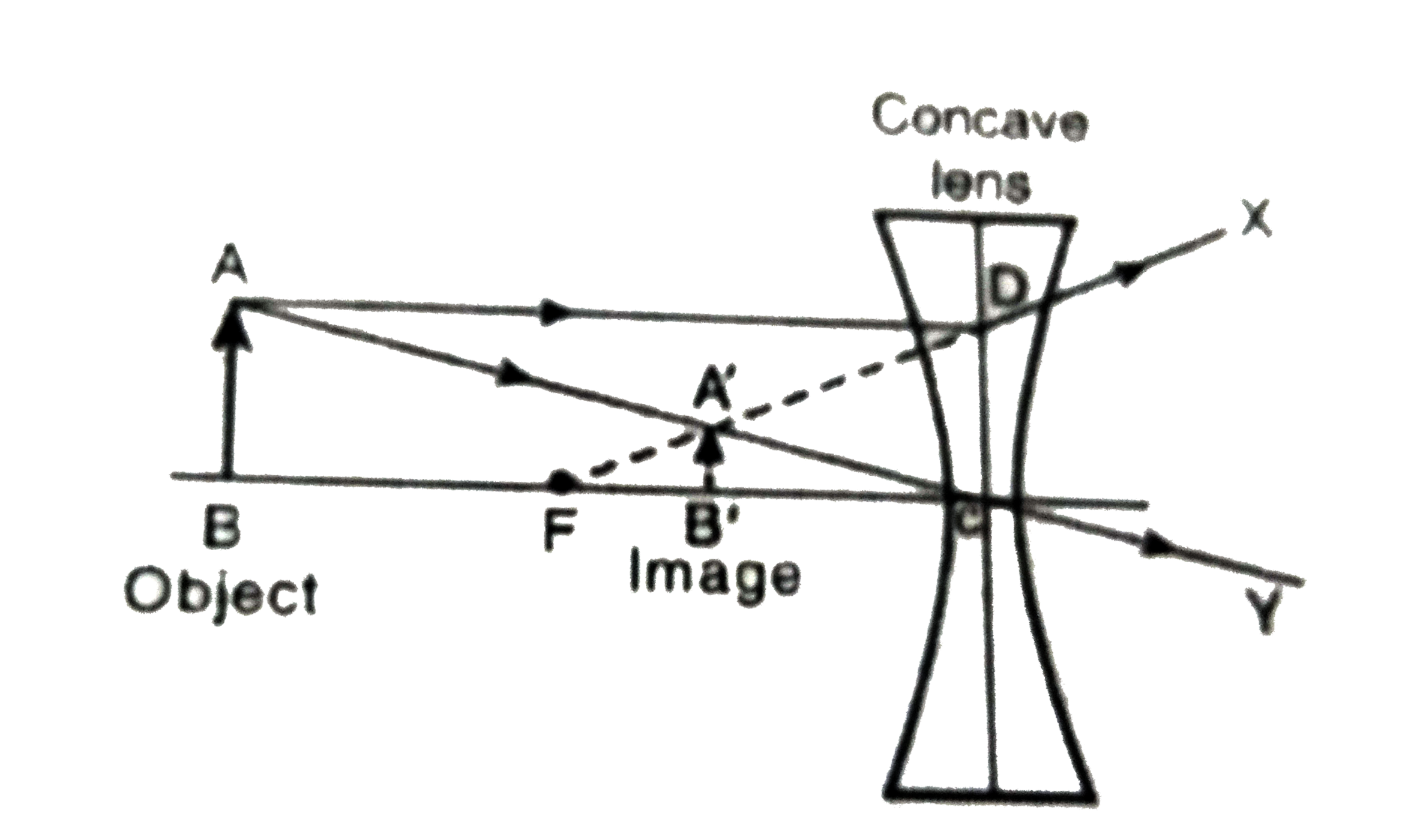
42 draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens)
A 4.0-cm tall object is placed 50.0 cm from a diverging lens having a focal length of magnitude 25.0 cm. Draw the ray diagram for this situation. What is the ...1 answer · 0 votes: a) b) We were unable to transcribe this image Object Far From Lens object near f distance from the mirror to the object is p. We will draw the diagram with p > R , but our results will hold true for any value of p. Draw two rays from the object to the mirror: one ray passes through the mirror's center of curvature, and therefore is perpendicular to the mirror at the incidence point and returns directly back to the object.
A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens.The ray tacing needs to have the three principal rays.Also draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principle waves converge.. B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram.

Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens)
Lens formula is defined as the relationship between object distance (u), image-distance (v) and the focal length (f). Following is the mathematical representation of lens formula: 1 f = 1 v − 1 u 1 f = 1 v − 1 u. Where, f is the focal length of the lens. v is the distance of the image from the optical centre of the lens. Ray diagrams help us trace the path of the light for the person to view a point on the image of an object. Ray diagram uses lines with arrows to represent the incident ray and the reflected ray. It also helps us trace the direction in which the light travels. Plane Mirror vs Spherical Mirrors. Drawing a ray diagram for an object far from a convex lens requires how many rays? three. If an object is placed at twice the focal length of a convex lens, where is the image located on the other side of the lens? ... If an object is located inside the focal length of a diverging lens, then compared to the object, the image will be _____. smaller.
Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens). Step-by-Step Method for Drawing Ray Diagrams. The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below. The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the ... a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Refer to Section 26.4 of Serway & Jewett for further guidance on how to construct principal rays. Problem: A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three ...1 answer · Top answer: Lens equation: 1so+1si=1fThe three principal rays used in ray tracing include:1. An incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging ... Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Refer to Section 26.4 of Serway & Jewett for further guidance on how to construct principal rays.
Draw a ray diagram in each of the following cases to show the formation of image, when the object is placed : (i) between optical centre and principal focus of a convex lens. (ii) anywhere in front of a concave lens. (iii) at 2F of a convex lens. State the signs and values of magnifications in the above mentioned cases (i) and (ii). a) draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tacing needs to have the three principal ... Here, Object AB is beyond 2F 1. First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. So, it passes through focus after refraction. We draw another ray which passes through Optical Center. So, the ray will go through without any deviation. Where both rays meet is point A'. And the image formed is A'B'. This image is formed between F 2 and 2F 2. a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three ... Rating: 5 · 3 votes
Drawing a ray diagram for an object far from a convex lens requires how many rays? three. If an object is placed at twice the focal length of a convex lens, where is the image located on the other side of the lens? ... If an object is located inside the focal length of a diverging lens, then compared to the object, the image will be _____. smaller. Ray diagrams help us trace the path of the light for the person to view a point on the image of an object. Ray diagram uses lines with arrows to represent the incident ray and the reflected ray. It also helps us trace the direction in which the light travels. Plane Mirror vs Spherical Mirrors. Lens formula is defined as the relationship between object distance (u), image-distance (v) and the focal length (f). Following is the mathematical representation of lens formula: 1 f = 1 v − 1 u 1 f = 1 v − 1 u. Where, f is the focal length of the lens. v is the distance of the image from the optical centre of the lens.

Class 10 Physics Lakhmir Singh And Manjit Kaur Solutions Chapter 5 Refraction Of Light Cbse Sample Papers Ncert Solutions Educationapp In
Cbse Free Ncert Solution Of 10th Science Light Reflection And Refraction An Object 5 Cm In Length Is Held 25 Cm Away From A 10th November 2021 Saralstudy
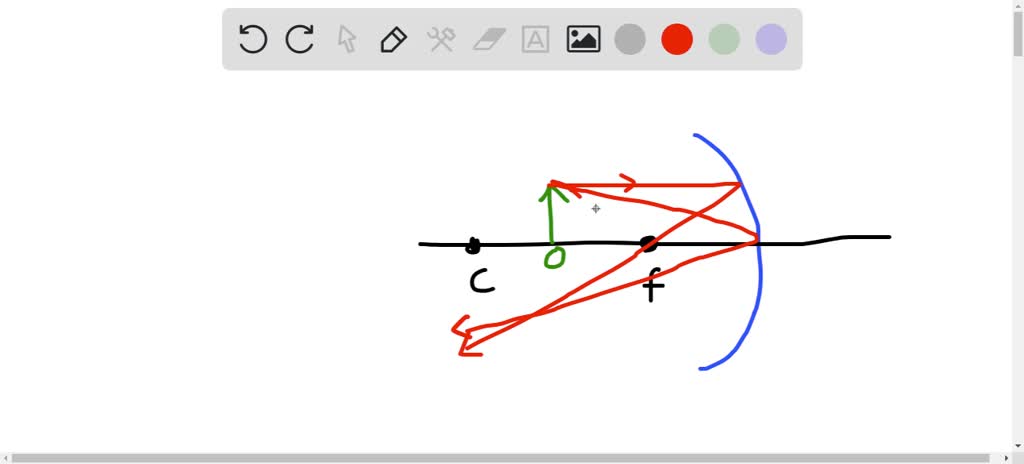
Solved Draw A Ray Tracing Diagram For The Following Situation An Object Is Placed Between The Focal Point F And A Concave Mirror Also Indicate If The Image Is Real Or Virtual And If

Draw A Ray Diagram In Each Of The Following Cases To Show The Formation Of Image When The Object Is Placed I Between Optical Centre And Principal Focus Of A Convex Lens Ii

Convex Lens Concave Lens How To Determine Focal Length Ray Diagrams Image Properties Real Virtual Inverted Size Correction Of Eye Defects Causes Of Long Sight Short Sight Igcse Gcse 9 1 Physics Revision Notes

Convex Lens Concave Lens How To Determine Focal Length Ray Diagrams Image Properties Real Virtual Inverted Size Correction Of Eye Defects Causes Of Long Sight Short Sight Igcse Gcse 9 1 Physics Revision Notes
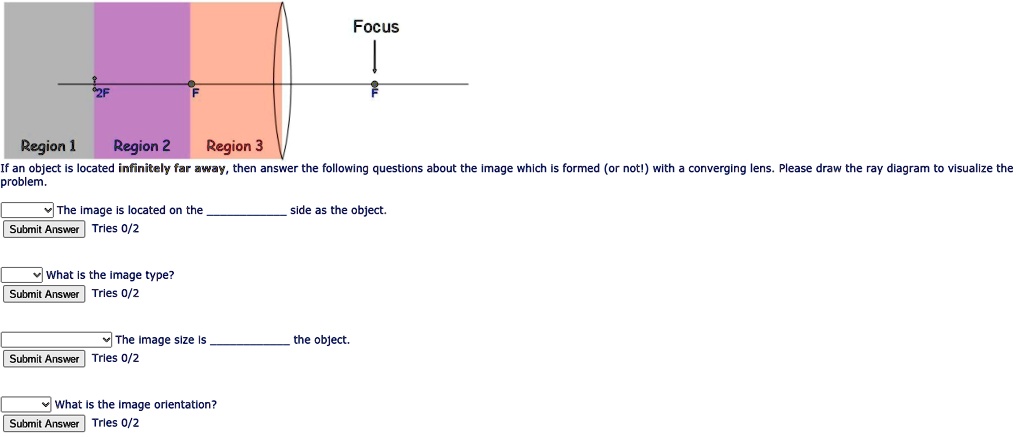
Solved Focus Region Region 2 Region 3 If An Object Located Infinitely Far Away Then Answer The Following Questions About The Image Whlch Tormed Or Noti With Converging Lens Please Draw The Ray

Draw A Ray Diagram In Each Of The Following Cases To Show The Formation Ofimage When The Object Is Brainly In

Solved Censider A Diverging Lens With Focal Length F 10 Cm And An Object Of Height H 3 Cm Draw The Ray Diagram To Find The Image In The Following

A Draw Labelled Ray Diagrams For Each Of The Following Cases To Show The Position Nature And Size Brainly In
Draw A Ray Diagram In Each Of The Following Cases To Show The Formation Of Image When The Object Is Placed I Between Optical Centre And Principal Focu Physics Topperlearning Com

Gibly Drawn To Scale Ray Diagrams Showing H Ation Ng Configuration Converging Lens Of 15em Fixed Focal Length Em In Length An Object Is Placed At 0 0 Em Can Be Detected Is
Draw Ray Diagram To Show The Formation Of Images When The Object Is Placed In Front Of A Concave Mirror Converging Mirror Between Its Pole And Focus Studyrankersonline

Solved 5 43 0 Cm Tall Object Is 30 M In Front Of A Converging Lens That Has 20 Cin Foca Length A Calculate The Image Position And The Image Height B Calculate The Image
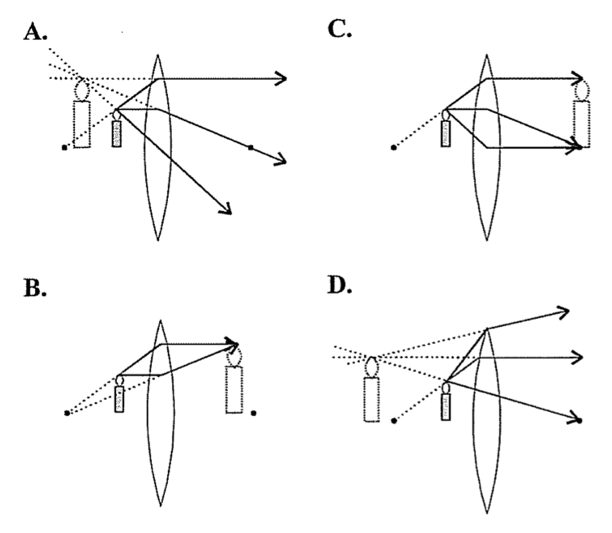

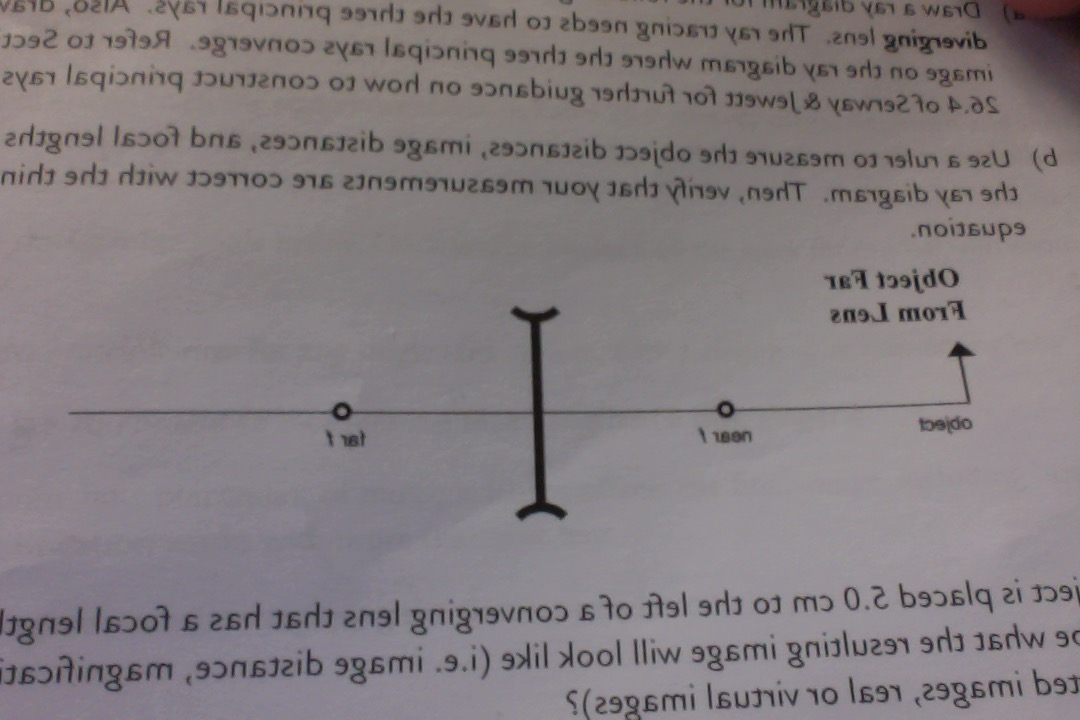


















0 Response to "42 draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens)"
Post a Comment