41 concave mirror ray diagram
Ray diagrams and curved mirrors Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere. Khan Academy is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. Applications of Concave Mirror. In torchlight, headlamp, vehicle headlight, searchlight, and lighthouse, where a beam of light is converged to a certain point thus giving a better focus; As vanity mirrors for facial makeup and as shaving mirrors for shaving;
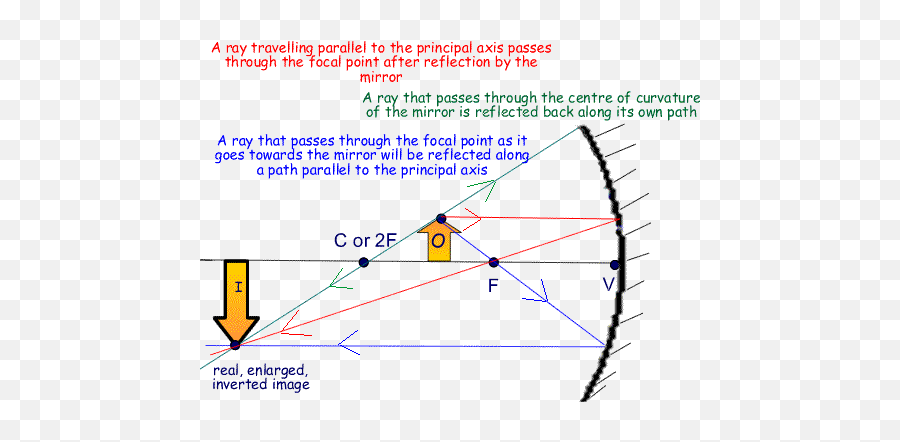
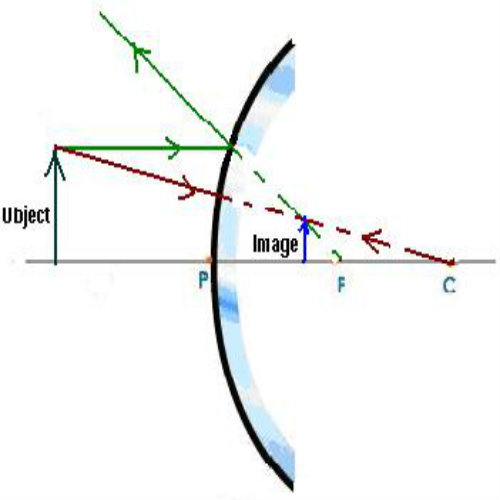
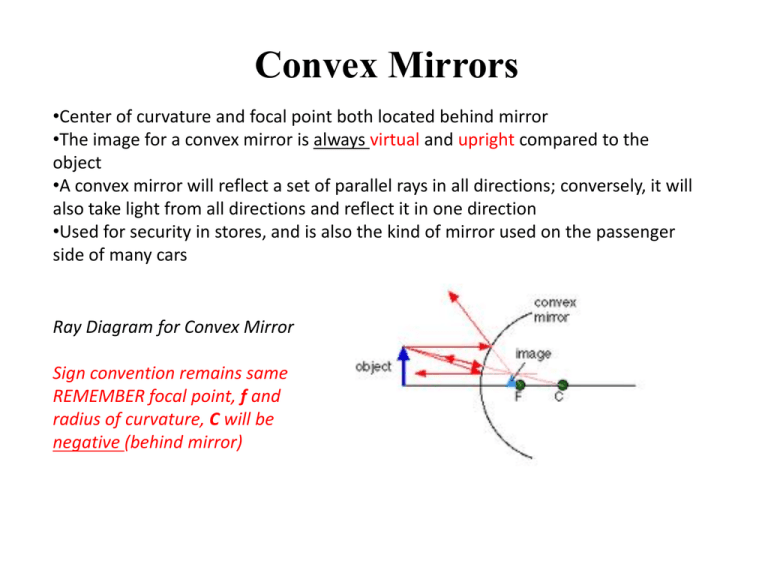
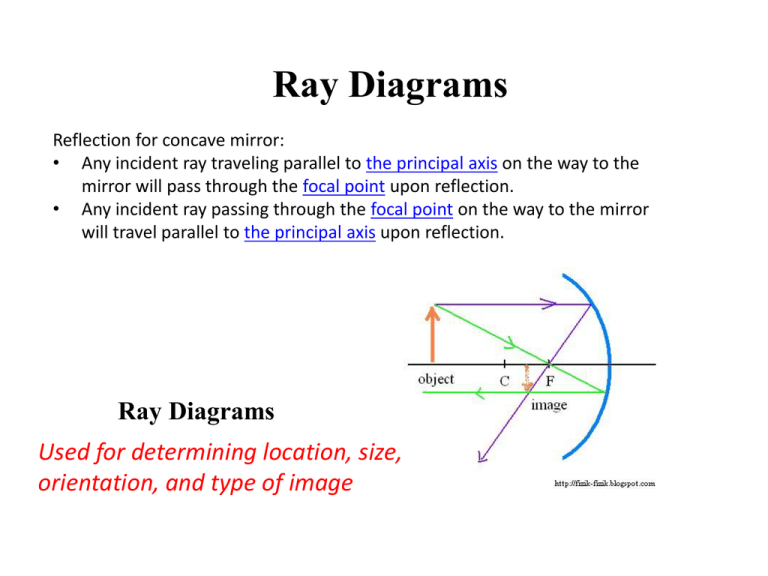
We draw another ray which passes through Center of Curvature. So, the ray will go back along the same path after reflection. Where both reflected rays meet is point A'. And the image formed is A'B'. This image is formed between Pole (P) and Focus (F) We can say that. Image is behind the Mirror (Virtual Image) Image is Erect.

Concave mirror ray diagram
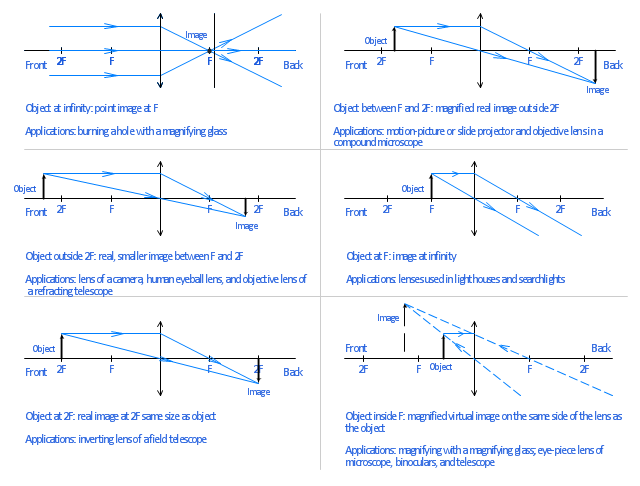
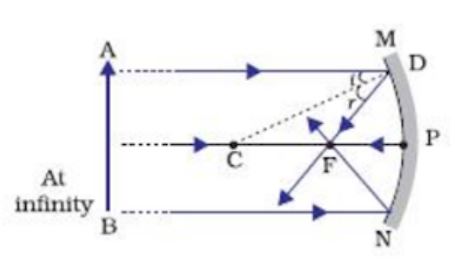
Draw ray diagram for concave mirror when (1) Object at centre of curvature (2) Object at focus (3) Object between centre of curvature and focus. Science | Science - NCERT Solutions All. Q4. The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object? Ray diagrams are drawn to scale - so whatever value you are given for the focal length of the mirror will be doubled for the radius of the circle that you draw for the mirror. Add the chevron shading. Label the point that your compass went through C (or 2F) and the point where the line of the principal axis cuts the mirror V. For a Concave mirror, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object AB is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes t
Concave mirror ray diagram. In concave mirrors, there are 4 ray diagrams through which an image of the object can be located. The four ray diagrams of concave mirrors are given below: (i) A ray parallel to the principal axis, after reflection, will pass through the principal focus (F). Source: NCERT Book. (ii) A ray passing through the principal axis, after reflection ... Images formed by concave mirror| Ray diagram of concave mirror | science with sachin deshmukhImages formed by concave mirror class 10images formed by concave... Concave mirrors are used by dentists to see large image of teeth of patients. (Teeth have to be placed between pole and focus) Concave mirror is used as shaving mirror to see a larger image of the face Large concave mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnace Ray Diagrams of Images formed by convex mirror Concave Mirror Ray Diagrams. Ray diagrams are necessary for understanding the formation of an image by a concave mirror. For constructing ray diagrams and for the better understanding of the image formation, we should consider at least two incident rays coming from the object. The intersection of these two rays after reflection gives the ...
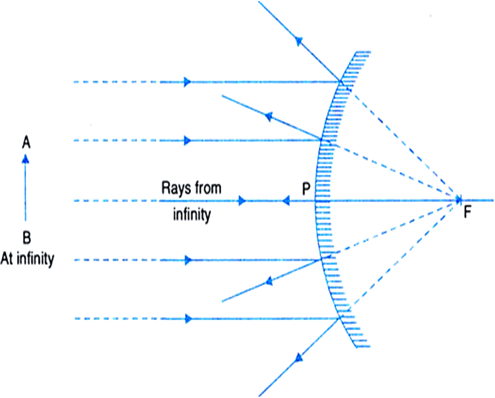
Mirrors: Principal Ray Diagram of a Concave Mirror Concave Mirror ray diagram. Author: Ray Tuck. This simulation shows a ray diagram for a concave mirror. Change the object position by dragging the yellow circle. Check the check boxes to show the distances S o and S i. F is the focal point. Light rays are shown in red, extensions to rays are shown as green dashed lines. Ray Diagram for Convex and Concave Mirror. A mirror is a part of a smooth and highly polished reflecting surface. Most commonly used mirrors are plane mirrors. A spherical mirror is a part of a spherical reflecting surface. There are two types of spherical mirrors - convex mirror and concave mirror. Concave spherical mirrors and ray diagrams A spherical mirror is a reflective segment of a sphere with a radius of curvature R. It can be convex (outside surface of a sphere) or concave (inside surface). First we will consider a concave spherical mirror. The mirror has a radius R, and the distance from the mirror to the object is p.
This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for concave and convex spherical mirrors. By manipulating the object and mirror locations, you can create real or virtual images. The ray parallel to the principal axis and the ray that hits the center of the mirror are drawn. A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Incident rays - at least two - are drawn along with their corresponding reflected rays. Each ray intersects at the image location and then diverges to the eye of an observer. Every observer would observe the same image location and every light ray would follow the law of reflection. J.M. Gabrielse Ray Diagrams 2. J.M. Gabrielse Spherical Mirrors (concave & convex) 3. J.M. Gabrielse Concave & Convex (just a part of a sphere) C: the centre of curvature (centre point of the sphere) F: the focus (focus) of the mirror (halfway between C and the mirror) • C • F Principal Axis Curved Surface ... Concave and Convex Mirror: In this article, we will discuss what are Concave Mirror and Convex Mirror, how they are formed, Concave and Convex Mirror differences, examples, ray diagrams, uses, and much more.But before understanding what is a Concave and Convex mirror, let's understand what is a Mirror. Take Mock Test On Reflection And Refraction Now
In this video you find out the basic trick to create ANY RAY DIAGRAM.Share if you like it!
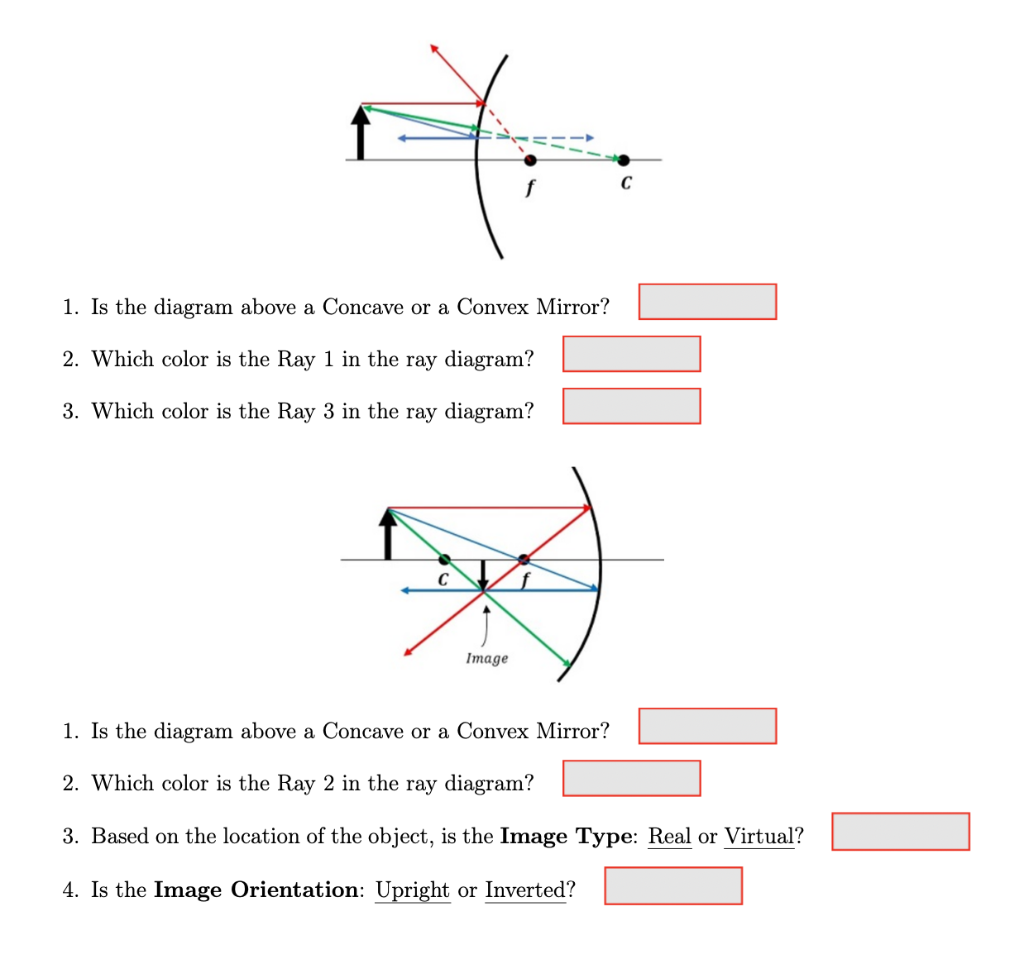
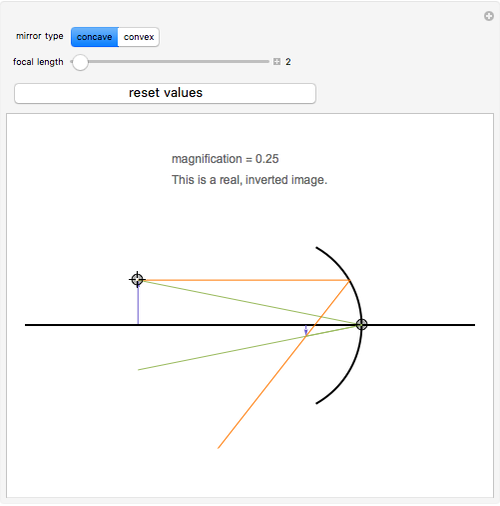
In this worksheet, we will practice drawing diagrams of light rays interacting with concave mirrors. Q1: The following figure shows two light rays from the same point on an object that are incident on a concave mirror. The object is between the center of curvature of the mirror and the focal point of the mirror. A real image is produced.
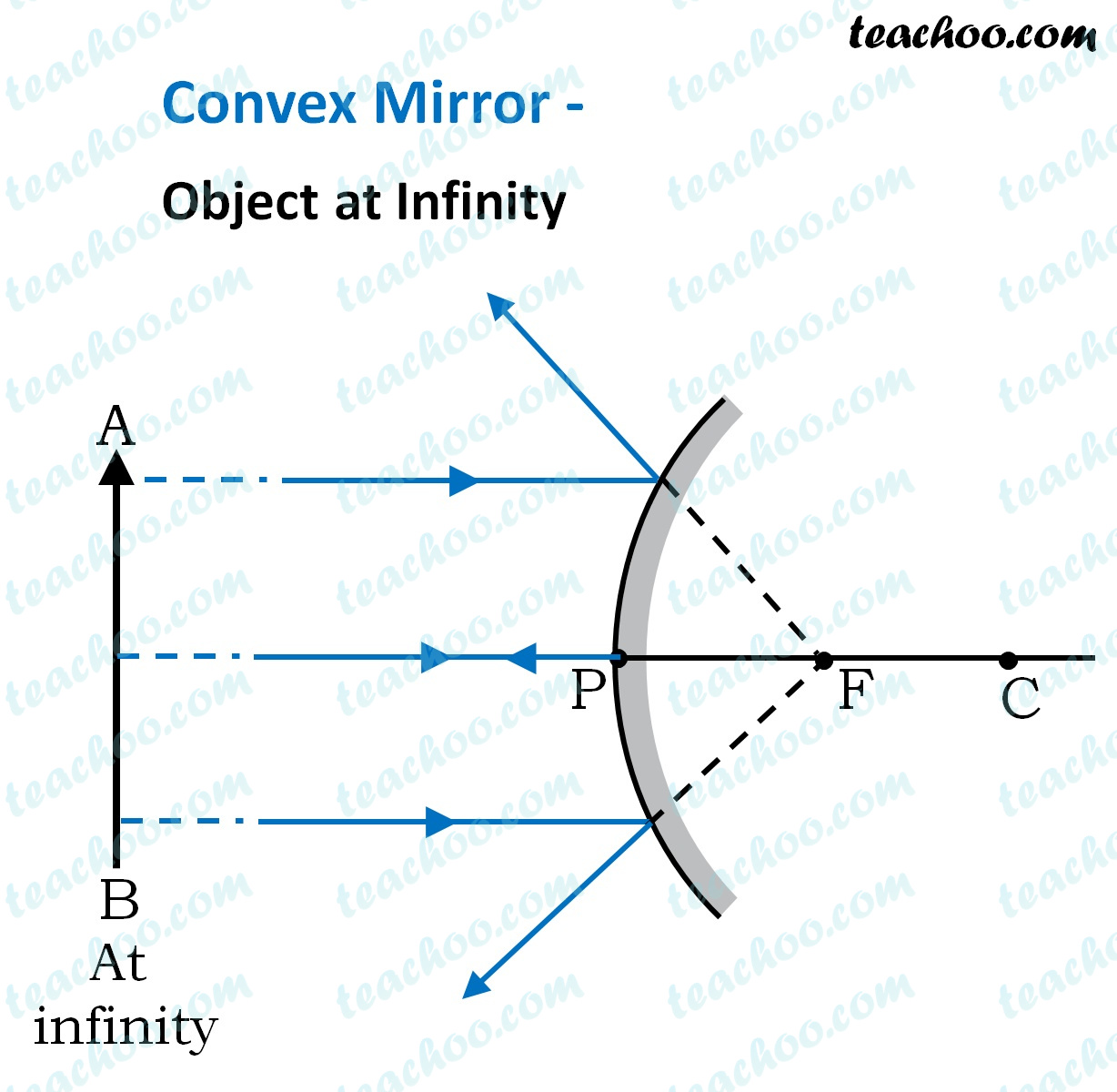
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus.
Ray Diagrams for Concave Mirrors and its use. For a Concave Mirror, an object can be placed at any position so that image is created at different - different positions. We can find image position, its nature, and its size using Ray Diagrams. To get an image of an object we need at least two rays coming from the object to meet somewhere.
Nov 18, 2021 · Concave Mirror Ray Diagram: Object Behind the Curvature Point. To find the image from an object using a concave mirror diagram, one must use at least two incident rays departing from the top of ...
Shows how to draw ray diagrams and locate the image for concave mirrors. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscience.c...
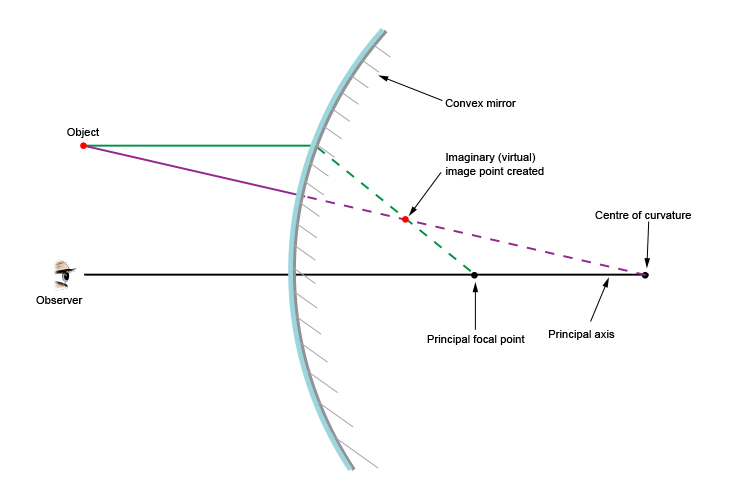
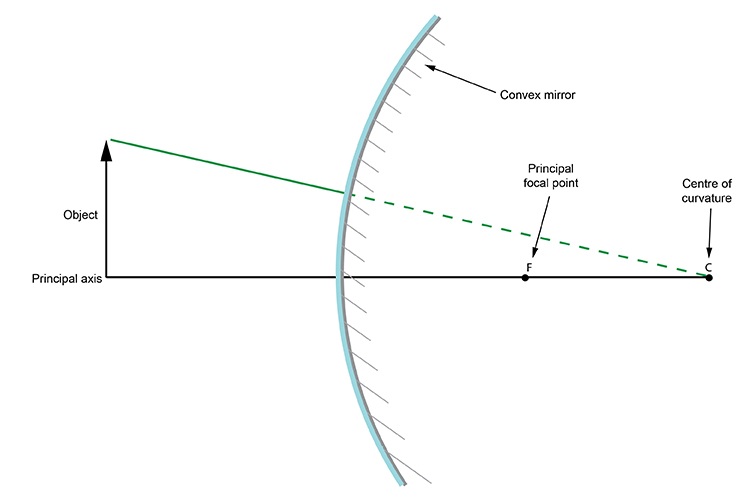
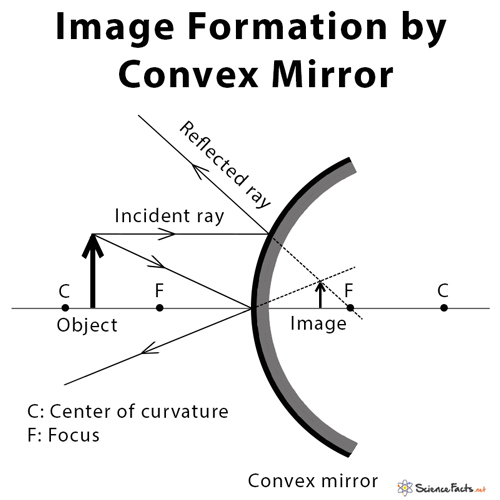
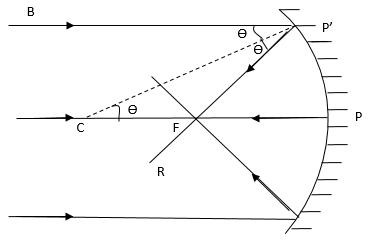
Convex Mirror Image. A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign convention is used here.. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror.

Draw A Neat Two Ray Diagram To Illustrate How A Concave Mirror Is Used As A Shaving Mirror Physics Shaalaa Com
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. With the help of ray diagrams, we can understand how images are formed in concave mirrors. We should consider at least 2 incident rays coming from an object to understand the image formation in Concave Mirrors. The intersection of 2 rays after reflection provides the image position of an object.
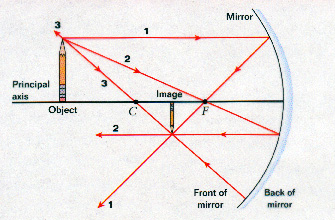
Concave Mirror Ray Diagrams. A ray diagram is used to show the path of light rays as they reflect from a surface. They can be used to illustrate the position of an image. An example of a ray ...
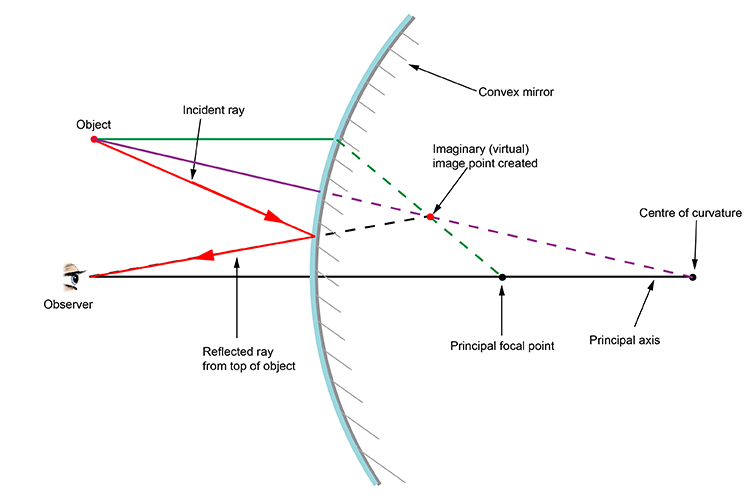
The main difference to concave mirrors is that these points are now on the other side of the mirror to the incoming beam of light. In this example, we will illustrate the method of drawing a ray diagram for a convex mirror, with a real object placed to the left of it.
Voronoi Diagrams with Cones; Juggling 13 Balls; Concave and Convex Mirrors. Description Simulation of image formation in concave and convex mirrors. Move the tip of the Object arrow or the point labeled focus. Move the arrow to the right side of the mirror to get a convex mirror. ...
Spherical & parabolic mirrors. Spherical mirrors, radius of curvature & focal length. Convex & concave mirror ray diagrams. This is the currently selected item. Practice: Ray diagrams. Practice: Ray diagrams and curved mirrors. Mirror formula derivation. "Objects in the mirror are ..." actually images in the mirror.
Optical Board - Ray Diagram - Concave Mirror Purpose. To locate the image of a concave mirror by using the three principal rays. Equipment. Optical board with parabolic concave mirror, half-silvered and full-silvered mirros on mount, convex lens. Images. Description. This is a short focal length concave parabolic mirror which produces a small ...

Draw A Ray Diagram Showing How A Concave Mirror Can Be Used To Produce A Real Inverted And Diminished Image Of An Object Science Shaalaa Com
For the following mirrors and corresponding object positions, construct ray diagrams. Then describe the Location of the image, Orientation (upright or inverted) of the image, the relative Size of the image (larger or smaller than object), and the Type of image (real or virtual). For Case 4, merely construct the ray diagram.
For a Concave mirror, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object AB is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes t
Ray Tracing Diagram For Convex Lens Physics Diagrams Optics Vector Stencils Library Ray Diagram Lenses
Ray diagrams are drawn to scale - so whatever value you are given for the focal length of the mirror will be doubled for the radius of the circle that you draw for the mirror. Add the chevron shading. Label the point that your compass went through C (or 2F) and the point where the line of the principal axis cuts the mirror V.

6 Draw The Ray Diagram Of The Image Formation By Concave And Convex Mirror And Lens All Position Brainly In
Draw ray diagram for concave mirror when (1) Object at centre of curvature (2) Object at focus (3) Object between centre of curvature and focus. Science | Science - NCERT Solutions All. Q4. The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object?
With The Help Of Ray Diagrams Explain The Formation Of Images By A Convex Mirror For The Following Position Of The Object I Object Between Pole And Infinity Ii Object At Infinity From Science

Diagram By Akita Your Diagram Source From Akita Concave Mirrors Spherical Mirror How To Memorize Things
Concave Mirrors Ray Diagram Concave Mirror Object Between C Png Icon With A Curved Arrow Crossword Free Transparent Png Images Pngaaa Com














0 Response to "41 concave mirror ray diagram"
Post a Comment