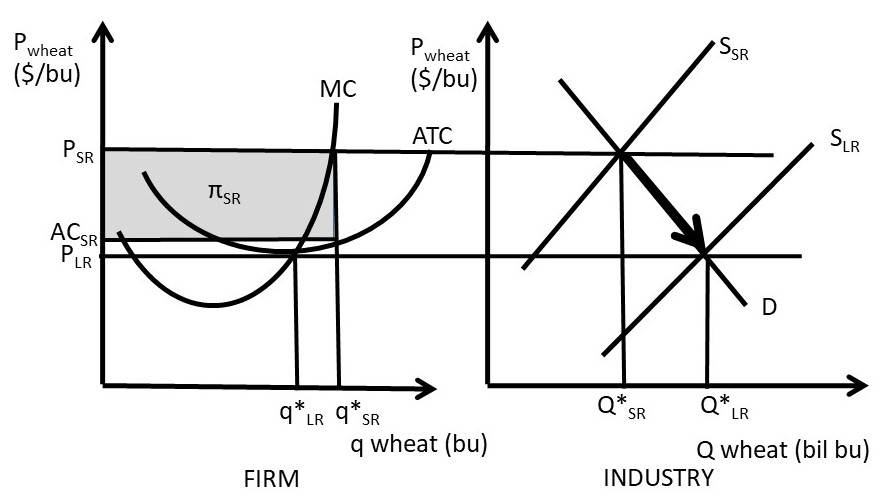
41 the monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is
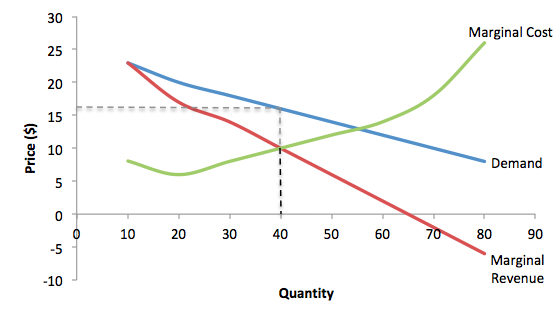
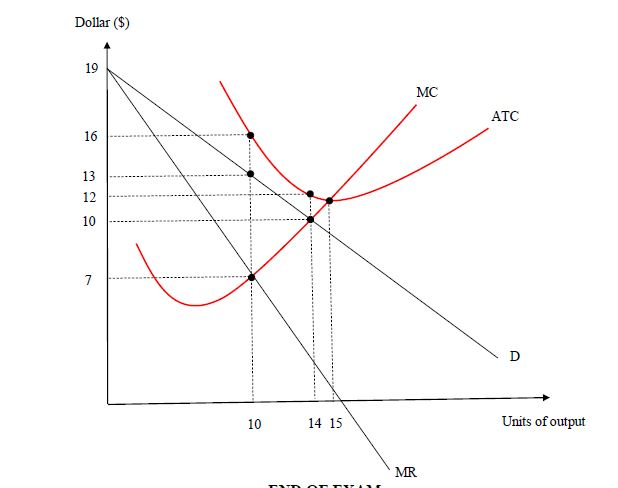
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive ... Refer to the information provided in Figure 15.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Figure 15.4 Refer to Figure 15.4. Assume The Hand Made Shirt Shop has fixed costs of $150 and is a monopolistically competitive firm. Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Multiple Choice ... D) fact that most monopolistically competitive firms encounter diseconomies of scale. Ans: Use the following to answer questions 35-38: 35. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: A) $10. B) $13. C) $16. D) $19. Ans: 36.
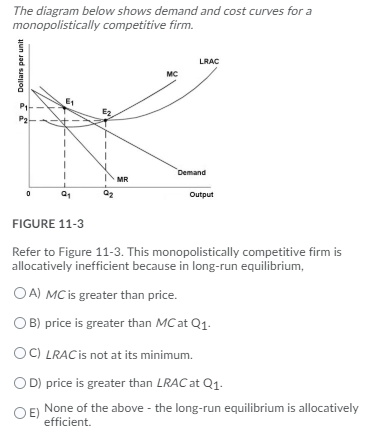
The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a ... Mar 03, 2022 · The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. FIGURE 11-3-Refer to Figure 11-3. If an increase in industry demand led to an outward shift in each firm’s demand curve, the typical firm would A) be making losses and some firms would exit the industry in the long run.
The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is
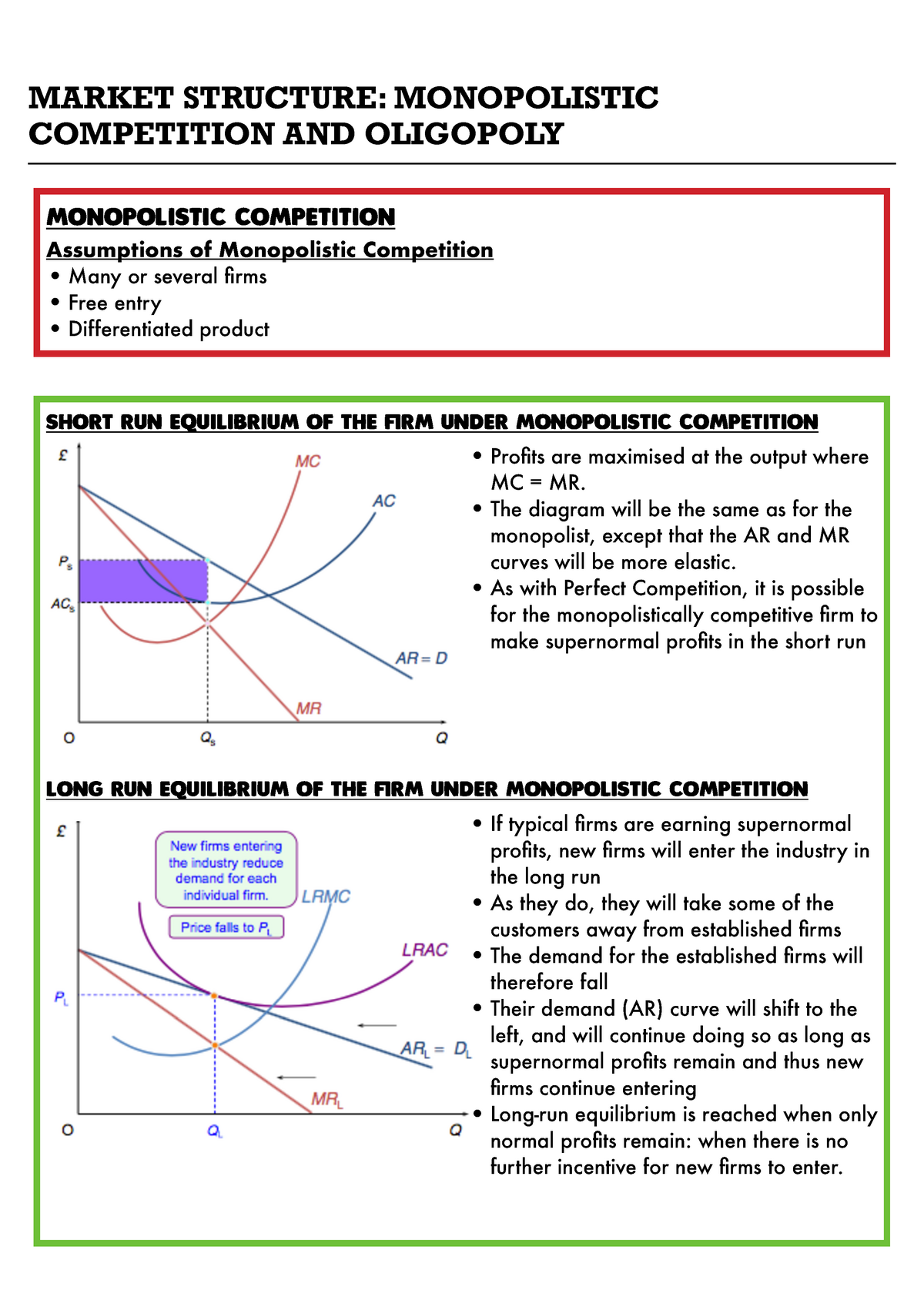
8.4 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Microeconomics The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price similar to the way that a monopolist does. Since they face a downward sloping demand curve, the same considerations about how elasticity affects revenue are relevant, and the firm will maximize profits where MR = MC when P > MR. Step 1. The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a ... The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. FIGURE 11-3-Refer to Figure 11-3. In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm will A) make profit by producing at QC and charging price PL. B) maximize profit by producing output level QC , the minimum point of its LRAC curve Microeconomics Chapter 13 Flashcards - Quizlet When a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium, MR = MC and minimum ATC > P. Refer to the above graphs. A short-run equilibrium that would produce profits for a monopolistically competitive firm would be represented by graph A. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. This firm is experiencing
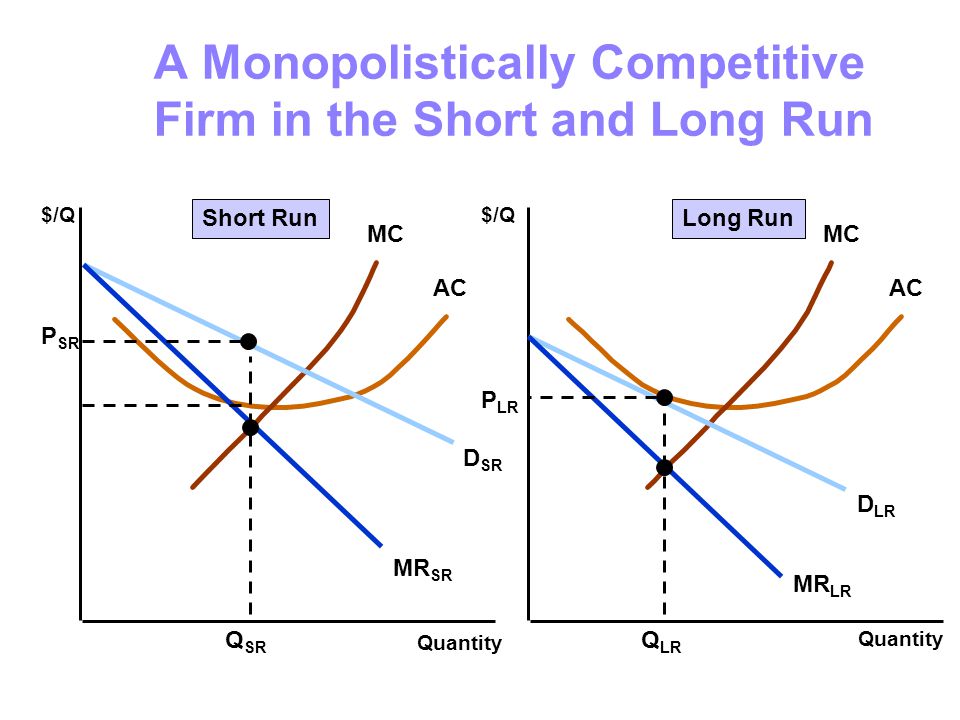
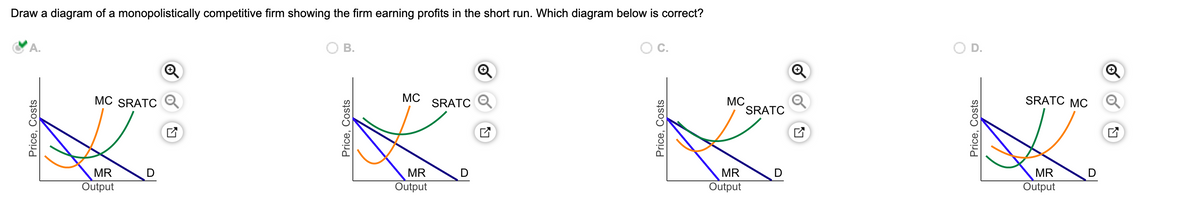
The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is. Chapter 16, Monopolistic Competition Video Solutions ... For each of the following characteristics, say whether it describes a monopoly firm, a monopolistically competitive firm, both, or neither. a. faces a downward-sloping demand curve b. has marginal revenue less than price c. faces the entry of new firms selling similar products d. earns economic profit in the long run The Effects of Trade in a Monopolistically Competitive ... A market equilibrium for a representative firm in a monopolistically competitive ( MC) market displays an output level such that MR = MC and establishes a price such that P = AC. When trade opens up between two countries that have MC markets, the consumer demand for variety inspires trade. Solved This Quiz: 27pts pos Draw a diagram of a | Chegg.com Transcribed image text: This Quiz: 27pts pos Draw a diagram of a monopolistically competitive firm showing the firm earning profits in the short run. Which diagram below is correct? OA OB OC MC SRATC MC SRATC MRO Draw a diagram of a monopolisticwly competitive em showing the firm in long-run equilibrium caming 20 Bros Which diambelow is correct? Monopolistic Competition - Managerial Economics In other words, a Monopolistic Competitive firm resembles a monopoly in the short run but displays outcomes similar to Perfect Competition in the long run.. b. Monopolistic Competition has a smaller output sold at a higher price as compared to Perfect Competition. The following diagram shows the comparison.
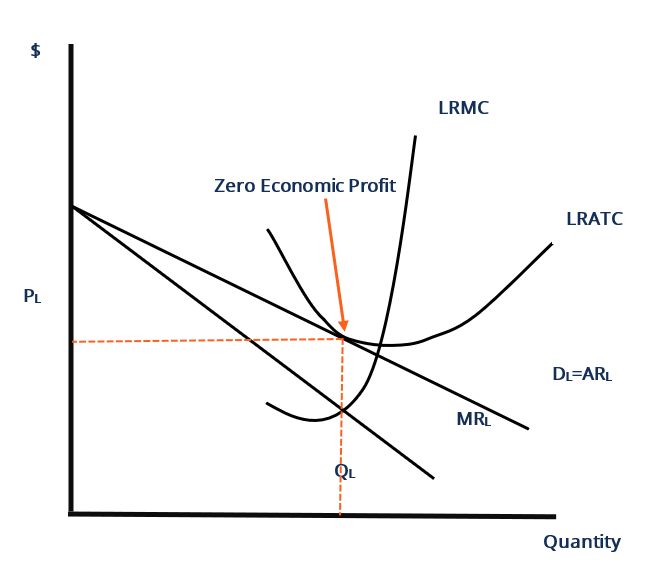
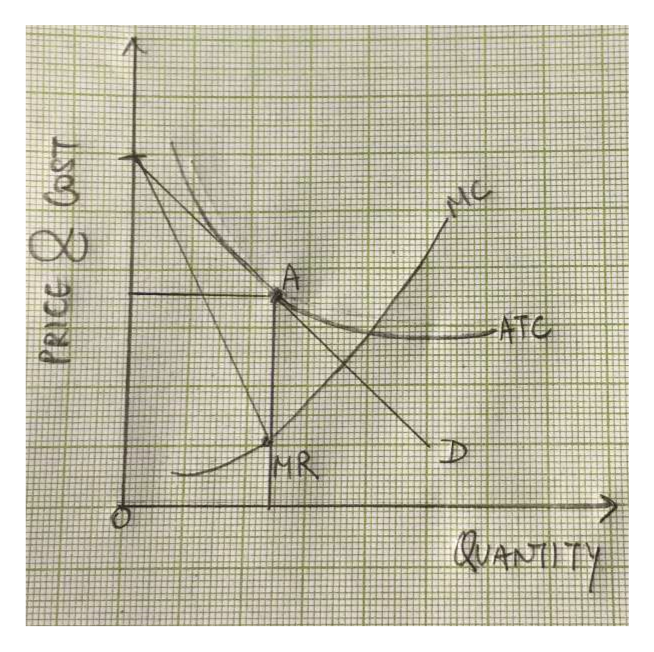
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive ... A monopolistically competitive firm in a long-run equilibrium produces where; Refer to the data. if the market price for the firm's product is $28, the competitive firm will: Both monopolistically competitive firms and perfectly competitive firms maximize profits; In long-run equilibrium, a monopolistically competitive producer achieves Monopolistic competition - Economics Online Monopolistic competition The model of monopolistic competition describes a common market structure in which firms have many competitors, but each one sells a slightly different product. Monopolistic competition as a market structure was first identified in the 1930s by American economist Edward Chamberlin, and English economist Joan Robinson. Chapter 25 Homework Flashcards - Quizlet In the diagram the demand curve (which shows prices that consumers will pay for various quantities) is tangent to the average total cost curve. Therefore (P minus− ATC) = 0, and economic profits are zero. The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is A.earning negative economic profits. Monopolistic competition - LegitWriting Monopolistic competition - LegitWriting Welcome to Legit Writing Draw the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm, label the level of output it will choose to produce in the short-run, and label the profit of the firm. Draw the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in the long-run and label its long-run level of output.
Monopoly Vs Monopolistic Competition (With Diagram) It means small fall in price, will lead to big increase in demand. Fig. 14 represents AR and MR under monopolistic competition. 6. Decision-Making: Under monopoly and monopolistic competition, a firm cannot determine both price and output at the same time. Under monopolistic competition, the firm has to spend more on selling costs. Monopolistic Competition in the Long-run The monopolistically competitive firm's long‐run equilibrium situation is illustrated in Figure . The entry of new firms leads to an increase in the supply of differentiated products, which causes the firm's market demand curve to shift to the left. Pricing in Theory (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion Monopolistic competition is similar to pure competition in that there are a large number of firms selling a product that has been differentiated from that sold by other firms in the industry. That is, although the products sold by monopolistically competitive firms are good substitutes, they are not perfect substitutes. PDF Krugman Model - Monopolistic Competition Demand facing typical monopolistically competitive firm: X = S[1/n - b(P - Pavg)], where X is the firm's sales, S is the total sales of the industry, n the number of firms in the industry, P the price charged by the firm itself, and Pavg the average price charged by its competitors. The following intuition follows from this
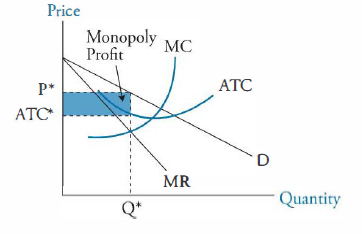
PDF Characteristics of Monopolistic competition Output and Price in Monopolistic Competition Diagram at right shows long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm. economic profits? price mark-up (P vs MC)? excess capacity? socially efficient output? deadweight loss? 3 Output and Price in Monopolistic Competition
Solved The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram ... The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is O A. eaming positive accounting profits but negative economic profits. O B, earning positive economic profits. ° C. earning negative economic profits. 0 D. earning economic profits equal to zero.
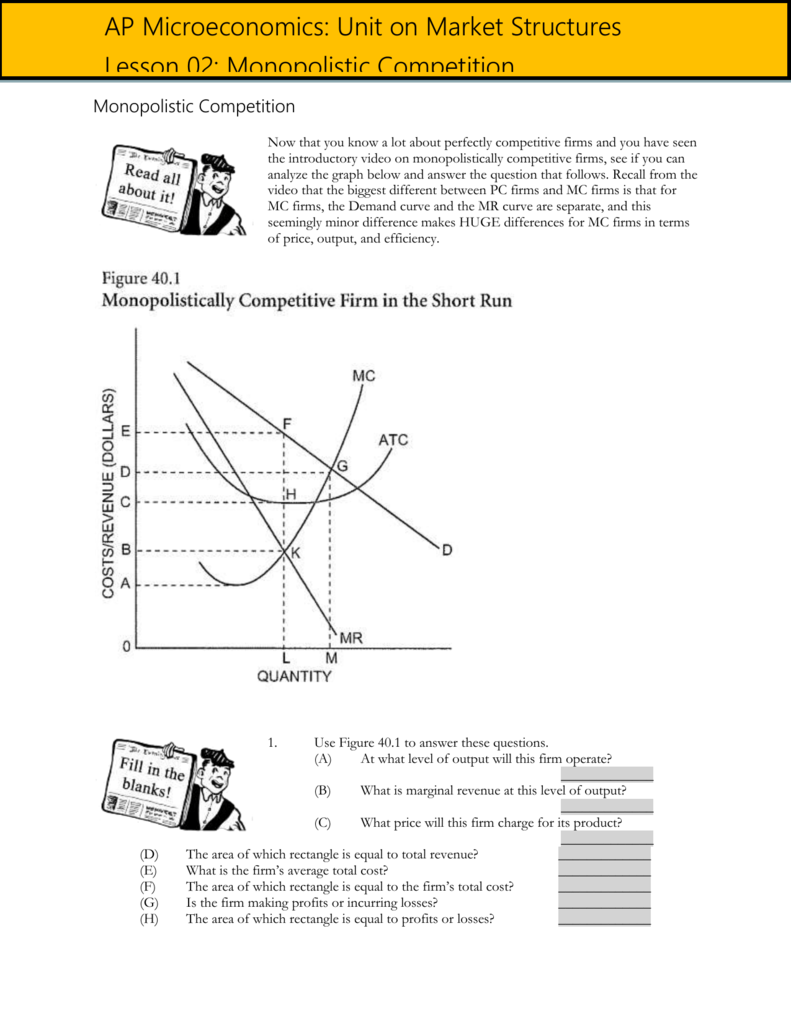
Solved lace The following graph represents a ... - Chegg Transcribed image text: lace The following graph represents a typical monopolistically competitive firm in the short ruh. the labels onto the appropriate areas of the diagram. Total Cost Consumer Surplus Total Revenue Profit Drag each item above to its appropriate location in the image. Note that every item may not have a match, while some items may have more than one match.
Monopolistic Competition - tutor2u AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC Monopolistic competition is a form of imperfect competition and can be found in many real world markets ranging from clusters of sandwich bars, other fast food shops and coffee stores in a busy town centre to pizza delivery businesses in a city or hairdressers in a local area.
Monopolistic Competition - Overview, How It Works, Limitations Monopolistic competition is a type of market structure where many companies are present in an industry, and they produce similar but differentiated products. None of the companies enjoy a monopoly, and each company operates independently without regard to the actions of other companies. The market structure is a form of imperfect competition.
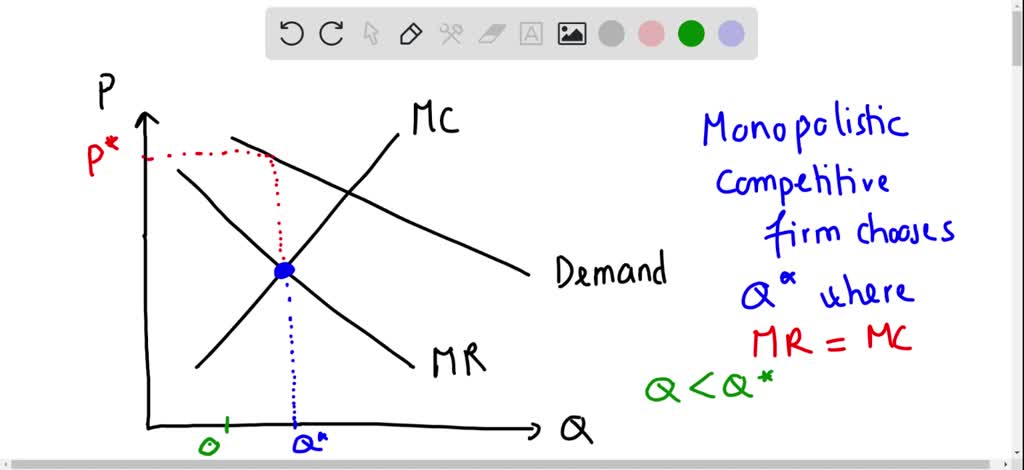
10.1 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Economics The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price in much the same way as a monopolist. A monopolistic competitor, like a monopolist, faces a downward-sloping demand curve, and so it will choose some combination of price and quantity along its perceived demand curve.
The monopolistic competitive firm is also a profit ... The monopolistic competitive firm is also a profit maximiser. So it will increase production as long as the addition to its total revenue is greater than the addition to its total costs. In other words, the firm under monopolistic competition will produce the quantity that equates its marginal revenue to its marginal cost. But, here, the firm produces less than the perfectly competitive firm.
Unit 5 Practice 2014.pdf - Unit 5 Practice Student: _ 1 ... 8. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Assume the firm is part of an increasing-cost industry. In the long run firms will: A.leave this industry, causing both demand and the ATC curve to shift upward. B.enter this industry, causing demand to rise and the ATC curve to shift downward.
Monopoly diagram short run and long run - Economics Help In a competitive market, firms may produce quantity Q2 and have average costs of AC2. A monopoly can produce more and have lower average costs. This enables efficiency of scale. Related. Monopolistic competition - where the short-run equilibrium is different from the long-run equilibrium; Monopoly - advantages and disadvantages.
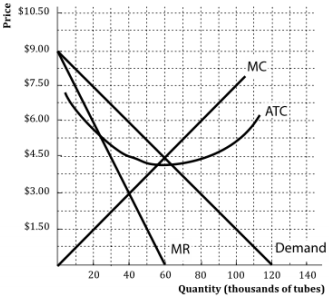
PDF Chap 13 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly MULTIPLE ... 29)In the above figure, the monopolistically competitive firm earns an economic profit of A)between $50.01 and $100 per day. B)greater than $100.01 per day. C)$0. D)between $0 and $50 per day. 29) 30)The above figure is for a firm in monopolistic competition. The diagram represents the short run rather than the long run because
Answered: Draw a diagram of a monopolistically… | bartleby Solution for Draw a diagram of a monopolistically competitive firm showing the firm earning profits in the short run. Which diagram below is correct? OB. Oc.…
Microeconomics Chapter 13 Flashcards - Quizlet When a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium, MR = MC and minimum ATC > P. Refer to the above graphs. A short-run equilibrium that would produce profits for a monopolistically competitive firm would be represented by graph A. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. This firm is experiencing
The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a ... The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. FIGURE 11-3-Refer to Figure 11-3. In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm will A) make profit by producing at QC and charging price PL. B) maximize profit by producing output level QC , the minimum point of its LRAC curve
8.4 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Microeconomics The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price similar to the way that a monopolist does. Since they face a downward sloping demand curve, the same considerations about how elasticity affects revenue are relevant, and the firm will maximize profits where MR = MC when P > MR. Step 1.






















0 Response to "41 the monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is"
Post a Comment