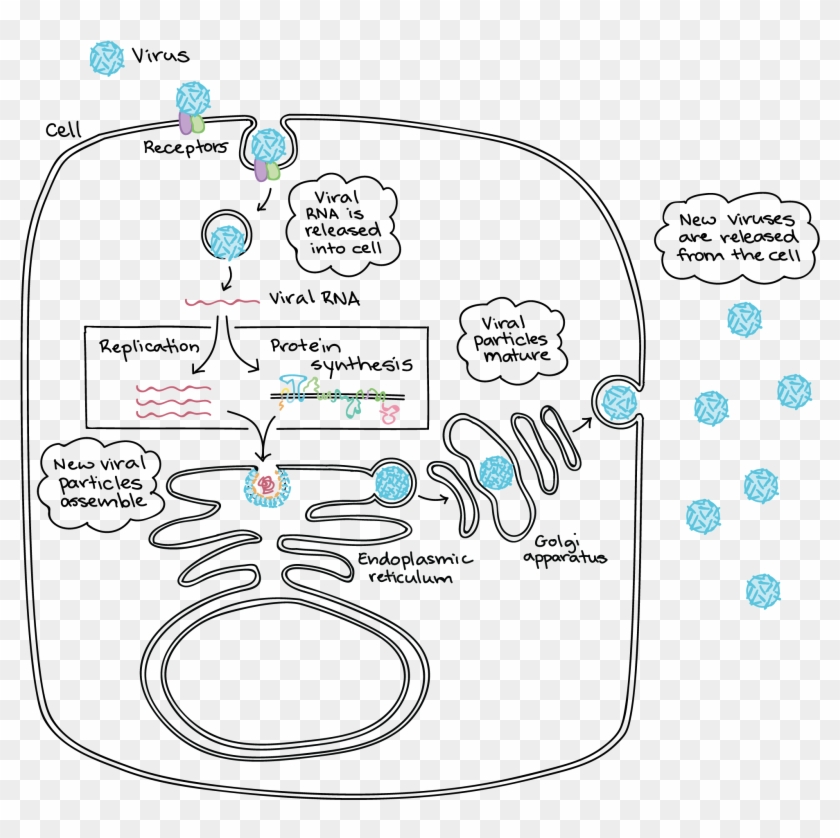
38 life cycle of a virus diagram
Virus Life Cycle: Introduction, Life Cycle, FAQs Viruses encode proteins that hinder the host genome, aid in viral replication and have a major role in the life cycle of viruses. 4) Assembly Capsomers are the outer covering of proteins that protect the genetic information of a virus. Virus Life Cycle Worksheet Diagram Answers : Targethiv Org Virus Life Cycle Worksheet Diagram Answers : Targethiv Org -. You can see real examples of viral lifecycles in the . Like the lytic cycle, in the lysogenic cycle the virus attaches to. Understand how replication cycles of lytic and lysogenic viruses differ among. Each time the host's cells go through replication, the virus's dna .
PDF Life cycle: the mosquito Mosquito life cycle It takes about 7-10 days for an egg to develop into an adult mosquito. Aedes aegypti Pupae live in the water. They develop into adult, flying mosquitoes in 2-3 days. Adult Eggs Female mosquitoes lay eggs in containers that hold water. Eggs hatch within a few days to months when covered with water.

Life cycle of a virus diagram
Bacteriophage - Structure And Life Cycle Of Bacteriophage In the Lytic Cycle, a bacteriophage infects a bacteria and kills it to release progeny virus. This cycle takes place in the following steps: Adsorption. The bacteriophage attaches itself on the surface of bacteria. This process is known as adsorption. The tips of the tail fibres attach to specific receptors on the surface of the bacterial cell. The Hantavirus Lifecycle and Structure | Hanta Virus The lifecycle begins when the Hantavirus attaches to a cell using one of two proteins, called G1 and G2. G1 and G2 work by binding to a cellular receptor, which allows the virus into the cell through endocytosis. Endocytosis is a process in which the cellular membrane caves inward, drawing everything nearby into the cell, and then pinching off ... Virus Life Cycle - RABIES VIRUS INFORMATION The Life Cycle of the Rabies Virus involves transmission between a rabid individual and a healthy individual because rabies, like all viruses is an obligate intercellular parasite. In most cases, the virus is transmitted via the salvia of an infected animal (often raccoons, skunks, bats, foxes, or dogs) to another animal or human.
Life cycle of a virus diagram. Life cycle of a poliovirus | Media Library | Integration ... Life cycle of a poliovirus. Conceptual diagram illustrating the life cycle of a poliovirus. diagram poliovirus life cycle enteroviruses asymptomatic infection illness vaccine excretion blood cell bloodstream nerve cell virus. Author (s) Kate Bentsen. Author Company. Integration and Application Network. SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle: Stages and Inhibition Targets Stages of the SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle: 1. Virus Entry 2. Translation of Viral Replication Machinery 3. Replication 4. Translation of Viral Structure Proteins 5. Virion Assembly 6. Release of Virus SARS-CoV-2 Replication Cycle SARS-Cov-2 Replication Cycle and Inhibitors. Possible targets for inhibitors are marked in red and numbered in roman numerals. Potyvirus - Wikipedia Potyvirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Potyviridae.Plants serve as natural hosts. The genus is named after member virus potato virus Y.Potyviruses account for about thirty percent of the currently known plant viruses.Like begomoviruses, members of this genus may cause significant losses in agricultural, pastoral, horticultural, and ornamental crops. The Life Cycle of Rous Sarcoma Virus diagram drawing (1 ... RE: Calisphere: Request high-resolution copy of item for The Life Cycle of Rous Sarcoma Virus diagram drawing (1) Message Check to send a copy of this message to your email.
CDC - Malaria - About Malaria - Biology The malaria parasite life cycle involves two hosts. During a blood meal, a malaria-infected female Anopheles mosquito inoculates sporozoites into the human host .Sporozoites infect liver cells and mature into schizonts , which rupture and release merozoites . (Of note, in P. vivax and P. ovale a dormant stage [hypnozoites] can persist in the liver (if untreated) and cause relapses by … Virus Life Cycle The life cycle of virus. The virus life cycle could be divided into six steps: attachment, penetration, uncoating, gene expression and replication, assembly, and release. The viral capsid (blue) and genome (brown) are schematically drawn for the purpose of explanation. The nucleus is omitted for clarity. 3.2. Viral Entry PDF The HIV Life Cycle - University of Nevada, Reno School of ... The HIV Life Cycle Binding and Fusion: HIV begins its life cycle when it binds to a CD4 receptor and one of two co-receptors on the surface of a CD4 + T- lymphocyte. The virus then fuses with the host cell. After fusion, the virus releases RNA, its genetic material, into the host cell. Reverse Transcription: An HIV enzyme called reverse ... The HIV Life Cycle | NIH What are the seven stages of the HIV life cycle? The seven stages of the HIV life cycle are: 1) binding, 2) fusion, 3) reverse transcription, 4) integration, 5) replication, 6) assembly, and 7) budding. To understand each stage in the HIV life cycle, it helps to first imagine what HIV looks like.
The Viral Life Cycle - Microbiology Life Cycle of Viruses with Animal Hosts Lytic animal viruses follow similar infection stages to bacteriophages: attachment, penetration, biosynthesis, maturation, and release (see Figure 4). However, the mechanisms of penetration, nucleic-acid biosynthesis, and release differ between bacterial and animal viruses. Virus Structure | Forms of Viruses | Virus Structure Types ... A virus is an infectious non-living particle that cannot survive on its own. The life cycle of the virus is a series of steps that enable the virus to infect a host and replicate itself. Explore virus structure, structure of virus, viral structure types, and functions of virus structure. The typical different stages of virus life cycle. (1 ... Download scientific diagram | The typical different stages of virus life cycle. (1) Attachment: In this step, the viral envelope glycoproteins attach to certain host cell membrane receptors. (2 ... 6.2 The Viral Life Cycle - Microbiology | OpenStax Life Cycle of Viruses with Animal Hosts Lytic animal viruses follow similar infection stages to bacteriophages: attachment, penetration, biosynthesis, maturation, and release (see Figure 6.10 ). However, the mechanisms of penetration, nucleic-acid biosynthesis, and release differ between bacterial and animal viruses.
Influenza virus- Structure, Types, Life Cycle References. Influenza virus- Structure, Types, Life Cycle. Influenza commonly called a flue is a highly contagious viral infection of the respiratory tract mainly infects humans and animals. Influenza virus belongs to the family: Orthomyxoviridae. The annual attack rate of influenza virus is 5-10% in adults and 20-30% in children.
Life cycle of a virus - Communicable disease - Edexcel ... Life cycle of a virus. The life cycle of a virus. is the same as other pathogens. They can often survive outside a host. for long periods of time. When they do infect a suitable host cell or cells ...
Virus Structure & Life Cycle - Videos & Lessons | Study.com The life cycle of a virus includes several steps, including attachment, penetration, uncoating, replication, maturation, and release. Explore how viruses live, attack host cells, and replicate, and...
The Viral Life Cycle | Microbiology - Lumen Learning Life Cycle of Viruses with Animal Hosts Lytic animal viruses follow similar infection stages to bacteriophages: attachment, penetration, biosynthesis, maturation, and release (see Figure 4). However, the mechanisms of penetration, nucleic-acid biosynthesis, and release differ between bacterial and animal viruses.
HIV: Structure, Life Cycle, and Pathogenecity Human Immunodeficiency Virus: Structure, Life Cycle, and Pathogenecity . Jonathan Hughes . Viruses are the smallest infectious agents of animal and plant tissues. They range in size from 20 to 300 nm (lnm = one billionth ofa meter). To cause a disease, viruses
Arenavirus life cycle | Download Scientific Diagram Download scientific diagram | Arenavirus life cycle from publication: Epidemiological Trends of Lassa Fever Outbreaks and Insights for Future Control in Nigeria | The pattern of Lassa fever ...
Life Cycle - The Measles Virus Life Cycle of the Measles Virus. Figure 2. This graphic depicts the basic process of replication in a measles-infected host cell. The Hemagglutinin (H) and Fusion (F) proteins mediate transmission of the measles virus into host cells in the human respiratory tract (3). The virus is absorbed into the host cell when Hemagglutinin proteins bind to ...
Life Cycle of a Virus - Science with Amy The life cycle of HIV virus. Some infections are for life. HIV virus is one such example. A person infected with HIV can experience no symptoms for years as the virus remain dormant. The virus is sophisticated in avoiding detection from our immune cells and interfere with the body's immune function.
Ebola Virus Life Cycle: Definition & Stages | Study.com Life Cycle. The life cycle of the Ebola virus begins with the extracellular virion, or enveloped virus outside of a cell or host.Once it finds a host, the virus has to make its way inside. This ...
Life Cycle - Marburg Investigation Life Cycle. Figure 3: 3D structure of the Riemann-Pick C1 protein. For the Marburg Virus to infect the host's cell an essential element is needed. For Marburg and Ebola that element is the Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) membrane protein (1). This protein mediates infection by binding to the viral envelope glycoprotein.
Difference Between Lytic and Lysogenic Cycle - BYJU'S Lysogenic cycle, not a common method of viral reproduction, majorly is dependant on the lytic cycle. In this method, the virus unites its genetic details with that of the host, turning dormant and lets the host to reproduce while continuing its regular activities.
Phosphorus Cycle - Definition, Steps, Human Impact ... Jun 05, 2017 · Phosphorus Cycle Definition. The phosphorus cycle is the process by which phosphorus moves through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. Phosphorus is essential for plant and animal growth, as well as the health of microbes inhabiting the soil, but is gradually depleted from the soil over time. The main biological function of phosphorus is that it is …
4 Major Phases of the Cell Cycle (With Diagram) The following points highlight the four major phases of the cell cycle. The phases are: 1. G 1 (gap1) phase 2. S (synthesis) phase 3. G 2 (gap 2) phase 4. M (mitosis) phase. Cell Cycle: Phase # 1. G 1 Phase: . The G 1 phase is set in immediately after the cell division. It is characterised by a change in the chromosome from the condensed mitotic state to the more extended interphase …
Viral Life Cycle - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The natural baculovirus life cycle starts with ingestion into the gut of a suitable host, for example, an insect larva, and primary infection of cells of the gut lumen. It takes about 30 min for the virus to enter the cytosol through endosomes. In the first 10-20 h postinfection, the viral DNA is replicated and new virions are produced, which ...
mosquito | Description, Life Cycle, & Facts | Britannica The life cycle may be as short as 10 days or, in cool weather, as long as several months. A. aegypti, the important carrier of the virus responsible for yellow fever, has white bands on its legs and spots on its abdomen and thorax.
Life cycle and morphogenesis of the hepatitis E virus In this review, the current knowledge of the hepatitis E virus life cycle, the established model systems, and the status of vaccine development will be discussed. HEV entry The hepatitis E virus can present as either a nonenveloped virus, where the capsid shell interacts with the surrounding environment, or as a quasi-enveloped virus, where the ...
The 7 stages of the HIV life cycle explained - IAS The 7 stages of the HIV life cycle explained. #1 Binding. This is the very first stage of the HIV Lifecycle. The HIV virus attacks the CD4 cell and attaches Itself to the cell on its surface. It does this by first attaching to the CD4 cell's receptor than the CCR5 or the CXCR4 coreceptor. #2 Fusion.
Ebola Virus Life Cycle & Ebola Virus Structure Ebola Virus Structure: progressive dissection of an Ebola virus particles. Above image measures 600 pixels across, original image is 5879 x 5609 pixels. See all Ebola pictures. Ebola References for Life Cycle picture: EBOLA AND MARBURG VIRUS MORPHOLOGY AND TAXONOMY FREDERICK A. MURPHY, GUIDO VAN DER GROEN, SYLVIA G. WHITFIELD, JAMES V. LANGE
Virus Life Cycle - RABIES VIRUS INFORMATION The Life Cycle of the Rabies Virus involves transmission between a rabid individual and a healthy individual because rabies, like all viruses is an obligate intercellular parasite. In most cases, the virus is transmitted via the salvia of an infected animal (often raccoons, skunks, bats, foxes, or dogs) to another animal or human.
The Hantavirus Lifecycle and Structure | Hanta Virus The lifecycle begins when the Hantavirus attaches to a cell using one of two proteins, called G1 and G2. G1 and G2 work by binding to a cellular receptor, which allows the virus into the cell through endocytosis. Endocytosis is a process in which the cellular membrane caves inward, drawing everything nearby into the cell, and then pinching off ...
Bacteriophage - Structure And Life Cycle Of Bacteriophage In the Lytic Cycle, a bacteriophage infects a bacteria and kills it to release progeny virus. This cycle takes place in the following steps: Adsorption. The bacteriophage attaches itself on the surface of bacteria. This process is known as adsorption. The tips of the tail fibres attach to specific receptors on the surface of the bacterial cell.

0 Response to "38 life cycle of a virus diagram"
Post a Comment