39 curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
PDF Lab 12: Perfectly Competitive Market | minimum point of ATC curve). All the firms in a perfectly competitive market earn economic profit equal to zero. (Since economic profit is the profit after accounting for the implicit cost e. Shutdown point and break-even point are the same in the long run: the minimum point of ATC curve (compare to the shutdown point in the short... Perfect competition II: Taxes | Policonomics | Taxing firms - Perfect competition II: Taxes. Summary. Firms in a perfectly competitive market may encounter some problems that can decrease their competitiveness and may even force them out of the market. The way they deal with problems will determine whether they can stay in the market.
Unit 9 The labour market: Wages, profits, and ... - CORE Exercise 9.3 The price-setting curve. In your own words and using a diagram like Figure 9.9, ... The elasticity of the firm’s demand curve is greater the more competition the firm faces from other firms, so the higher the elasticity, the lower the firm’s price and markup. ... unemployment is purely cyclical. At B, the firms are able to make ...
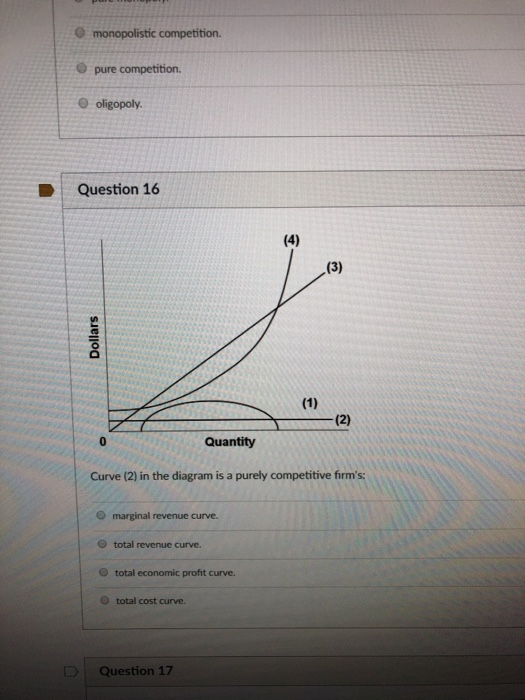
Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
Competition - BE 3 Unit 12 A level playing field = a situation of fair competition. It is not a level playing field anymore. As a small, family-owned company, it is very difficult of us to compete with the big and the big multinationals in terms of price. Marginal Revenue Questions and Answers - Study.com A perfectly competitive firm's marginal cost is $5, marginal revenue is $4, and the average variable cost is $3. To maximize profits (or minimize losses), the firm should a) shut down. b) lower the... Perfect Competition Definition Pure or perfect competition is a theoretical market structure in which a number of criteria such as perfect information and resource mobility are met. Perfect competition is a benchmark or ideal type to which real-life market structures can be compared.
Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. The Psychological Contract - BusinessBalls.com A quick key is shown with the diagram. A more detailed explanation is below the diagram. Here is a PDF version of the Psychological Contract iceberg diagram. Note that this diagram is an example of a very basic employee/employer relationship in which only work and pay are formally agreed and contracted. Monopolistic competition - Wikipedia Short-run equilibrium of the firm under monopolistic competition. The firm maximizes its profits and produces a quantity where the firm's marginal revenue (MR) is Monopolistic competition is a type of imperfect competition such that there are many producers competing against each other, but selling... Man 503 The firm's cost function is given by C = 60Q + 25,000. Assume that the firm maximizes profits. a. What is the level of production, price, and total profit per week? Thus, it does not matter who sends the tax payment to the government. The burden of the tax is reflected in the price of the good. Porter's Five Forces Model | Strategy framework | Cleverism Porter's Five Forces model was developed to help companies assess the nature of an industry's competitiveness & to develop corporate strategies accordingly. On the other hand in the film business, there is a high threat of substitutes from various other forms of entertainment.
Market Models: Pure Competition, Monopolistic Competition... In a purely competitive market, there are large numbers of firms producing a standardized product. Market prices are determined by consumer demand The producer surplus that would've been earned by the suppliers in the market if it were a competitive market is shown as area #2 in the diagram. Porter's Five Forces EXPLAINED with EXAMPLES | B2U Porter's Five Forces analysis is a framework that helps analyzing the level of competition within a certain industry. It is especially useful when starting a new business or when entering a new industry sector. According to this framework, competitiveness does not only come from competitors. Definition of competitive advantage and a discussion of its sources... A competitive advantage exists when the firm is able to deliver the same benefits as competitors but at a lower cost (cost advantage), or deliver benefits that exceed those of competing products (differentiation advantage). This decision is a central component of the firm's competitive strategy. Chapter-3 Traditional competitors: Existing firms that share a firm's market space. New market entrants: New companies have certain advantages, such as not being locked into old A core competency is an activity for which a firm is a world-class leader, such as being the world's best miniature parts designer.
The demand schedule or curve confronted by the individual, purely... Question Content Area The use of reversing entries is a.required whenever adjusting entries are omitted. b.required. c.optional unless computerized ac … counting systems are used. d.optional. Ответы на Тесты по Английскому языку для всех курсов ПОЛИТЕХ... Выберите один ответ: Верно Неверно. 1. Trends can be _ traced back over the centuries. 2. Trends are a bit slower paced but represent something that occurs on a тисВ wider scale than a fad. 6. Everyone working in the fashion industry needs _ to be aware of social and cultural movements. MicroEcon Ch 9,10,12 Flashcards | Quizlet A purely competitive firm should produce in the short run if its total revenue is sufficient to cover its Refer to the two diagrams for individual firms. In Figure 2 the firm's demand and marginal revenue curves are represented by Microeconomics Questions and Answers - Study.com 1. A perfectly competitive firm's marginal cost is MC=75+3q. The firm's short run supply curve is: a. q=-75+3P b. q=25+0.33P c. q=75+3q d. q=-25+0.33P 2. Which of the following market characteristi...
ECON 150: Microeconomics | Factors that Shift the Supply Curve It states that there is an inverse (or negative) relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded. Another factor that determines the demand for a good is the price of related goods. These can be broken down into two categories - substitutes and complements.
MicroEconomics Flashcards A purely competitive firm's output is currently such that its marginal cost is $4 and marginal revenue is $5. If a purely competitive firm shuts down in the short run: Definition. it will realize a loss equal to its total fixed If a firm is a price taker, then the demand curve for the firm's product is: Definition.
Diagrams for Supply and Demand - Economics Help In this diagram the supply curve shifts to the left. It leads to a higher price and fall in quantity demand. It is possible, that if there is an increase in demand (D1 to D2) this encourages firms to produce more and so supply increases as well.
a. Calculate the price elasticity of demand when the Label the curves in the diagram below. a. At what range of prices will the firm earn a negative profit? Positive profit or zero profit? b. At what price will the firm shut down? A competitive firm has the following short run cost function: C(q) = q - 8q +30q + 5. 3 a. 2 Find MC, AC, and AVC and sketch...
IELTS, TOEFL Writing task. Describing a graph/chart/diagram Example: The diagrams present information on the percentages of teachers who has expressed their views on different problems they face when dealing with There are certain phrases you can use to start your body paragraph and following is a list of such phrases: 1. As is presented in the diagram(s)...
Solved Question three The figure below shows a unit step | Chegg.com (A) shows the block diagram representation of a control system. When this system is excited with a unit step input, it responds as shown in the graph of Fig (B). Find, 1- The overall transfer function C(s)y/R(s). 2- The damping ratio g 3- The natural undamped frequency o 4- The damped natural...
4.7 Taxes and Subsidies - Principles of Microeconomics Use the diagram below to answer the following TWO questions. Consider the supply and demand diagram below. Assume that: (i) there are no externalities; and (ii) in the absence of government regulation the market supply curve is the one labeled S1.
Untitled 1 Technological advances that reduce the cost of producing computer chips represent a decline in an input price for producing a computer. The result is a shift to the right in the supply of computers, as shown in Figure. The equilibrium price falls and the equilibrium quantity rises, as the figure shows.
PDF Microsoft Word - Solution Manual October 31.DOC 4-4. Consider a firm for which production depends on two normal inputs, labor and capital, with prices w and r, respectively. Initially the firm faces market After the price shift, the slope is 2. In other words, labor has become relatively more expensive than capital. As a result, there will be a substitution away...
Pricing in Theory (With Diagram) | Economics Discussion Purely Competitive Firm and Industry: A perfectly competitive market has the following features An equilibrium price prevails for all the firms in the industry. The demand curve facing an individual firm in this case is thus, perfectly elastic, i.e., horizontal.
Microeconomics Lecture #12 Flashcards - Quizlet The diagram depicts a cost curve graph of a price-taking firm that is currently operating and producing cherries. Identify each item in the graph of this cherry producer. The average total cost (ATC), marginal cost (MC), and marginal revenue (MR) curves are already labeled.
Short Run Average Costs: Marginal Cost, AFC, AVC, Formulas, etc While the total cost of production helps firms understand the overall expenses incurred, the average costs help identify the expenditures involved in manufacturing a single unit. If the average cost falls due to an increase in the output, the marginal cost is less than the average cost.
Chapter 12 - Pure Monopoly Flashcards - Quizlet A. is less elastic than a purely competitive firm's demand curve. If a nondiscriminating imperfectly competitive firm is selling its 100th unit of output for $35, its marginal revenue: A. may be either greater or less than $35.
Economies of Scale and International Trade - GitHub Pages The production feature that is present when a firm’s average cost curve is downward sloping. Of many or few, this is the assumption made about the number of firms in a monopolistically competitive industry. The long-run value of firm profit in a monopolistically competitive industry.
PDF sol_10.PDF | a. Calculate the firm's marginal revenue curve. The marginal revenue curve corresponding to a linear demand curve is a line with the same intercept as the a. On a diagram, draw the marginal cost curves for the two factories, the average What is the firm's degree of monopoly power at this price? If the regulatory authority sets a price below $6 competitive industry. Therefore, the regulatory agency should set a price ceiling of $6, thus making...
Perfect competition - Wikipedia In economics, specifically general equilibrium theory, a perfect market, also known as an atomistic market, is defined by several idealizing conditions, collectively called perfect competition, or atomistic competition.In theoretical models where conditions of perfect competition hold, it has been demonstrated that a market will reach an equilibrium in which the quantity supplied for …
Regression Analysis: How Do I Interpret R-squared and Assess the... There are two major reasons why it can be just fine to have low R-squared values. In some fields, it is entirely expected that your R-squared values will be low. Regardless of the R-squared, the significant coefficients still represent the mean change in the response for one unit of change in the predictor...
Помогите пожалуйста с тестами по английскому языку which type of... 3Choose the synonym of social security Ответы [a]welfare [б] tax [в] apartment [г] rent. 4.What is a financial plan, showing how much money a person or organization?
Externality - Wikipedia A negative externality (also called "external cost" or "external diseconomy") is an economic activity that imposes a negative effect on an unrelated third party. It can arise either during the production or the consumption of a good or service. Pollution is termed an externality because it imposes costs on people who are "external" to the producer and consumer of the polluting …
PDF Microsoft Word - Solution to Chapter 7 From the firm's point of view, the wage paid to the worker is an explicit cost whether she was previously unemployed or not. The firm's opportunity cost is equal to the wage, because if it did not hire this worker, it would have had to hire someone else at the same wage.
Perfect Competition | Boundless Economics | Firm Revenues A firm in a competitive market wants to maximize profits just like any other firm. The profit is the difference between a firm's total revenue and its total cost. A perfectly competitive firm faces a demand curve is a horizontal line equal to the equilibrium price of the entire market.
Marginal Revenue and Price Elasticity of Demand The following one is a perfectly elastic demand curve. This is often used to depict the price and output behaviour of a firm under pure competition. Here dP/dQ = 0. Therefore, the graphing of P in terms of Q in Figure 10.7, has a slope of zero. In other words, the demand curve is completely (perfectly) elastic.
Perfect Competition Definition Pure or perfect competition is a theoretical market structure in which a number of criteria such as perfect information and resource mobility are met. Perfect competition is a benchmark or ideal type to which real-life market structures can be compared.
Marginal Revenue Questions and Answers - Study.com A perfectly competitive firm's marginal cost is $5, marginal revenue is $4, and the average variable cost is $3. To maximize profits (or minimize losses), the firm should a) shut down. b) lower the...
Competition - BE 3 Unit 12 A level playing field = a situation of fair competition. It is not a level playing field anymore. As a small, family-owned company, it is very difficult of us to compete with the big and the big multinationals in terms of price.
0 Response to "39 curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's"
Post a Comment