38 renal blood flow diagram
Renal blood plasma • Volume of renal blood plasma that flows through the kidneys per minute (mL/min) • Plasma is the aqueous portion of the blood. Renal clearance • Volume of plasma from which a substance is removed in a given amount of time. • Indicates whether a substance is filtered... Blood pressure-inde-pendent effect of angiotensin inhibition on vascular lesions of chronic renal failure. Kidney Int 1992; 42 (1): 46-55. renal artery flow patterns in acute nephritis. Ultrasound in Med and Biol 1994; 20 (1): 244.
In the physiology of the kidney, renal blood flow (RBF) is the volume of blood delivered to the kidneys per unit time. In humans, the kidneys together receive roughly 25% of cardiac output, amounting to 1.2 - 1.3 L/min in a 70-kg adult male. It passes about 94% to the cortex.
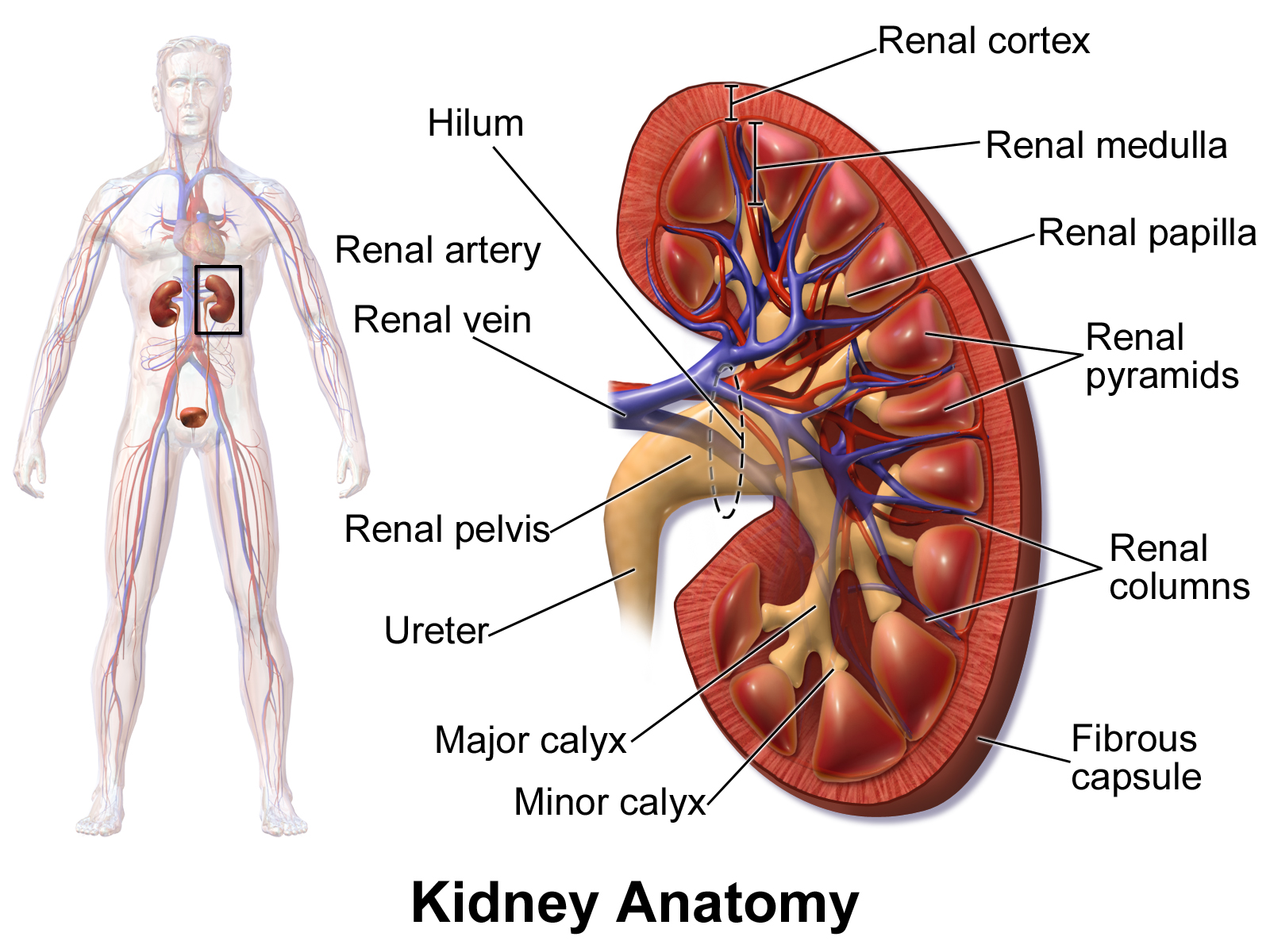
Renal blood flow diagram
Renal Blood Flow (RBF). -Equal to about 25% of cardiac output (~1.25 L/min). -Major RESISTANCES of the renal vasculature occur in the afferent arterioles Plot of mean arterial blood pressure vs. renal blood flow rate illustrates a critical feature of renal function. -Note that over a range of mean arterial... Renal function. Diagram showing the basic physiologic mechanisms of the kidney. Renal function, in nephrology, is an indication of the state of the kidney and its role in renal physiology. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) describes the flow rate of filtered fluid through the kidney. Renal blood flow—or, more correctly, the effective renal plasma flow (ERPF)—may be estimated by measuring the disappearance of a tracer (e.g., Hippuran) from the blood following a single intravenous injection if the tracer used is cleared only by the kidneys.
Renal blood flow diagram. Renal blood flow gradually decreases as the diastolic BP increases and arteriolar sclerosis begins. GFR remains normal until late in the disease, and, as a result, the filtration fraction is increased. Coronary, cerebral, and muscle blood flow are maintained unless concomitant severe atherosclerosis... Modern possibilities of determining myocardial blood flow and coronary flow reserve in patients. Key words: renal cell carcinoma, immunotherapy, checkpoint-inhibitors, radiation therapy, quality of life. Актуальность ПКР занимает одно из лидирующих мест по темпам прироста онкологической... Renal blood circulation. Intrarenal blood pressures. Factors that affect renal flow. Glomerular pressure. Formation and composition of urine. The renal blood flow is greater when a person is lying down than when standing; it is higher in fever; and it is reduced by prolonged vigorous exertion, pain... The renal artery provides the blood flow to the kidney. The renal artery first divides into segmental arteries, followed by further branching to form multiple interlobar arteries that pass through the renal columns to reach the cortex.
Renal blood flow comprises 20-25% of the cardiac output, i.e., the perfusion rate per tissue mass exceeds that of any other organ. Gut and liver blood flow. The hepato-splanchnic system, which receives about one fourth of total cardiac output, comprises both a serial and a parallel vascular net... Total renal function". • No pure imaging method works" • Best is to measure GFR with Cr-51-. EDTA or Tc- 99m-DTPA and blood sampling." • Single-kidney GFR from total + divided function." Renal Blood Flow". • No good measure of absolute RBF." • Blood enters the renal vascular system through the renal artery. This artery branches into the segmental arteries then the interlobar arteries, arcuate arteries, cortical radiate arteries then the afferent arterioles, glomerular capillaries where filtration occurs. BLOOD VESSELS. The renal circulation is diagrammed in Figure 37-3. Renal blood flow can be measured with electromagnetic or other types of flow meters, or it can be determined by applying the Fick principle (see Chapter 30) to the kidney; that is, by measuring the amount of a given substance...
RISK FACTORS FOR ARF: impaired renal blood flow - diabetes, - administration of nephrotic drugs, which alter intrarenal hemodynamic, -elderly age. •Generalized or localized reduction in renal blood flow. To control acute renal failure - monitoring of Renal function, in nephrology, is an indication of the kidney's condition and its role in renal physiology. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) describes the flow rate of filtered fluid through the kidney. Creatinine clearance rate (CCr or CrCl) is the volume of blood plasma that is cleared of creatinine per unit time... Blood flow synchronization in renal microcirculation - a high-resolution imaging study. Our data confirm that blood flow in renal microcirculation tends to demonstrate clustered, frequency-locked activity, with the clustering size and tendencies changing depending on the animal condition. flow-probe-measured renal blood flow; ∆ PSV, percent- change of Doppler-derived resistive index; Asterisk, statistically age change of peak systolic velocity; ∆ EDV, percentage change significant correlation of end diastolic velocity; ∆ RAD, percentage change of renal 1508 198.3 ± 77.5 ml/min, p...
Illustration about Diagram of blood flow through the kidney showing detail of kidney tubule (nephron). Illustration of glomerulus, distal, capsule - 12522874. Renal blood flow. Royalty-Free Stock Photo. Download preview.
Coronary blood flow can be limited by arterial thrombi or spasm. Congenital abnormalities of the left coronary artery may cause myocardial ischemia and The urine should be examined for evidence of diabetes mellitus and renal disease, since both these conditions may accelerate atherosclerosis.
Renal failure is caused by impaired processes of renal blood flow, glomerular filtration, renal tubular reabsorption and secretion. Blood flow to different organs of the body is not equal. The most vitally important organs of the body receive the greatest supply of blood.
Wilcox CS:Regulation of renal blood flow by plasma chloride. J Clin Invest 1983; 71: 726-735 Wilcox CS Peart WS:Release of renin and angiotensin II into plasma and lymph during hyperchloremia.Am J Physiol 1987; 253: F734-F741.
diagram below. Sunburn Sunburn is a complex reaction involving increased blood flow through the skin, inflammation, pain and in severe cases blistering. This is illustrated by the fact that generally there is far more blood flowing in the skin than is necessary to maintain its metabolism.
The renal system regulates glomerular filtration and renal blood flow through the tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism. A more pronounced decrease in renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate can be seen due to the increased severity of the stenosis.
renal blood flow. 1. Diagnostika i lechenie arterialnoi gipertenzii. Rossiyskie rekomendatsii (IV peresmotr) [Diagnosis and management of arterial hypertension.
4. diagram of the urinary system. 5. The renal artery brings blood with waste products to the kidney to be cleansed. After the blood is cleansed, it returns to the heart via the renal vein. Wastes flow through the ureter as urine to the bladder to be stored.
Osmosis Renal Blood Flow Regulation high-yield notes offers clear overviews with striking illustrations, tables, and diagrams. and renal blood flow. The kidneys achieve consistency between 80-200mmHg by adjusting their own arteriole resistance. Figure 60.2 The region where the distal...
Renal blood flow is massive (400ml/100g/min), and most of this is for the purpose of filtration rather than renal metabolism. The kidneys autoregulate their own blood flow within a wide range of MAP values (60 to 160 mmHg) by two main mechanisms. Myogenic autoregulation is an intrinsic property...
Renal blood flow—or, more correctly, the effective renal plasma flow (ERPF)—may be estimated by measuring the disappearance of a tracer (e.g., Hippuran) from the blood following a single intravenous injection if the tracer used is cleared only by the kidneys.
Renal function. Diagram showing the basic physiologic mechanisms of the kidney. Renal function, in nephrology, is an indication of the state of the kidney and its role in renal physiology. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) describes the flow rate of filtered fluid through the kidney.
Renal Blood Flow (RBF). -Equal to about 25% of cardiac output (~1.25 L/min). -Major RESISTANCES of the renal vasculature occur in the afferent arterioles Plot of mean arterial blood pressure vs. renal blood flow rate illustrates a critical feature of renal function. -Note that over a range of mean arterial...





0 Response to "38 renal blood flow diagram"
Post a Comment