37 diagram and explain electron transport
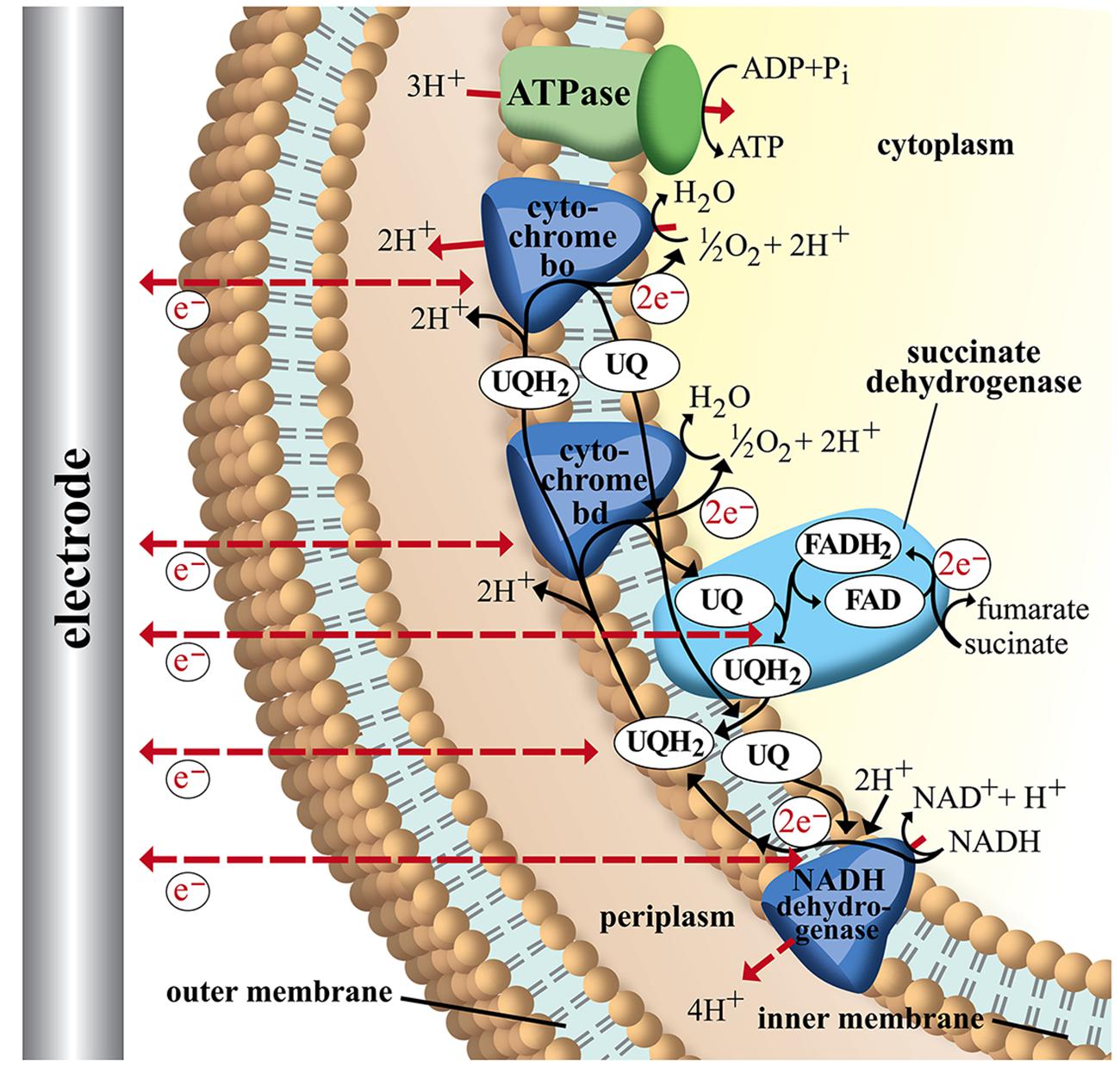
ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the structure of bacteria. This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of bacteria. 1. A bacterial cell remains surrounded by an outer layer or cell envelope, which consists of two components – a rigid cell wall and beneath it a cytoplasmic membrane or […] An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors ...Mitochondrial electron... · Reverse electron flow · Bacterial electron transport...
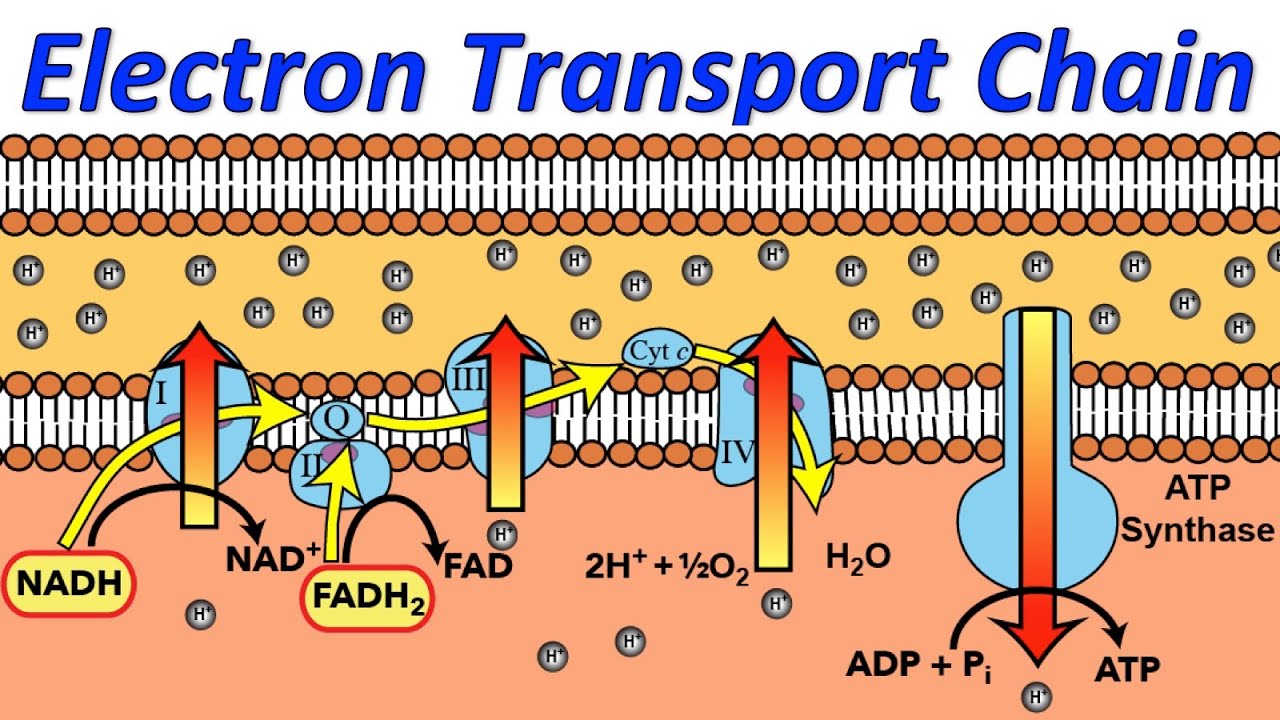
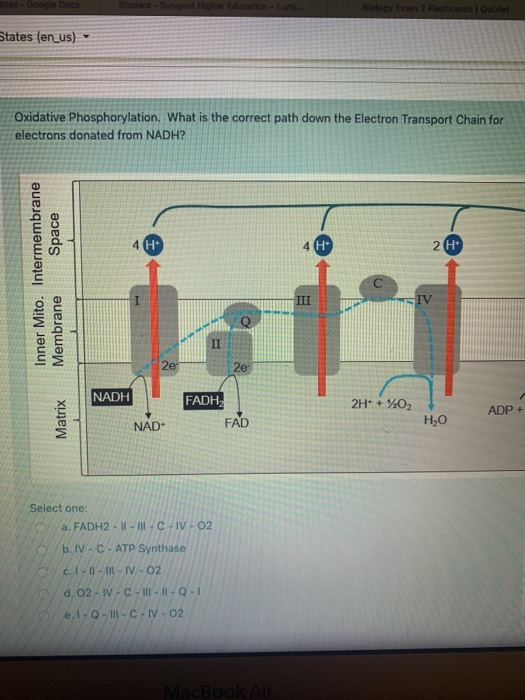
Electron Transport Chain · The hydrogen carriers (NADH and FADH2) are oxidised and release high energy electrons and protons · The electrons are transferred to ...

Diagram and explain electron transport
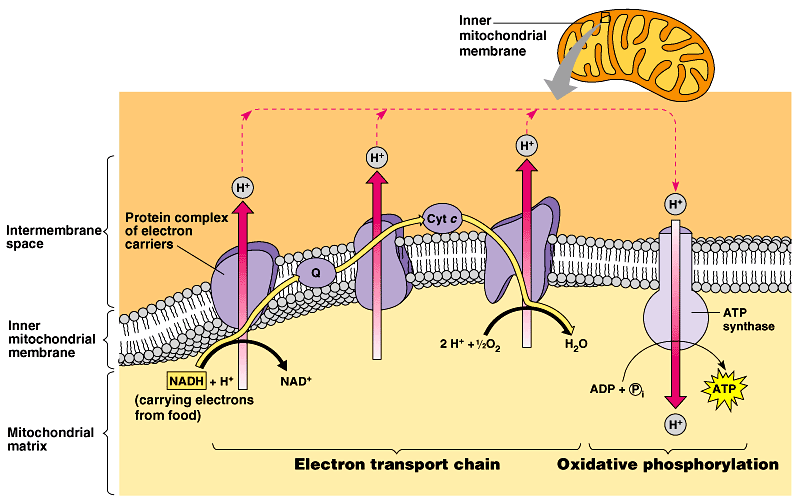
Chloroplast, structure within the cells of plants and green algae that is the site of photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are a type of plastid that are distinguished by their green color, the result of specialized chlorophyll pigments. In plants, chloroplasts occur in all green tissues. The electron transport chain (Figure 1) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of glucose metabolism that uses atmospheric oxygen. Aug 20, 2019 · This is diagram of aerobic cellular respiration including glycolysis, Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle), and the electron transport chain. RegisFrey/Wikimedia Commons/ CC BY-SA 3.0 Aerobic cellular respiration consists of three stages: glycolysis , citric acid cycle (Krebs Cycle), and electron transport with oxidative phosphorylation.
Diagram and explain electron transport. There are numerous proteins moving within or upon this layer that are primarily responsible for transport of ions, nutrients and waste across the membrane. Periplasmic Space : This cellular compartment is found only in those bacteria that have both an outer membrane and plasma membrane (e.g. Gram negative bacteria). Jun 19, 2019 — The electron transport chain is a cluster of proteins that transfer electrons through a membrane to create a gradient of protons that ... by M Ahmad · 2020 · Cited by 14 — The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that ... Paul Andersen covers the processes of aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. He starts with a brief description of the two processes. He then describe...
Electron microscope studies reveal that chitin occurs as elongated variously oriented microfibrillar units. These are laid down in layers and form the basis of the structural rigidity of fungal cell walls. The microfibril layers generally run parallel to the surface. Associated with the microfibrillar components is the nonfibrillar material. Simple diagram of the electron transport chain. The electron transport chain is a series of proteins embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. In the matrix ... Jun 2, 2019 — As shown from this diagram, electron flow from NADH to O2 is facilitated by several intermediate electron carriers, for example electrons move ... This is a schematic diagram illustrating the transfer of electrons from NADH, through the electron carriers in the electron transport chain, to molecular oxygen. Please click on the pink button below to view a QuickTime animation of the functions of the proteins embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane that are necessary for oxidative ...
Aug 20, 2019 · This is diagram of aerobic cellular respiration including glycolysis, Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle), and the electron transport chain. RegisFrey/Wikimedia Commons/ CC BY-SA 3.0 Aerobic cellular respiration consists of three stages: glycolysis , citric acid cycle (Krebs Cycle), and electron transport with oxidative phosphorylation. The electron transport chain (Figure 1) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of glucose metabolism that uses atmospheric oxygen. Chloroplast, structure within the cells of plants and green algae that is the site of photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are a type of plastid that are distinguished by their green color, the result of specialized chlorophyll pigments. In plants, chloroplasts occur in all green tissues.


























:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration-8fcc3f1ad3e54a828dabc02146ce4307.jpg)

0 Response to "37 diagram and explain electron transport"
Post a Comment