular orbital diagram for O2. e. hybridization of atomic orbitals in O2. 4. He2 doesn't exist naturally. Using MO theory, explain why. 5. (Note: Some instructors provide a blank MO orbital diagram on exams.) a. Draw the MO diagram for B2-2; include only the valence electrons in both the atomic and molecular orbitals. b. 04.09.2021 · The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Each horizontal line represents one orbital that can hold two electrons. The molecular orbitals …
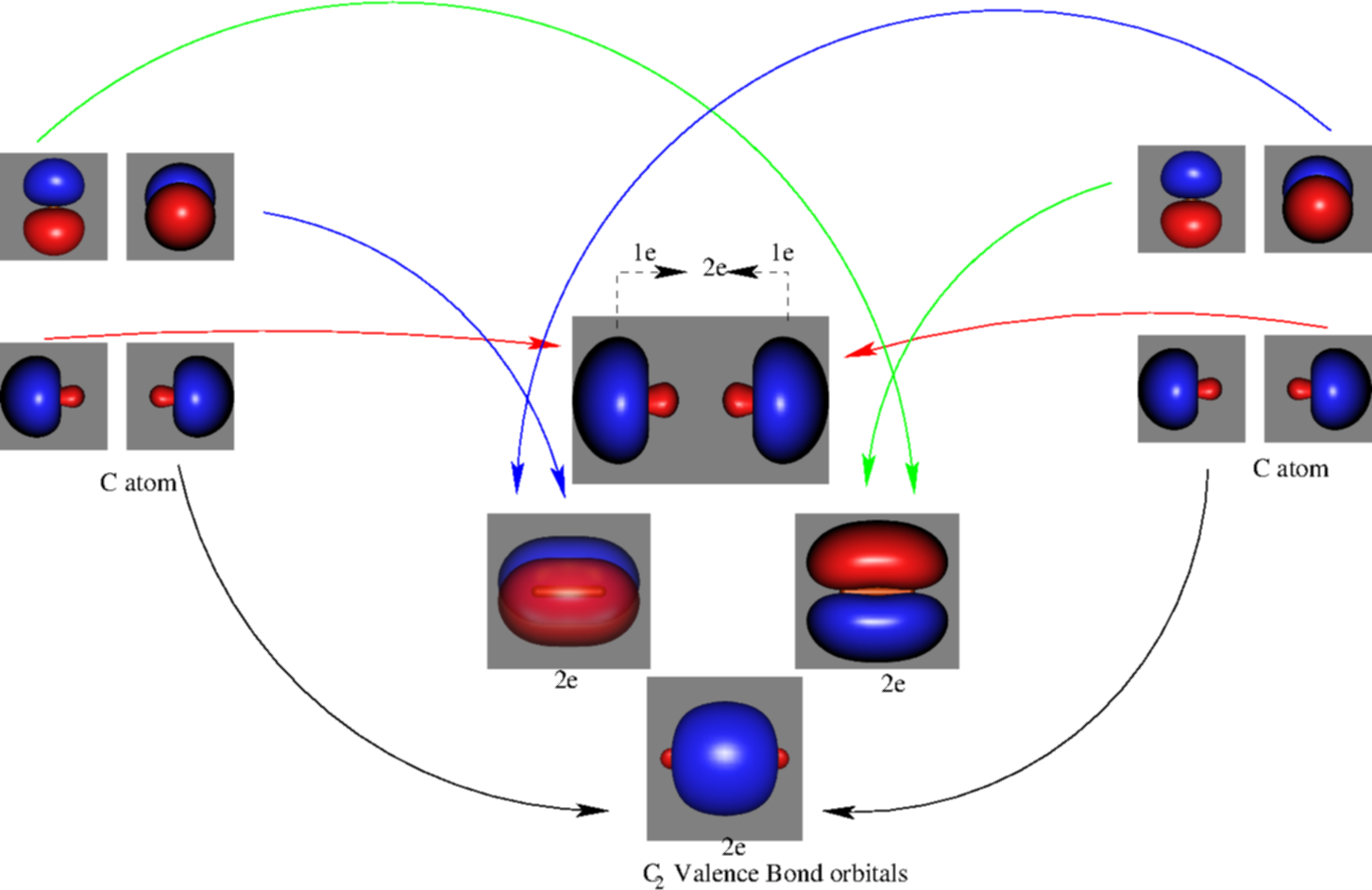
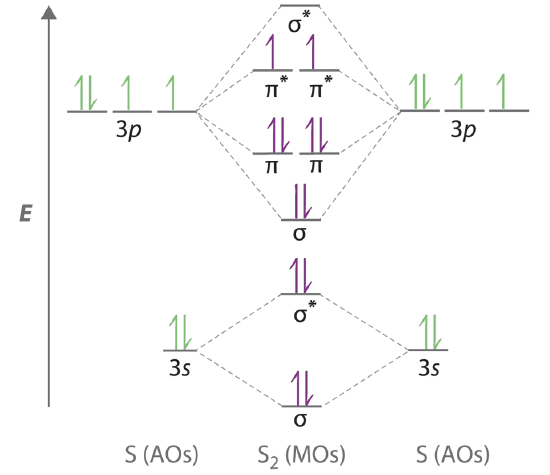
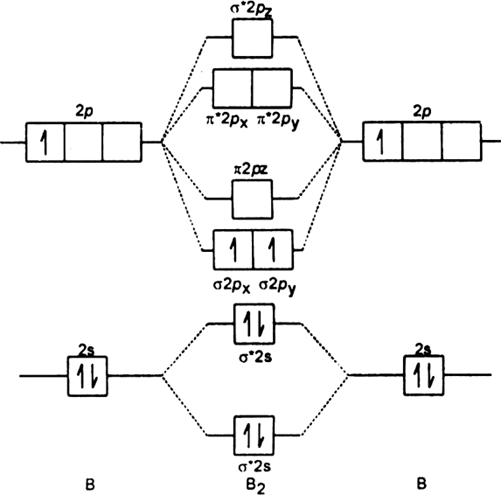
Molecular orbital diagram c2. 16.02.2017 · In the last post, we showed how to build a molecular orbital (MO) diagram for a typical C-C pi bond. We saw that: The number of molecular orbitals equalled the number of contributing atomic orbitals. The overlap of two atomic (p) orbitals gave rise to two molecular (pi, or π ) orbitals; The lowest-energy molecular orbital had all the phases in the contributing p … Answer (1 of 14): bond order = 3 Explanation = (1) no of electron in C = 6 (2) no of electron in O = 8 So, total no of electron = 14, so bond order = 3 Trick No. of electron = Bond order 12 = 2 13 = 2.5 14 = 3 15 = 2.5 16 = 2 17 =1.5 18 = 1 Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. Hydrogen | Fluorine | Nitrogen | Hydrogen Fluoride | Carbon Monoxide | Methane | Ammonia | Ethylene | Acetylene | Allene | Formaldehyde | Benzene 26 Feb 2018 — write molecular orbital configuration of c2+ predict magnetic behaviour and calculate its bond order. ... The C2 molecule is diamagnetic because ...
2 Dec 2016 · 1 answerHere's what I got. Explanation: The problem provides you with the MO diagram for the C2 molecule, so all you really have to do here is add ... A) The total number of molecular orbitals formed doesn't always equal the number of atomic orbitals in the set. B) A bond order of 0 represents a stable chemical bond. C) When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals, one molecular orbital will be lower in energy than the two separate atomic orbitals and one molecular orbital will be higher in … Molecular orbital theory shows that it has two sets of paired electrons in a degenerate bonding set of orbitals. This gives a bond order of two, which means ... 04.09.2021 · The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Each horizontal line represents one orbital that can hold two electrons. The molecular orbitals …
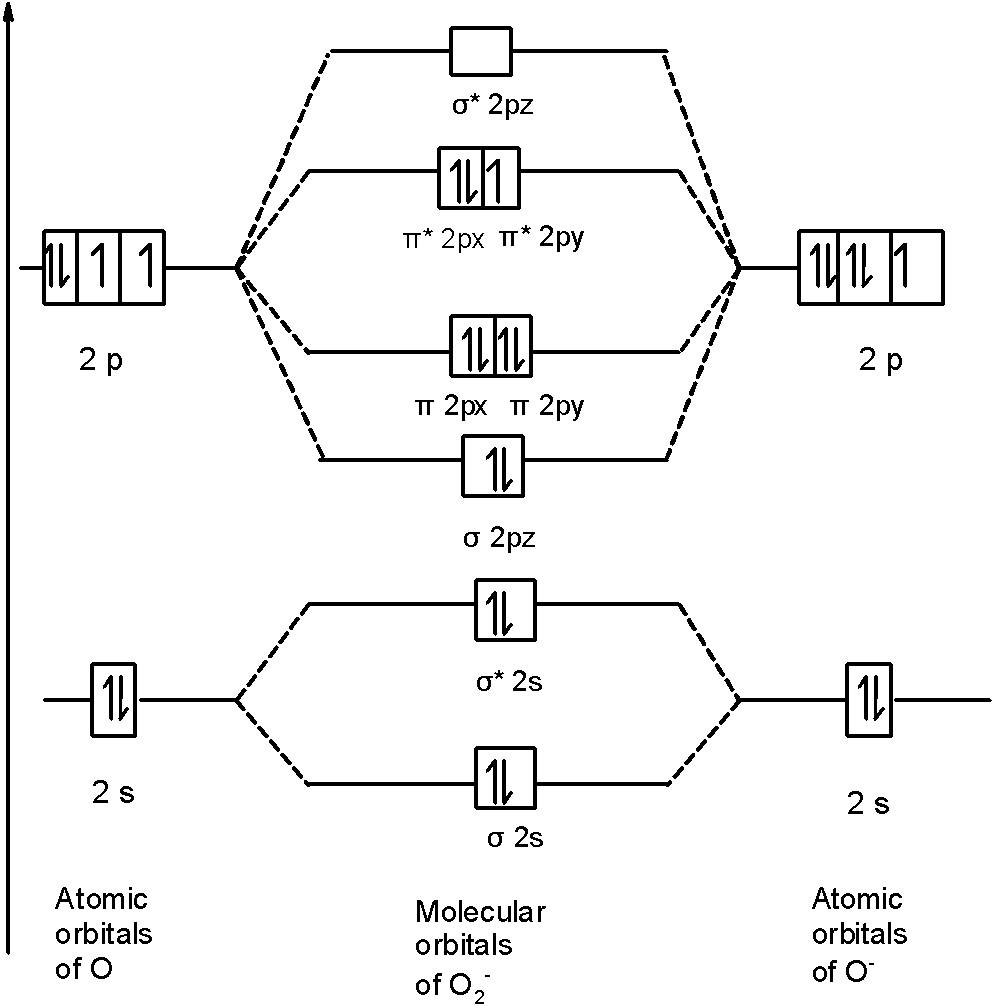
d. the molecular orbital diagram for O2. e. hybridization of atomic orbitals in O2. 4. He2 doesn't exist naturally. Using MO theory, explain why. 5. (Note: Some instructors provide a blank MO orbital diagram on exams.) a. Draw the MO diagram for B2-2; include only the valence electrons in both the atomic and molecular orbitals. b. Place the following molecular orbitals in order of decreasing energy for species of B2, C2, and N2. start with the highest energy orbital. σ₂p* π₂p* σ₂p π₂p. Match each term with the appropriate electron arrangement paramagnetic diamagnetic. A molecular species with one or more unpaired electrons in an MO is _____ and will be attracted to a magnetic field, whereas a species with …
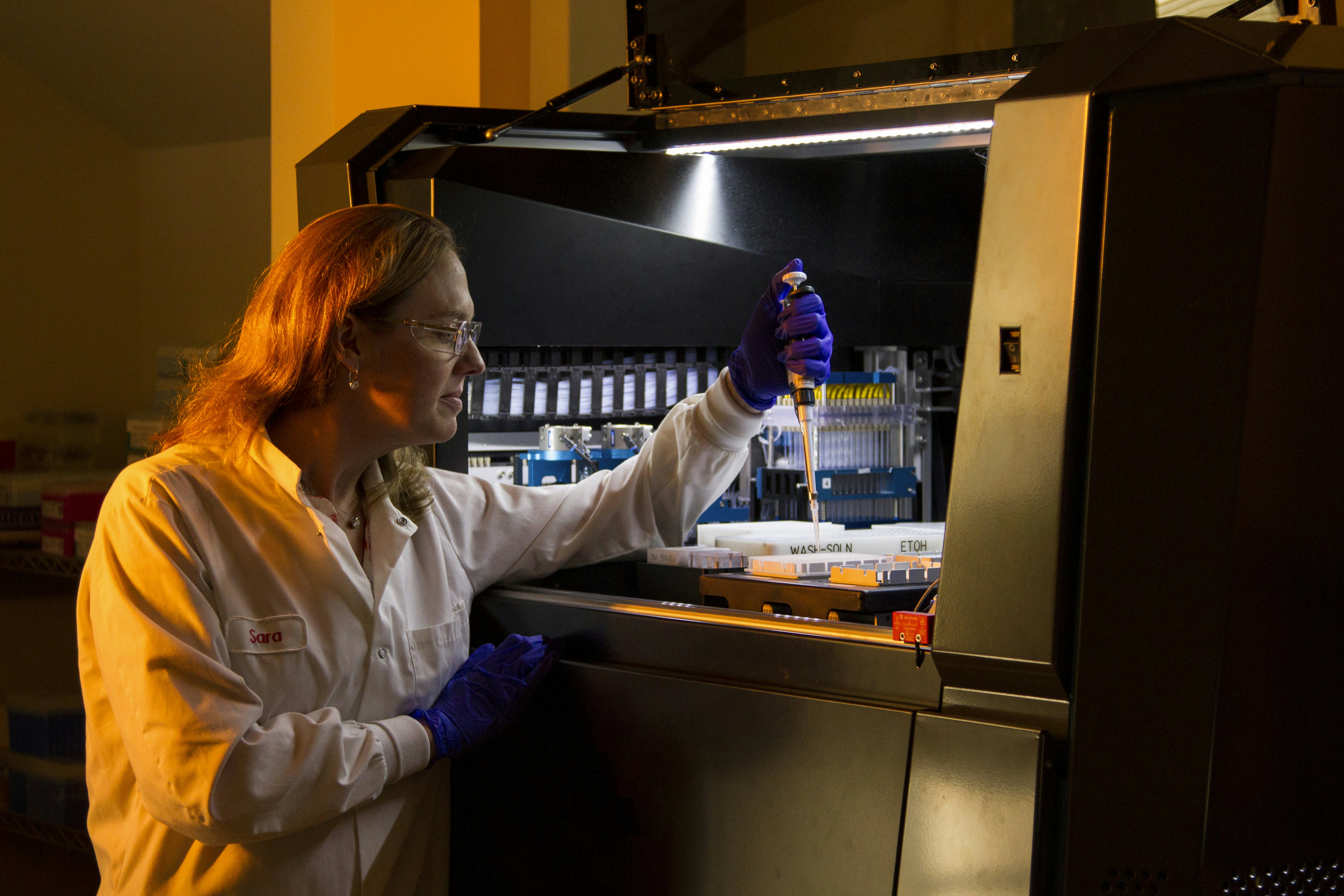

DNA Genotyping and Sequencing. Technician loads robot for genetic studies of the human papillomavirus (HPV) at the Cancer Genomics Research Laboratory, part of the National Cancer Institute's Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics (DCEG).
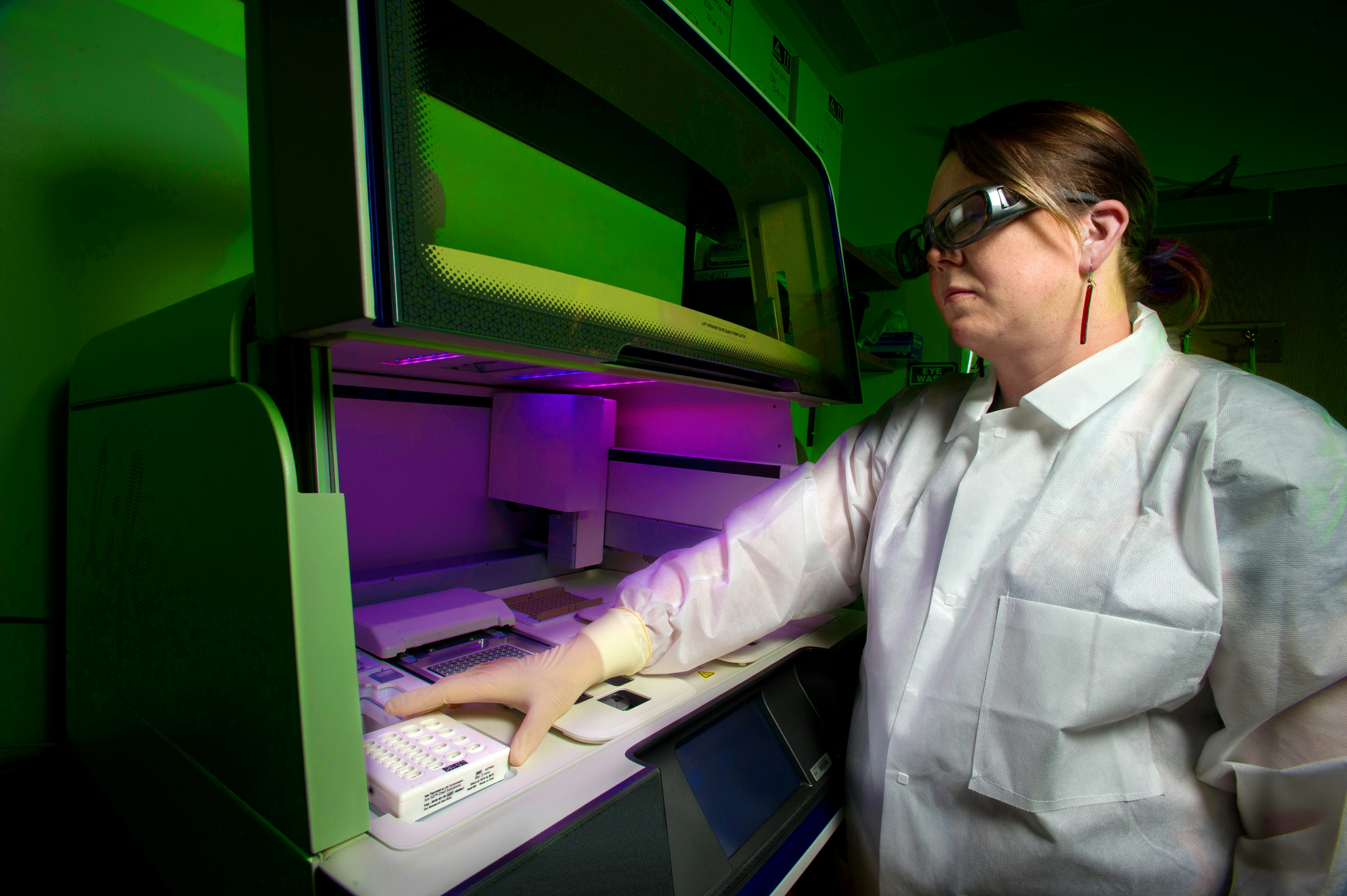

Enteric Diseases Laboratory Branch (EDLB) Public Health scientist, who was using a whole genome DNA sequencer, in order to determine the “DNA fingerprint†of a specific bacterium. Photographer James Gathany

Vaccine. Dr. J. Michael Hamilton preparing the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) vaccinia vaccine used to try to prevent cancer. He is diluting the concentrated vaccinia virus into a dose level appropriate for administration to a patient. This vaccinia marks any cancer cells expressing the CEA.

A female lab technician loading a semiconductor DNA sequencing chip used to identify specific cancer mutations in an individual. Photo taken at the Advanced Technology Research Facility (ATRF) at the Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute.





















0 Response to "41 molecular orbital diagram c2"
Post a Comment