39 trigeminal nerve branches diagram
Simplified diagrams of the main branches and sensory supply of the trigeminal nerve. Case Discussion Simplified illustrations of the trigeminal nerve , its main branches, and its sensory supply. Trigeminal neuralgia affecting the ophthalmic, maxillary or mandibular branches accompanied by lacrimation has been reported. 87,111 These may mimic TACs, particularly SUNCT or even cluster headache. 32,33 However, SUNCT is typically resistant to trigeminal neuralgia therapy, has prominent and multiple autonomic signs 111 and has no refractory ...
Jan 23, 2018 · The facial nerve is also known as the seventh cranial nerve (CN7). This nerve performs two major functions. It conveys some sensory information from the tongue and the interior of the mouth.
Trigeminal nerve branches diagram
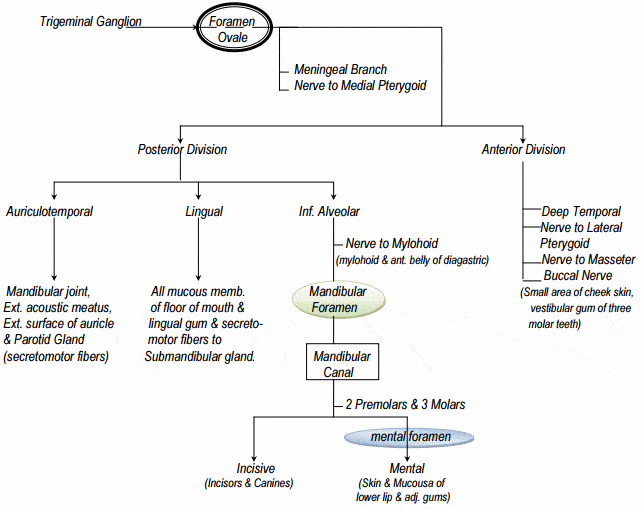
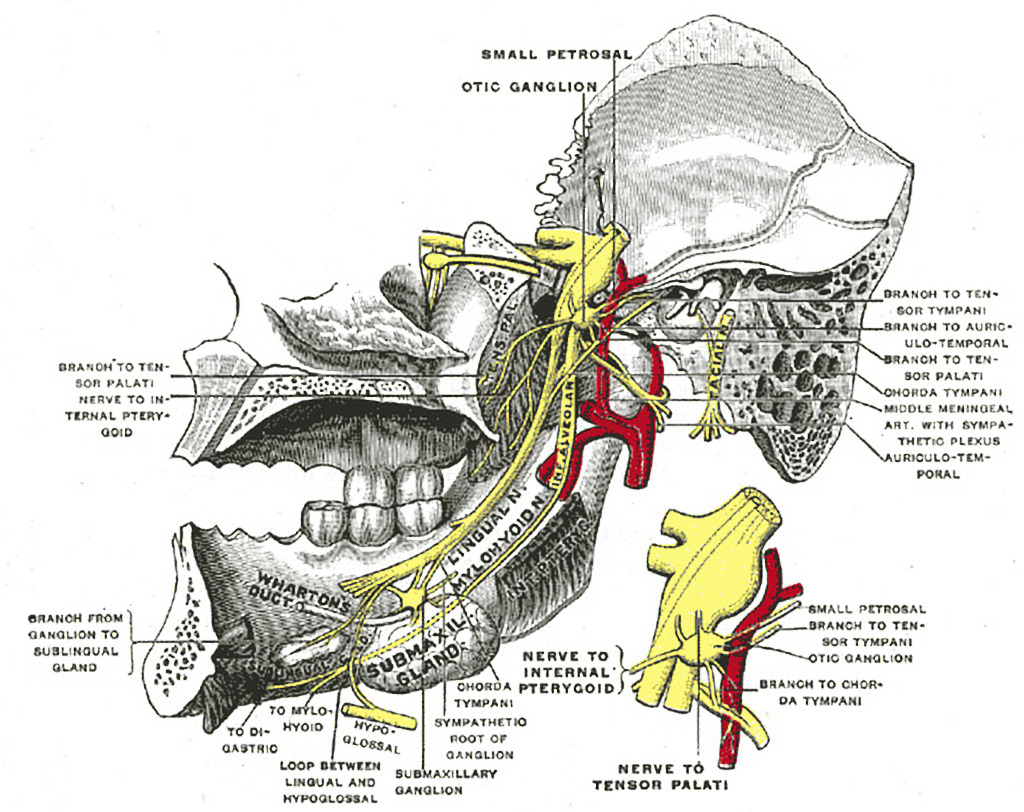
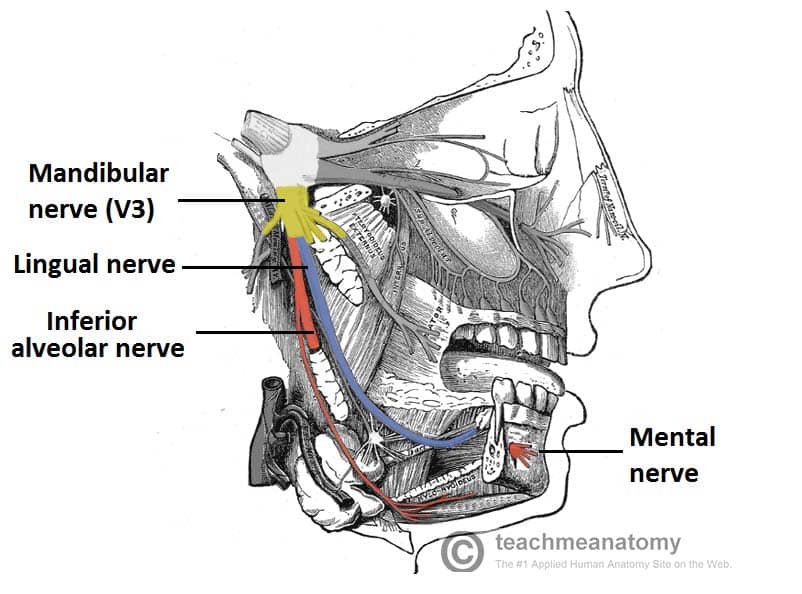
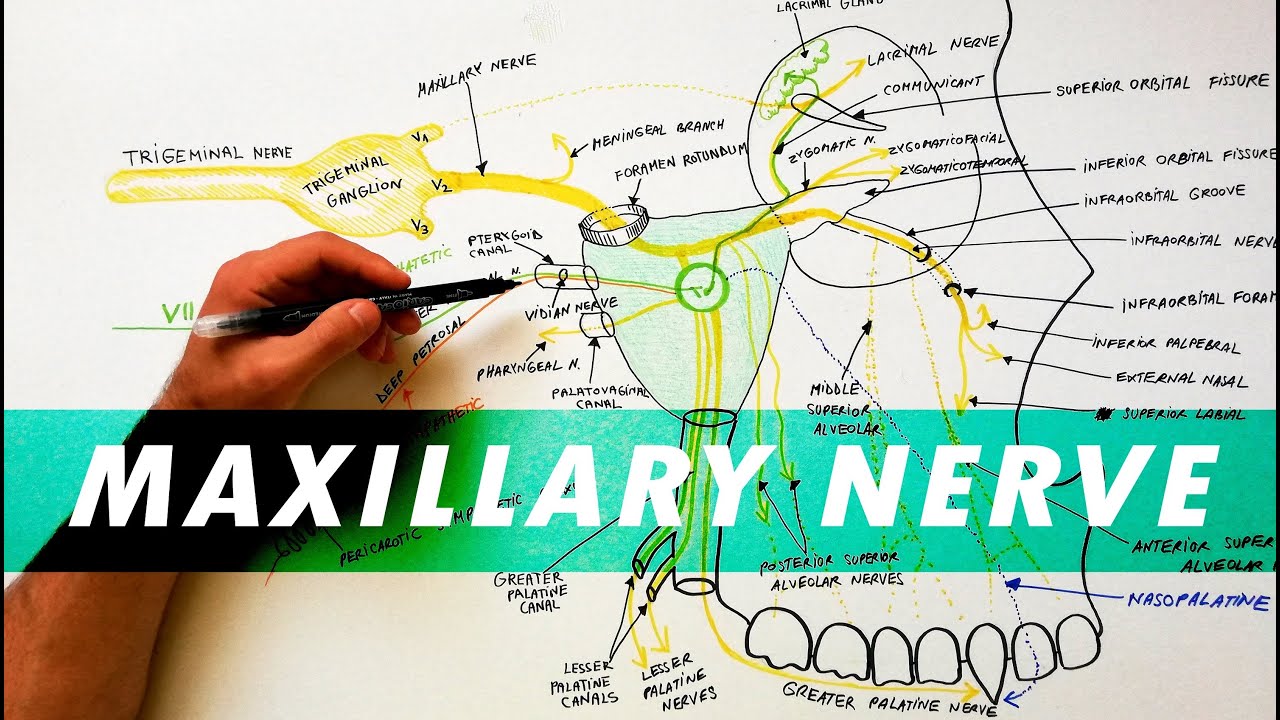
The nerve of the pterygoid canal ... they travel on the branches of the maxillary nerve to provide sympathetic innervation to blood vessels. Additional images. Alveolar branches of superior maxillary nerve and pterygopalatine ganglion. Diagram of the cervical sympathetic. See also. Vidus Vidius; References ... May 12, 2017 · The branches of the trigeminal nerve take sensations of touch and pain to the brain from your face, teeth and mouth. The trigeminal nerve also controls the muscles used in chewing and in the production of saliva and tears. Usually one or both of the maxillary and mandibular branches are affected by trigeminal neuralgia. Oct 28, 2021 · The mandibular teeth are primarily supplied by the inferior alveolar nerve which is a branch of the mandibular nerve (third division of the trigeminal nerve). The mandibular nerve carries fibers that are both sensory and motoric due to the merger of its large sensory and small motor roots just after it exits the skull via the foramen ovale .
Trigeminal nerve branches diagram. Dec 27, 2021 · Within the cavernous sinus the oculomotor nerve is located uppermost, above the trochlear nerve in the lateral wall of the sinus. Orbital portion It enters the orbit via the superior orbital fissure as two branches: superior division and inferior division, with the nasociliary nerve (a branch of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve ... Thanks for the diagram. What I've learned over the last year and a half is that there are little branches from the TN nerve that go to each of the teeth -- that's why a lot of us experience 'toothache' like pain. And the diagram shows that it connects into the nose area -- that's where I had my first electric zap. Dec 06, 2017 · The lateral walls of the nasal cavity and the septum are innervated by the maxillary nerve branch known as the nasopalatine nerve, and the ophthalmic nerve branch called the nasociliary nerve. The trigeminal nerve innervates the outer skin of the human nose [8]. Function of the Nose What Does the Nose Do in the Respiratory System Helping in ... Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy: Gross Anatomy, Branches of the Trigeminal Nerve, Microscopic Anatomy The trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the 12 cranial nerves (CNs). It supplies sensations to the face, mucous membranes, and other structures of the head.
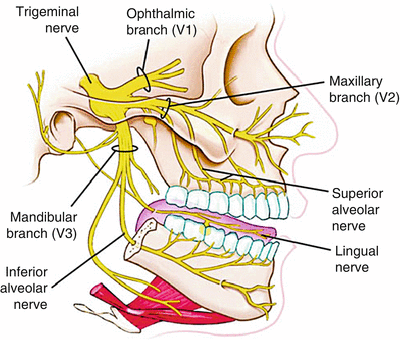
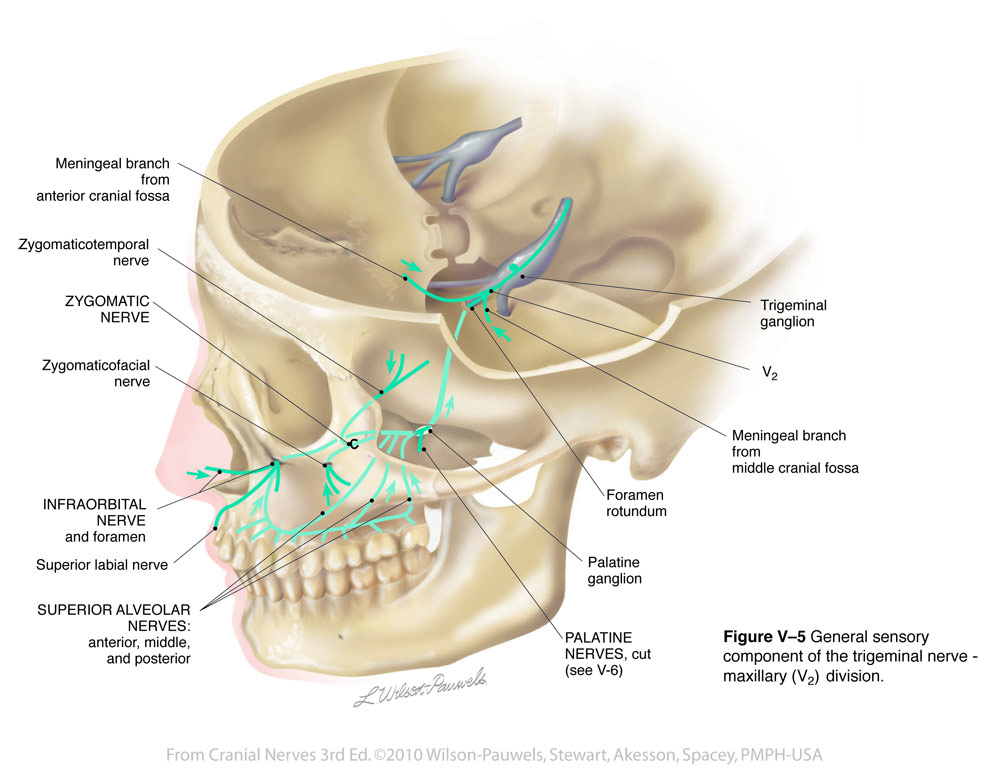
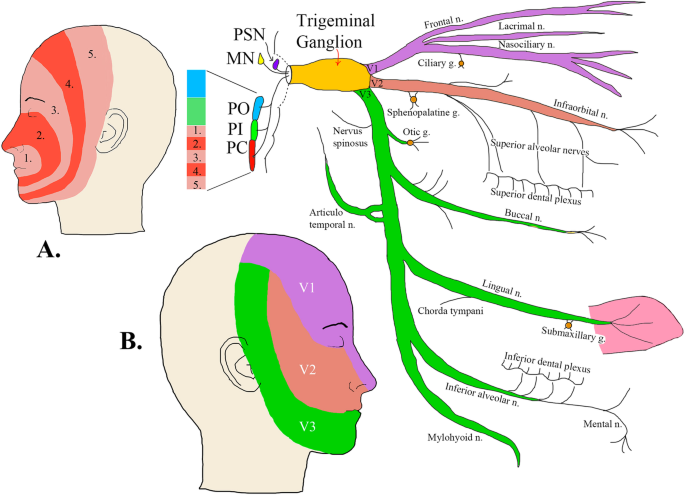
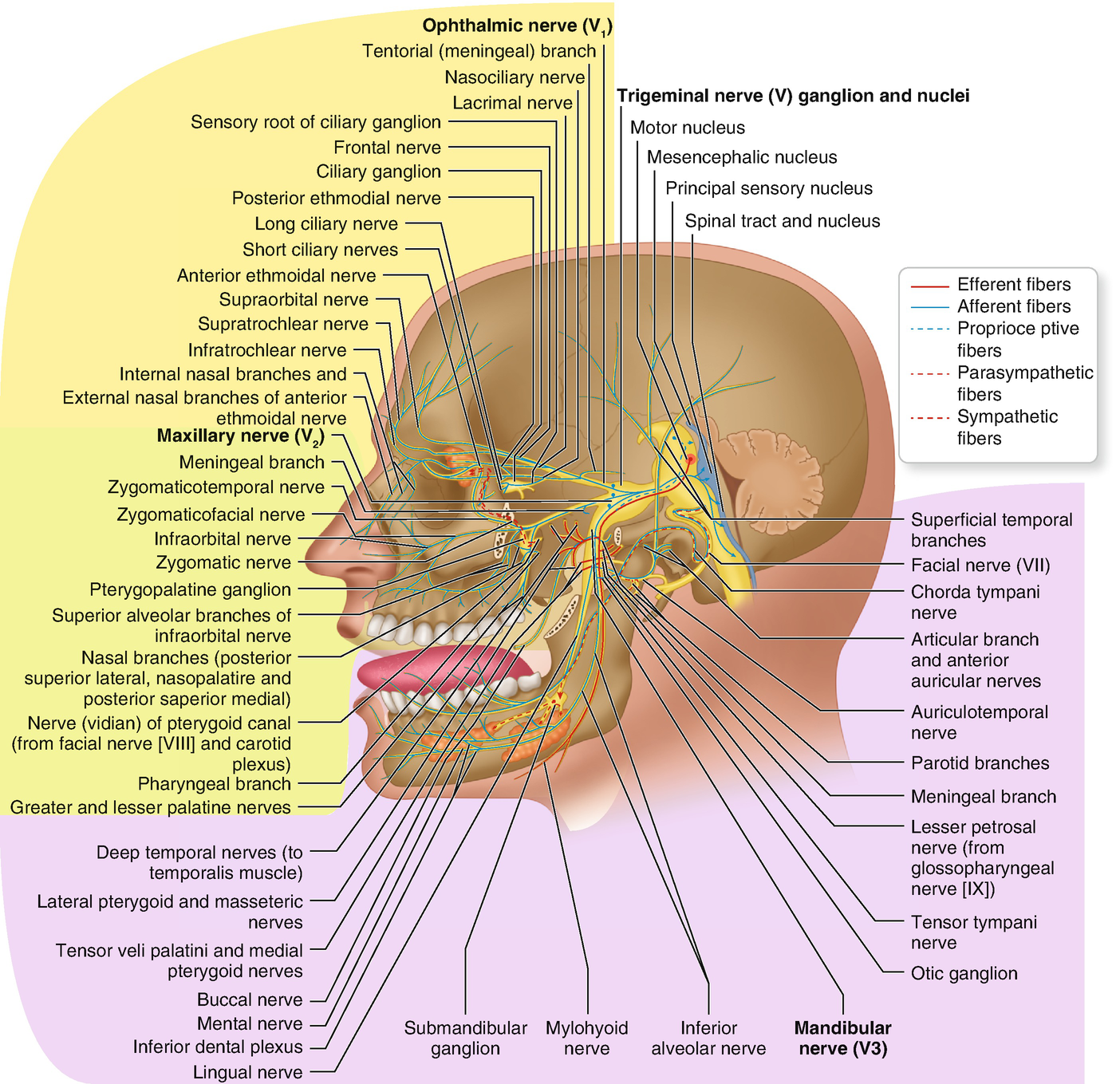
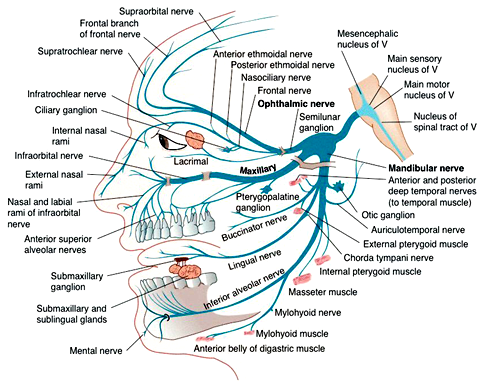
1. Identify on a skull, diagram, and by narrative description the bones, sutures, foramina, soft tissue and muscles of the head that are associated with dental injections. 2. Name the divisions of the Trigeminal Nerve, its exit from the cranium, branches and areas of supply. 3. The trigeminal nerve is responsible for carrying most of the sensation of the face to the brain. The sensory trigeminal nerve branches of the trigeminal nerve are the ophthalmic, the maxillary, and the mandibular nerves, which correspond to sensation in the V1, V2, and V3 regions of the face, respectively. Ophthalmic nerve: This nerve detects ... Diagram shows trigeminal nerve (TGN), trigeminal ganglion, and peripheral divisions and their branches. From fora-men rotundum ossis sphenoidalis, maxil-lary nerve (thin underline) gains access to pterygopalatine fossa and continues in floor of orbit as infraorbital nerve. Inferior alveolar and lingual nerves ( thick underline ) Trigeminal nerve branches diagram. Jan 22, 2018 · Trigeminal Nerve Overview Medically reviewed by Heidi Moawad, M.D. FInd information about the trigeminal nerve, including its functions, how doctors test it, and the conditions associated. The Trigeminal Nerve is the fifth cranial nerve. It is also represented as CN V.
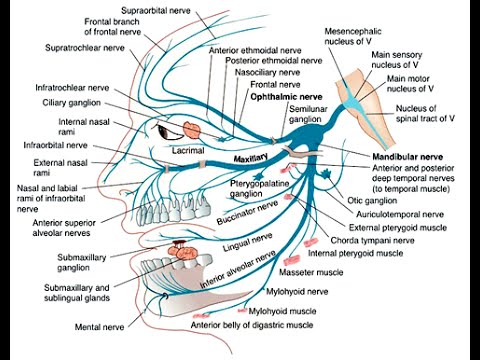
Dec 29, 2014 · The mandibular nerve is the third and the most inferior branch of the trigeminal nerve or the fifth cranial nerve. The lower branch is called the mandibular nerve. The nerve enters the mandible through the mandibular foramen on the medial surface of the ascending mandibular ramus. Trigeminal nerve route of entry. (A) Schematic showing the three branches of the trigeminal nerve: V1, V2, and V3. Branches V1 and V2 innervate the nasal cavity and project to the brain stem (BS). The trigeminal nerve is associated with derivatives of the 1st pharyngeal arch. Sensory: The three terminal branches of CN V innervate the skin, mucous membranes and sinuses of the face. Their distribution pattern is similar to the dermatome supply of spinal nerves (except there is little overlap in the supply of the divisions). Trigeminal Nerve. Create healthcare diagrams like this example called Trigeminal Nerve in minutes with SmartDraw. SmartDraw includes 1000s of professional healthcare and anatomy chart templates that you can modify and make your own.
Mar 14, 2019 · The trigeminal nerve is the largest of your cranial nerves and has both sensory and motor functions.. The trigeminal nerve has three divisions, which are: Ophthalmic. The ophthalmic division sends ...
Branches of the trigeminal nerve. Print. Sections. Products and services. Trigeminal neuralgia results in pain occurring in an area of the face supplied by one or more of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy: Gross Anatomy, Branches of the Trigeminal Nerve, Microscopic Anatomy The trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the 12 cranial nerves (CNs). It supplies sensations to the face, mucous membranes, and other structures of the head.
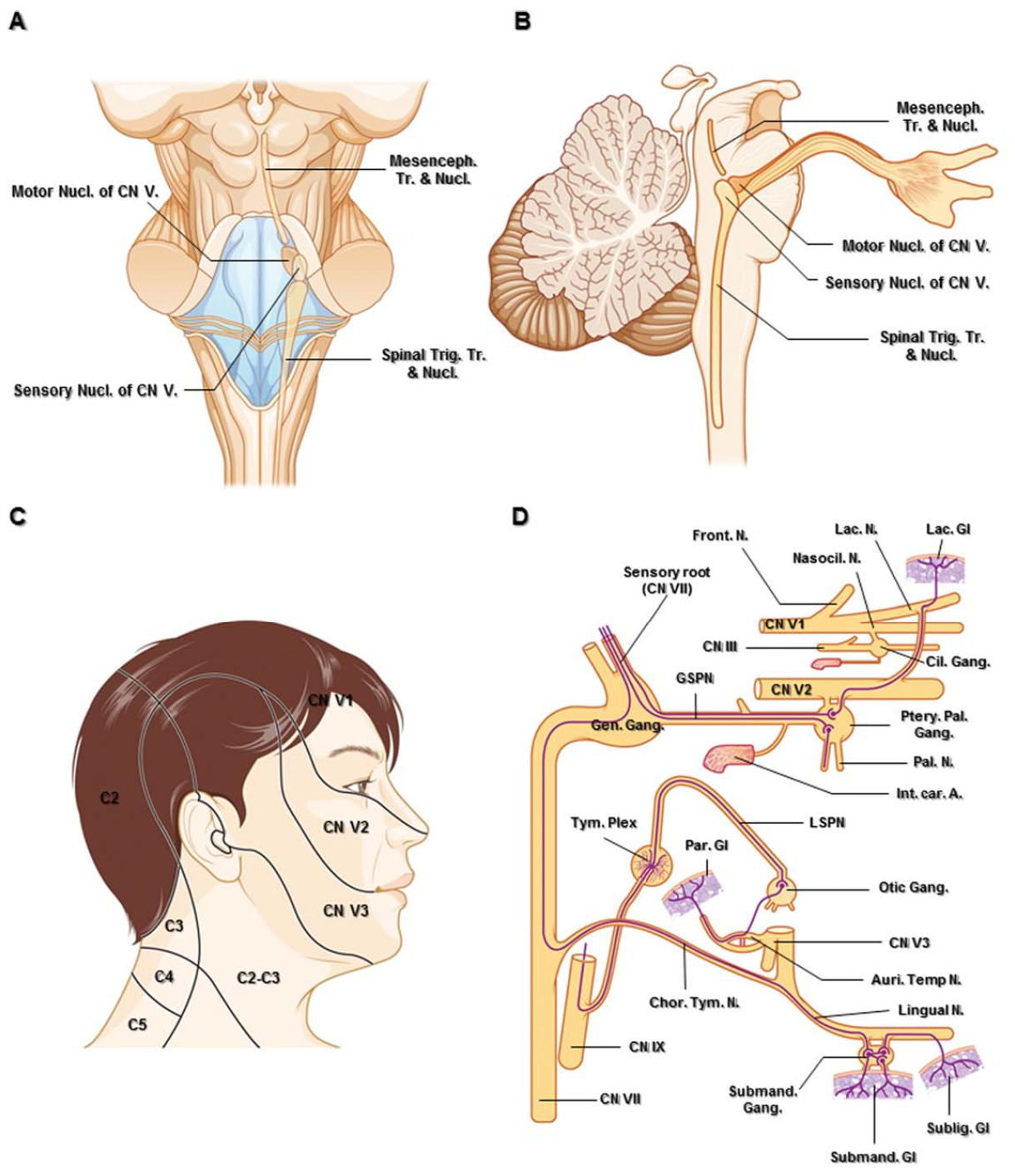
The trigeminal nerve is the largest cranial nerve and is the great sensory nerve of the head and face, and the motor nerve of the muscles of mastication.: It emerges from the side of the pons, near its upper border, by a small motor and a large sensory root—the former being situated in front of and medial to the latter.: Motor Root.—The fibers of the motor root arise from two nuclei, a ...
The trigeminal ganglion (or Gasserian ganglion, or semilunar ganglion, or Gasser's ganglion) is a sensory ganglion of the trigeminal nerve (CN V) that occupies a cavity (Meckel's cave) in the dura mater, covering the trigeminal impression near the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone
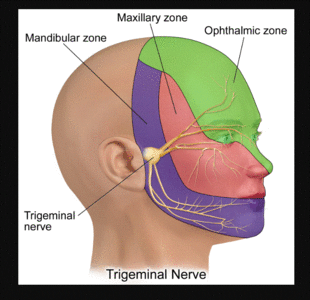
The trigeminal nerve consists of three branches on either side that extend to different territories of the face. These branches join at the trigeminal ganglia which are located within the Meckel cave of the cranial cavity. The different branches are namely the ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2), and mandibular (V3) nerves.
The trigeminal nerve (the fifth cranial nerve, or simply CN V) is a nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves.Its name ("trigeminal" = tri-, or three, and - geminus, or twin: so "three-born, triplet") derives from each of the two nerves (one on each side of the pons) having three major branches: the ...
The ophthalmic branch is the first division of the trigeminal nerve. It is a purely sensory nerve that carries afferent stimuli of pain, light touch, and temperature from the upper eyelids and supraorbital region of the face, up to the vertex of the head. The nerve also acts as a conduit for sympathetic fibers that require access to the ciliary body, lacrimal glands, cornea, and conjunctiva ...
Dec 27, 2021 · The corpus callosum (plural: corpora callosa) is the largest of the commissural fibers, linking the cerebral cortex of the left and right cerebral hemispheres. It is the largest white matter tract in the brain. Summary located inferior to the c...
The trigeminal nerve is the fifth of the twelve Cranial Nerves. It consists of both afferent and efferent motoric and sensory fibers as well as proprioceptive, sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers that are divided into three main branches: the ophthalmic nerve, the maxillary nerve, and the mandibular nerve.
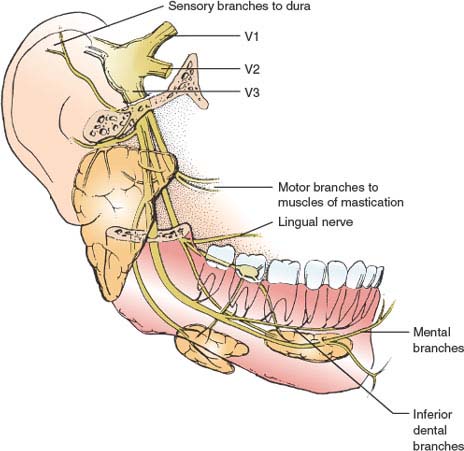
What are the 3 branches of the trigeminal nerve? 1. Ophthalmic (sensory) 2. Maxillary (sensory) 3. Mandibular (mixed) Ophthalmic branch -afferent (sensory) -little dental significance; may have side effects if LA is given incorrectly -smallest branch The ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve exits the cranium through....
Nov 28, 2017 — The ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular branches of the trigeminal nerve leave the skull through 3 separate foramina: the superior orbital ...Main location: Trigeminal areaPain intensity: SeverePain duration: Seconds to 2 minutes
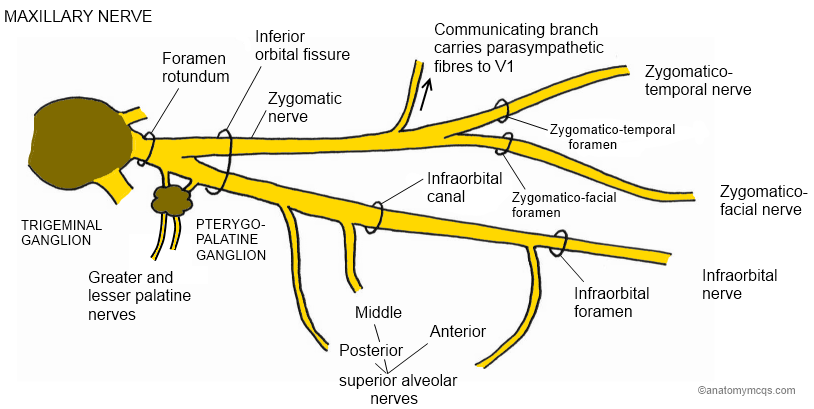
The maxillary nerve is divided into 3 branches: the zygomatic, pterygopalatine (or sphenopalatine), and posterior superior alveolar nerves. Diagram of the second branch (maxillary) of the trigeminal nerve with its branches.
The mandibular nerve is a terminal branch of the trigeminal nerve (along with the maxillary and ophthalmic nerves).. It has a sensory role in the head, and is associated with parasympathetic fibres of other cranial nerves. However unlike the other branches of the trigeminal nerve, the mandibular nerve also has a motor function.. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the mandibular ...
Start studying Trigeminal Nerve Distribution. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
The trigeminal nerve is one of 12 pairs of nerves that are attached to the brain. The nerve has three branches that conduct sensations from the upper, middle, and lower portions of the face, as well as the oral cavity, to the brain. The ophthalmic, or upper, branch supplies sensation to most of the scalp, forehead, and front of the head.
—Sagittal diagram shows three peripheral divisions of trigeminal nerve entering convexity and root bundles leaving concavity of sickle-shaped trigeminal ganglion. Motor root (solid arrowhead) bypasses ganglion and reunites with mandibular nerve in foramen ovale basis cranii. Open arrowhead indicates descending spinal trigeminal tract.
2. Three nerve roots give rise to: a. Ophthalmic nerve, (CN V-1) b. Maxillary nerve, (CN V-2) c. Mandibular nerve, (CN V-3) 3. Peripheral distribution of three branches. Back of head and the angle of the jaw are not supplied by the trigeminal (Areas around ear supplied by CNs
May 02, 2008 · The trigeminal nerve, also known as the fifth (or V) cranial nerve, is a cranial nerve and its primary role is relaying sensory information from the face and head, although it does provide motor control to the muscles of mastication.
The trigeminal nerve has three branches. It joins at the trigeminal ganglia and branches out to different parts of the face. Each branch division has a slightly different function. Ophthalmic...
The branches of the trigeminal nerve (V) are represented in three different diagrams The ophthalmic nerve (V1) in the orbital cavity with its main branches (frontal nerve, lacrimal nerve, anterior and posterior ethmoidal nerve, nasociliary nerve, branch communicating with the ciliary ganglion, supraorbital nerve, supratrochlear nerve, infra ...
Nov 22, 2020 · Clinical Relevance: Blood Supply to the Scalp. The posterior auricular, occipital and superficial temporal arteries (along with two branches of the internal carotid artery; supra-orbital and supratrochlear) combine to provide a dense blood supply to the scalp.Injuries to the scalp can cause excessive bleeding for various reasons: The walls of the arteries are tightly …
Trigeminal nerve. The large trigeminal nerve or 5th cranial nerve has three branches: ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2), and mandibular (V3) divisions. Trigeminal nerve is a mixed nerve providing sensations of the face for touch, temperature, and pain from the upper, middle, and lower portions of the face, as well as the oral cavity, to the brain.
Oct 28, 2021 · The mandibular teeth are primarily supplied by the inferior alveolar nerve which is a branch of the mandibular nerve (third division of the trigeminal nerve). The mandibular nerve carries fibers that are both sensory and motoric due to the merger of its large sensory and small motor roots just after it exits the skull via the foramen ovale .
May 12, 2017 · The branches of the trigeminal nerve take sensations of touch and pain to the brain from your face, teeth and mouth. The trigeminal nerve also controls the muscles used in chewing and in the production of saliva and tears. Usually one or both of the maxillary and mandibular branches are affected by trigeminal neuralgia.
The nerve of the pterygoid canal ... they travel on the branches of the maxillary nerve to provide sympathetic innervation to blood vessels. Additional images. Alveolar branches of superior maxillary nerve and pterygopalatine ganglion. Diagram of the cervical sympathetic. See also. Vidus Vidius; References ...




:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/522/hefybIAztz3WDIDI33S06g_the-mandibular-nerve_english.jpg)














![trigeminal_nerve [Operative Neurosurgery]](https://operativeneurosurgery.com/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=trigeminal_nerve.jpg)
0 Response to "39 trigeminal nerve branches diagram"
Post a Comment