38 bayes theorem tree diagram
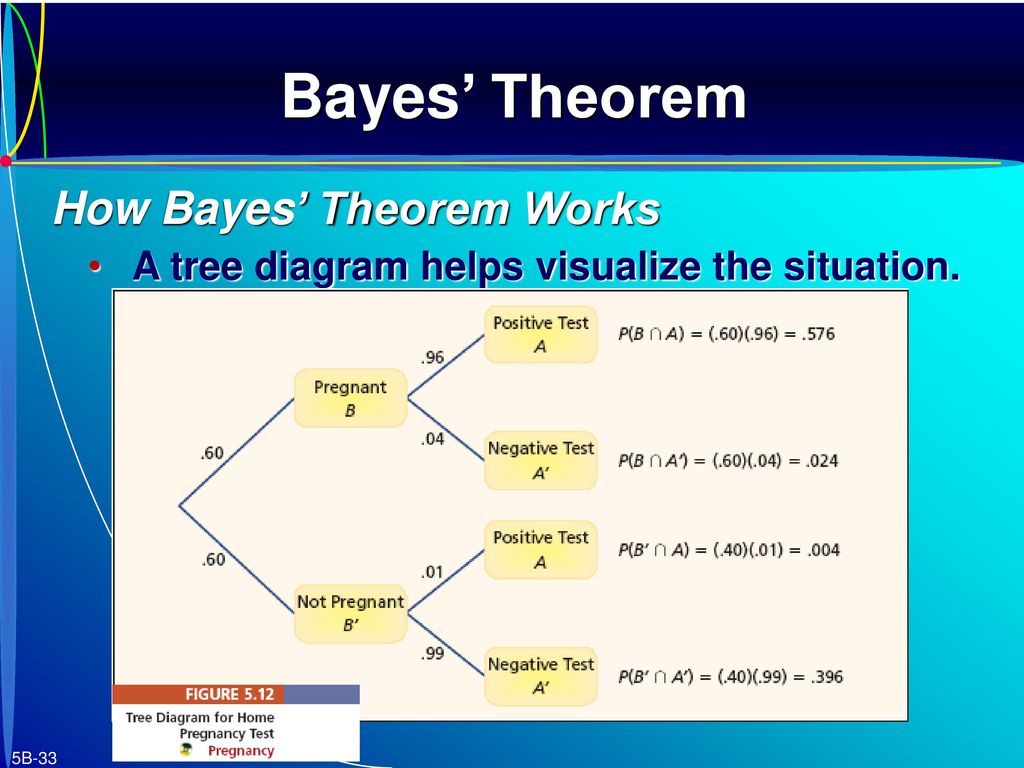
BAYES' THEOREM AND CONDITIONAL PROBABILITIES. by Klara Grodzinsky Suppose an experiment is conducted in two stages, where the first stage has four possible outcomes and the second stage has two possible outcomes. For example, say there are four different sections of your Math 1711 course (let's label them A, B, C, and D), and for each section we want to see how many students pass or fail. •Use tree diagrams to calculate probabilities •Apply these skills to diagnostic testing •Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, true positives, false positives, true negatives, and false negatives •Learn Bayes' theorem
Buying a car: Bayes with Tree Diagram Suppose you need to buy a car. I Based on previous experience you know that 30% of the cars have FAULTY transmission. To be sure you bring your car to a mechanic. Based on his past experience you know that I he correctly detects cars with good transmission 80% of the cases.
Bayes theorem tree diagram
Conditional probability with Bayes' Theorem. Conditional probability using two-way tables. ... Conditional probability tree diagram example. Tree diagrams and conditional probability. This is the currently selected item. Next lesson. Independent versus dependent events and the multiplication rule. Sort by: Top Voted. Use Bayes' theorem or a tree diagram to calculate | Chegg.com Math Statistics and Probability Statistics and Probability questions and answers 1. Use Bayes' theorem or a tree diagram to calculate the indicated probability. Round your answer to four decimal places. HINT [See Example 3.] 2. In this article, we will be analyzing the problem with 2 commonly used techniques in statistics, the Probability Tree Diagram and the Bayes' Theorem. In the end I will attach a computer ...
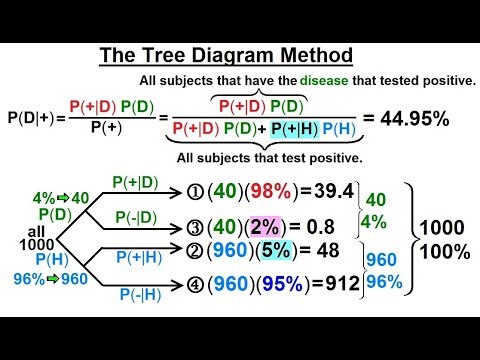
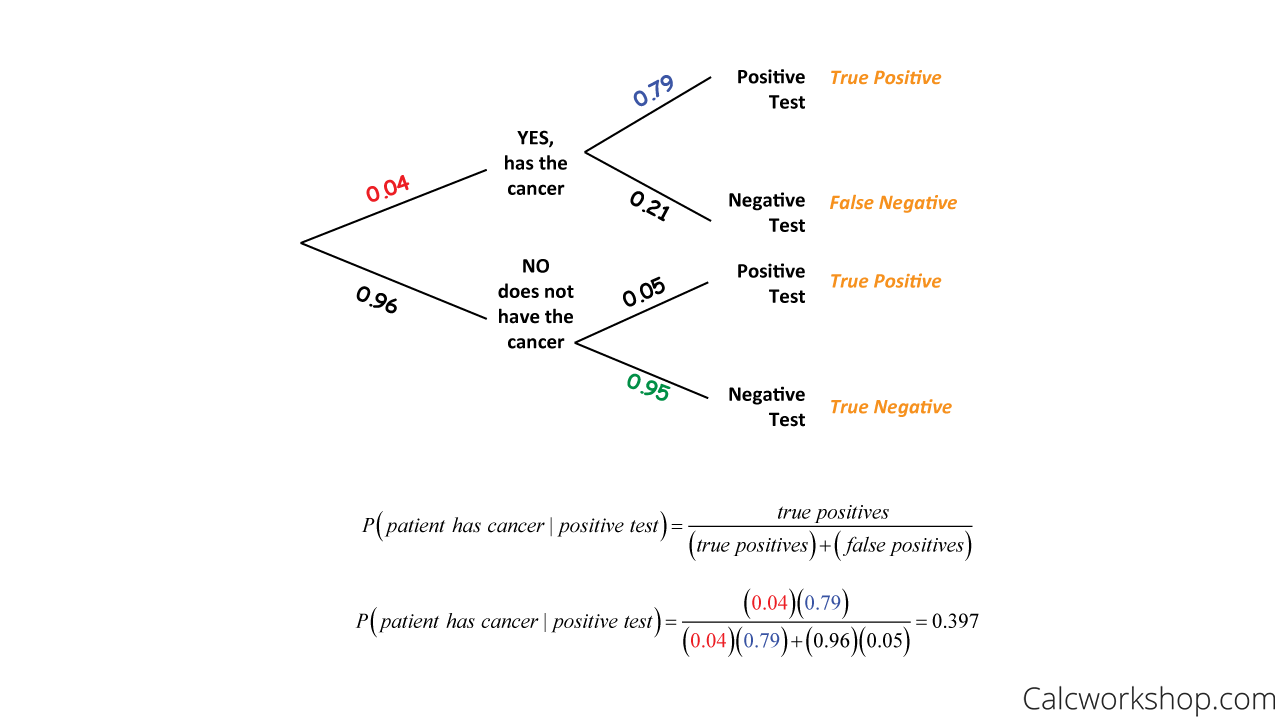
Bayes theorem tree diagram. The chance of any one overall outcome can found by multiplying the probabilities down one path in the tree diagram. Thus the chance of not being infected, and getting a negative test result is 0.98 × 0.995 = 0.9751. This can be done for all the paths. Then the total probability for all the paths when summed, must also sum to one. File:Bayes theorem tree diagrams.svg. Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 363 × 599 pixels. Other resolutions: 145 × 240 pixels | 291 × 480 pixels | 363 × 600 pixels | 465 × 768 pixels | 620 × 1,024 pixels | 1,240 × 2,048 pixels | 470 × 776 pixels. . More frequently, Bayesian probability can be calculated through a Tree Diagram: The probability of any student wearing pink, P (Wears pink) = P (Girl and Wears pink)+ P (Boy and Wears pink) = 23/100 + 2/100 = 25/100 = 0.25 The conditional probability of she wears pink given that the student is a girl, P (Wears pink|girl) is 23/55 = 0.418 First, let’s take a look at our suspects: Now, let’s present our evidence – the wand. Your job is to determine the likelihood that each suspect is responsible for conjuring the Dark Mark, given the fact the wand was found at the scene of the crime. We do this by reversing the question. Instead of saying, what is the chance that Winky committed the crime (if B is true), given the discovery of the wand (A is true), but rather, if the wand is real (if A is true), what is the probability that Winky conjured the Dark Mark (B is true)? At first glance, it appears that these are the same question, but mathematically, the slight change or reversal helps us solve the puzzle and is the key to understanding Bayes’ Rule!
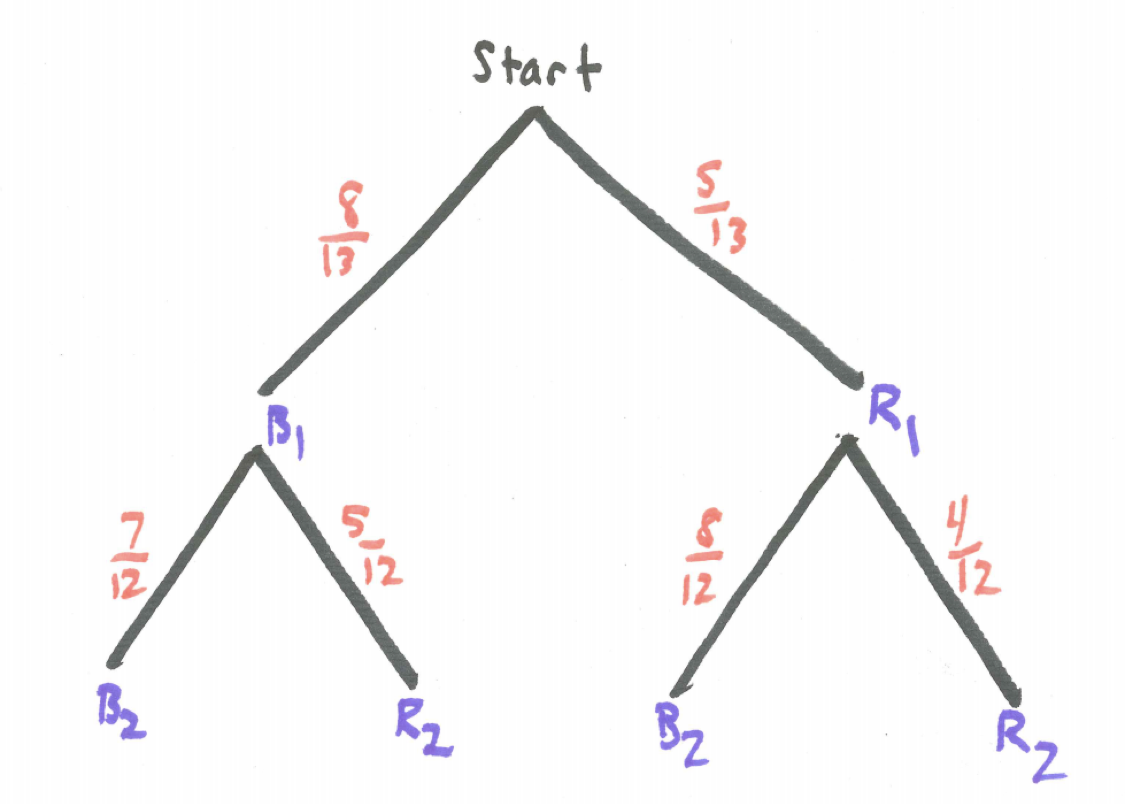
Bayes theorem tree diagram. Ask Question Asked 10 months ago. Active 4 months ago. Viewed 266 times 2 $\begingroup$ A bag I contain $4$ white and $6$ black balls while another Bag II contains $4$ white and $3$ black balls. One ball is drawn at random from one of the bags, and it is found to be black. Bayes Theorem & Tree Diagrams Consider the Following Scenario: Apple has two manufactures in producing its iPhone, M1 and M2. M1 produces 65% of all iPhone and M2 produces the rest 35%. You are a quality controller for Apple and you monitor these two manufacturers. You randomly draw a sample of 100 finished iPhones from the production line of each manufacture and you observe the following: 2% ... A tree diagram can be used to describe a probability space in probability theory. For calculating combined probabilities, probability trees are useful. ... Bayes' Theorem . The Bayes theorem is a mathematical formula for calculating conditional probability, named after 18th-century British mathematician Thomas Bayes. The theorem allows you to ... Bayes' theorem to find conditional porbabilities is explained and used to solve examples including detailed explanations. Diagrams are used to give a visual explanation to the theorem. Also the numerical results obtained are discussed in order to understand the possible applications of the theorem. Bayes' theorem From law of total probability
To simplify Bayes' theorem problems, it can be really helpful to create a tree diagram. If you're ever having trouble figuring out a conditional probability problem, a tree diagram is a great tool to fall back on, because it shows all of the sample space of the problem. PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON BAYES'S FORMULA AND ON PROBABILITY (NOT TO BE HANDED IN ) 1. remarks If you nd any errors in this document, please alert me. Remark 1. First, I'll make a remark about question 40 from section 12.4 in the book. Let A= event that rst card is a spade and B=event that second card is a spade. As part of this Bayes theorem deals with the probability of the cause. The equations of Bayes theorem are easy to understand and derivable from Venn diagrams and/or conditional probability equations. The image illustrates Bayes' Theorem using a tree diagram. At the top, there are two branches. The right branch, "Cab is blue," has a probability of .15, 15%. The left branch, "Cab is Green," has a probability of .85, 85%. These are the "prior probabilities," and represent what the chance of a cab being blue or green would be, if the cab were ...
This video tutorial provides an intro into Bayes' Theorem of probability. It explains how to use the formula in solving example problems in addition to usin...
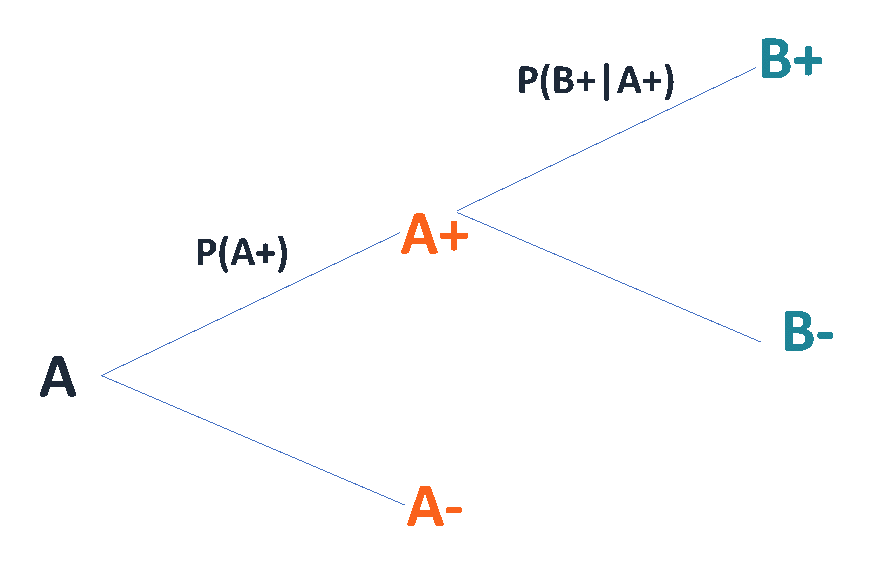
Bayes' 5: Bayes Theorem and Tree Diagrams There is another more intuitive way to perform Bayes' Theorem problems without using the formula. That is, using a Tree Diagram. If you look at how a tree diagram is created, these are really conditional probabilities. If we want to determine a conditional probability, the formula is 𝑃( | )=
Tree diagrams are annotated with marginal and conditional probabilities. This tree diagram splits the smallpox data by inoculation into the yes and no groups with marginal probabilities of 0.039 and 0.961 respectively. The secondary branches are conditioned on inoculation, so we assign conditional probabilities to these branches.
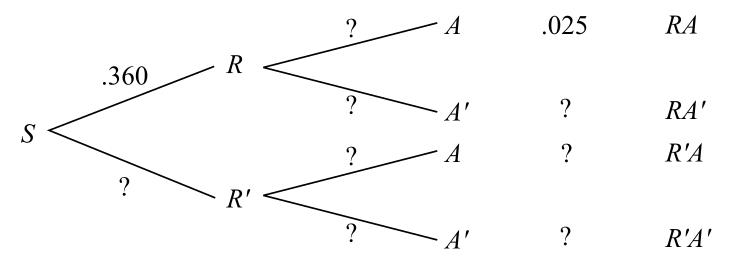
How do I go about solving for the missing probabilities in my tree diagram and answering the question of "What is the probability of testing positive? I'm trying to learn how to answer the following type of questions using Bayes Theorem. Let's walk through an example similar to the one given in class.
Matt and Ashish go over a few Bayes' Theorem problems and explain how to use the tree diagram.
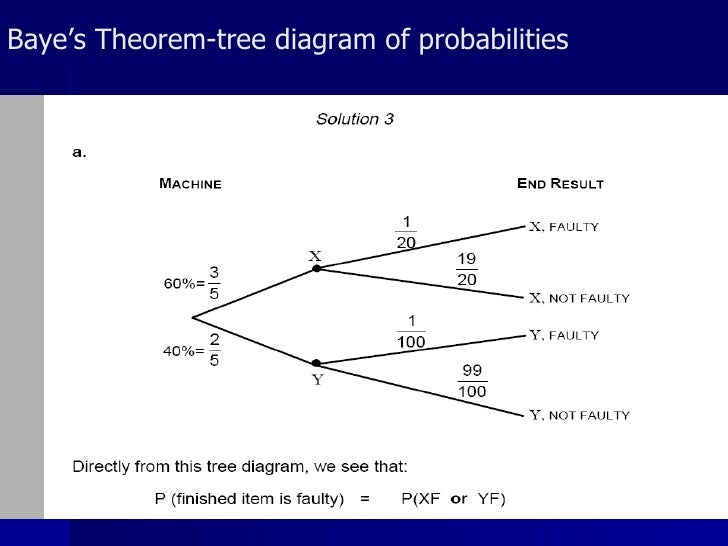
We can formulate that as a rule for applying Bayes theorem on a probability tree, for P. . ( A ∣ B), naming A as 'cause' and B as 'data': Eliminate all the paths through the tree made impossible by the conditioning on data B. Denominator is sum of all path-probabilities consistent with B. Numerator is sum of all path-probabilities ...
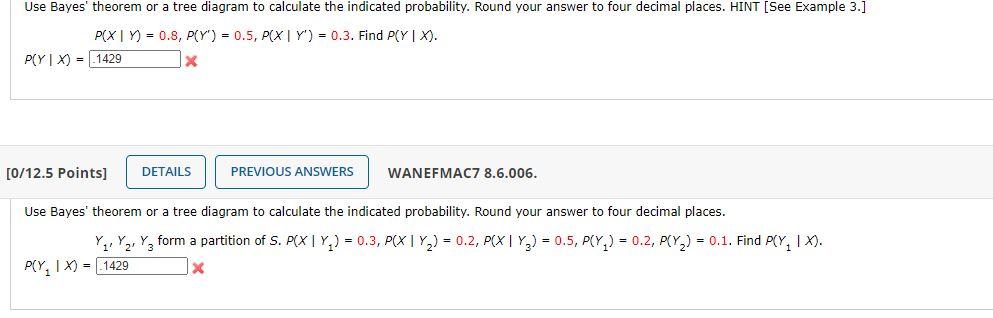
Use Bayes' theorem or a tree diagram to calculate the indicated probability. Round your answer to four decimal places. P (AB) = 0.7, P (B) = 0.8, P (AB) = 0.2. Find P ( BA). P ( BA) = :-/12.5 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES Use Bayes' theorem or a tree diagram to calculate the indicated probability. Round your answer to four decimal places.
Learn how base rates can impact a conditional probability; Calculate probabilities based on a tree diagram; Calculate probabilities based on Bayes' theorem.
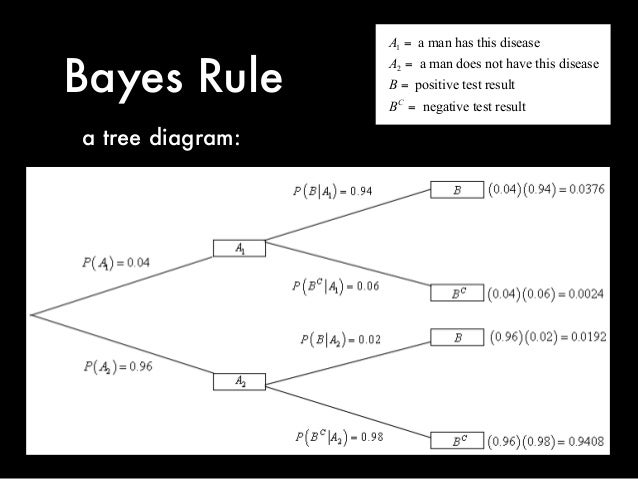
Bayes’ Theorem We can draw a tree diagram representing the information we are given. If we choose a touch screen at random from those produced in the factory, we let MA be the event that it came from Machine A and let MB be the event that it came from Machine B. We let D denote the event that the touch screen is defective and let ND denote the event that
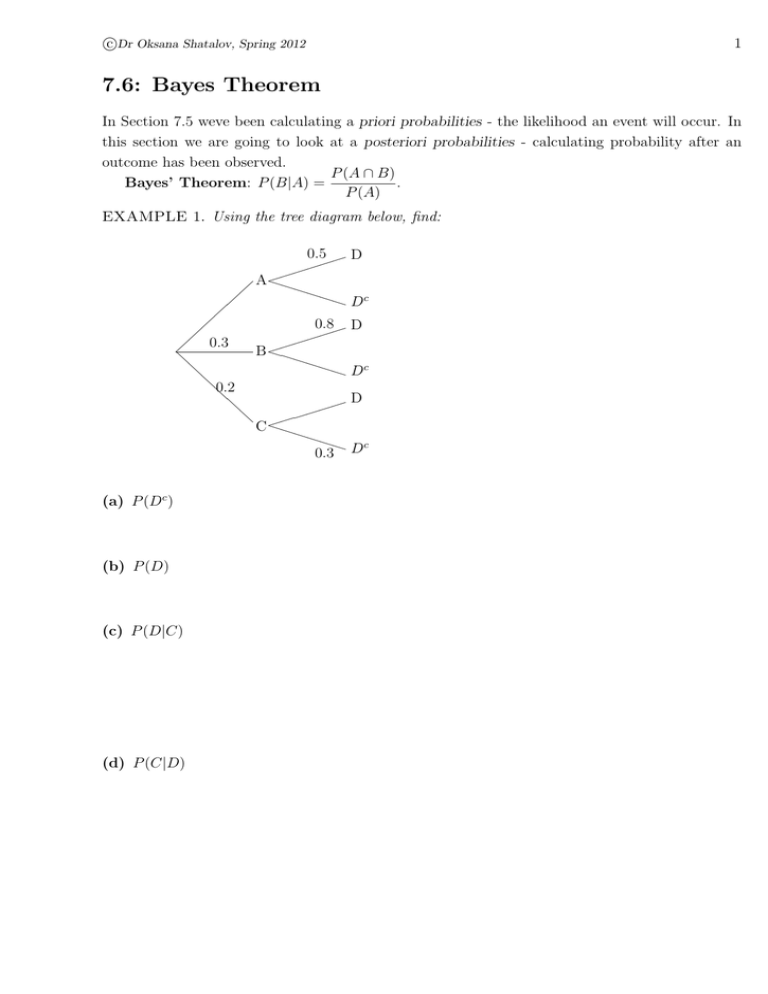
Bayes’ Theorem Bayes’ Theorem, named after the English mathematician Thomas Bayes (1702–1761), is an important formula that provides an alternative way of computing conditional probabilities. Before the formula is given, take another look at a simple tree diagram involving two events and as shown in Figure C.14. FIGURE C.14
In probability theory and statistics, Bayes' theorem (alternatively Bayes' law or Bayes' rule; recently Bayes-Price theorem: 44, 45, 46 and 67 ), named after Thomas Bayes, describes the probability of an event, based on prior knowledge of conditions that might be related to the event. For example, if the risk of developing health problems is known to increase with age, Bayes' theorem allows ...
In this article, we will be analyzing the problem with 2 commonly used techniques in statistics, the Probability Tree Diagram and the Bayes' Theorem. In the end I will attach a computer ...
Use Bayes' theorem or a tree diagram to calculate | Chegg.com Math Statistics and Probability Statistics and Probability questions and answers 1. Use Bayes' theorem or a tree diagram to calculate the indicated probability. Round your answer to four decimal places. HINT [See Example 3.] 2.
Conditional probability with Bayes' Theorem. Conditional probability using two-way tables. ... Conditional probability tree diagram example. Tree diagrams and conditional probability. This is the currently selected item. Next lesson. Independent versus dependent events and the multiplication rule. Sort by: Top Voted.





![∞ [ℵμ∰β⨊â„] â–¡ [+â„∈∅⪆γ] ∞ — A fantastic tree diagram ...](https://64.media.tumblr.com/674fb734e59ae6b688dcc0504a1af03a/tumblr_pohbckPYO91xzgpe1o2_r1_1280.png)














0 Response to "38 bayes theorem tree diagram"
Post a Comment