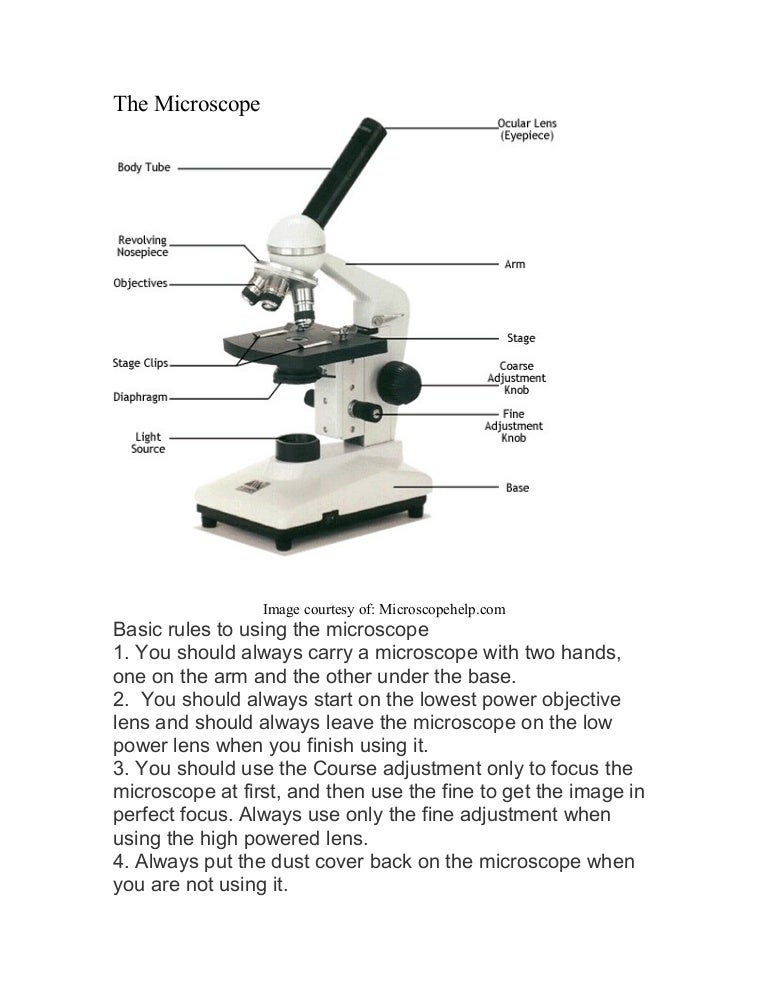
41 diagram of microscope parts
Let us take a look at the different parts of microscopes and their respective functions. 1. Eyepiece. it is the topmost part of the microscope. Through the eyepiece, you can visualize the object being studied. Its magnification capacity ranges between 10 and 15 times. 2. Description: Parts Of A Compound Microscope With Diagram And Functions with Diagram Of The Microscope Parts, image size 500 X 469 px, and to view image details please click the image.. Here is a picture gallery about diagram of the microscope parts complete with the description of the image, please find the image you need.
Labeled diagram of a compound microscope Major structural parts of a compound microscope Optical components of a compound microscope Eyepiece Eyepiece tube Objective lenses Nosepiece Specimen stage Coarse and fine focus knobs Rack stop Illuminator Condenser Abbe condenser Iris Diaphragm Condenser Focus Knob Summary An overview of microscopes

Diagram of microscope parts
Microscope Parts and Functions With Labeled Diagram and Functions How does a Compound Microscope Work?. Before exploring microscope parts and functions, you should probably understand that the compound light microscope is more complicated than just a microscope with more than one lens.. First, the purpose of a microscope is to magnify a small object or to magnify the fine details of a larger ... Microscope Parts and Functions Microscope One or more lenses that makes an enlarged image of an object. 8/7/2018 2 •Simple •Compound •Stereoscopic •Electron Simple Microscope •Similar to a magnifying glass and has only one lens. 8/7/2018 3 Compound Microscope Image : Labeled Diagram of compound microscope parts. See: Labeled Diagram showing differences between compound and simple microscope parts Structural Components. The three structural components include. 1. Head. This is the upper part of the microscope that houses the optical parts
Diagram of microscope parts. Microscope: Definition, Parts, Parameters, Types and Uses. Microscope: It is an instrument that produces enlarged images of small objects, allowing the observer an exceedingly close view of minute structures at a scale convenient for examination and analysis. It is scientific equipment that magnifies microscopic objects that are not visible to ... Microscope Optical Components Introduction. Modern compound microscopes are designed to provide a magnified two-dimensional image that can be focused axially in successive focal planes, thus enabling a thorough examination of specimen fine structural detail in both two and three dimensions. Most microscopes provide a translation mechanism ... B. NOSEPIECE microscope when carried Holds the HIGH- and LOW- power objective LENSES; can be rotated to change MAGNIFICATION. Power = 10 x 4 = 40 Power = 10 x 10 = 100 Power = 10 x 40 = 400 What happens as the power of magnification increases? The parts of the compound microscope can be categorized into: Mechanical parts Optical parts (A) Mechanical Parts of a Compound Microscope 1. Foot or base It is a U-shaped structure and supports the entire weight of the compound microscope. 2. Pillar It is a vertical projection. This stands by resting on the base and supports the stage. 3. Arm
Labeling the Parts of the Microscope. This activity has been designed for use in homes and schools. Each microscope layout (both blank and the version with answers) are available as PDF downloads. You can view a more in-depth review of each part of the microscope here. The parts of a compound microscope can be classified into two: Non-optical parts Optical parts Non-optical parts Base The base is also known as the foot which is either U or horseshoe-shaped. It is a metallic structure that supports the entire microscope. Pillar The connection between the base and the arm are possible through the pillar. Arm Get the best of Sporcle when you Go Orange.This ad-free experience offers more features, more stats, and more fun while also helping to support Sporcle. Thank you for becoming a member. Parts of a Compound Microscope Each part of the compound microscope serves its own unique function, with each being important to the function of the scope as a whole. The individual parts of a compound microscope can vary heavily depending on the configuration & applications that the scope is being used for. Common compound microscope parts include: Compound Microscope Definitions for ...
All microscopes share features in common. In this interactive, you can label the different parts of a microscope. Use this with the Microscope parts activity to help students identify and label the main parts of a microscope and then describe their functions.. Drag and drop the text labels onto the microscope diagram. If you want to redo an answer, click on the box and the answer will go back ... In this article we will discuss about the parts of dissecting microscope with its working and utility. 1. Foot or Base: ADVERTISEMENTS: It is the basal, horse-shoe shaped or circular part of dissecting microscope. It is made of heavy material. It provides support to other parts of microscope. The Microscope Parts and Use Name:_____ Period:_____ Historians credit the invention of the compound microscope to the Dutch spectacle maker, Zacharias Janssen, around the year 1590. The compound microscope uses lenses and light to enlarge the image and is also called an optical Stereo Microscope: A low power microscope or dissecting microscope with a separate eyepiece and objective lens for each eye. These separate optical channels enable stereo or three-dimensional images of the specimen. See Compound Microscope. Sub-Stage: The parts of the microscope below the stage, including the illumination system.
Having been constructed in the 16th Century, Microscopes have revolutionalized science with their ability to magnify small objects such as microbial cells, producing images with definitive structures that are identifiable and characterizable. So, what are microscopes? Microscope Definition- Microscopes are instruments that are used in science laboratories, to visualize very minute objects such as cells, microorganisms, giving a contrasting image, that is magnified. Microscopes are made up of lenses for magnification, each with its own magnification powers. Depending on the type of lens, it will magnify the specimen according to its focal strength. Their ability to function is because they have been constructed with special components that enable them to achieve high magnification levels. they can view very small specimens and distinguish their structural differences, for example, the view of animal and plant cells, viewing of microscopic bacterial cells. Microscopes are generally ma...
A simple or compound microscope is made of two important parts such as the Structural parts and Optical parts. The structural parts provide supports to the microscope, while the optical parts help to produce a magnified image of specimens. The structural parts of Microscope with their functions

Image from page 173 of "A healthy body. A textbook on anatomy, physiology, hygiene, alcohol, and narcotics. For use in intermediate grades in public and private schools" (1889)
One of the most important parts of a compound microscope, as they are the lenses closest to the specimen. A standard microscope has three, four, or five objective lenses that range in power from 4X to 100X. When focusing the microscope, be careful that the objective lens doesn't touch the slide, as it could break the slide and destroy the specimen.
Using the terms listed below, label the microscope diagram. arm - this attaches the eyepiece and body tube to the base. base - this supports the microscope. body tube - the tube that supports the eyepiece. coarse focus adjustment - a knob that makes large adjustments to the focus. diaphragm - an adjustable opening under the stage, allowing ...
microscope, instrument that produces enlarged images of small objects, allowing the observer an exceedingly close view of minute structures at a scale convenient for examination and analysis.Although optical microscopes are the subject of this article, an image may also be enlarged by many other wave forms, including acoustic, X-ray, or electron beam, and be received by direct or digital ...
Illuminator: Illuminator is the most important microscope parts and it serve as light source for a microscope during slide specimen visualization. It is a continuous source of light (110 volts) used in place of a mirror. The mirror of microscope is used to reflect light from the external light source up through the bottom of the stage.
Parts of the optical parts are as follows: Mirror - A simple microscope has a plano-convex mirror and its primary function is to focus the surrounding light on the object being examined. Lens - The biconvex lens is placed above the stage and its function is to magnify the size of the object being examined.
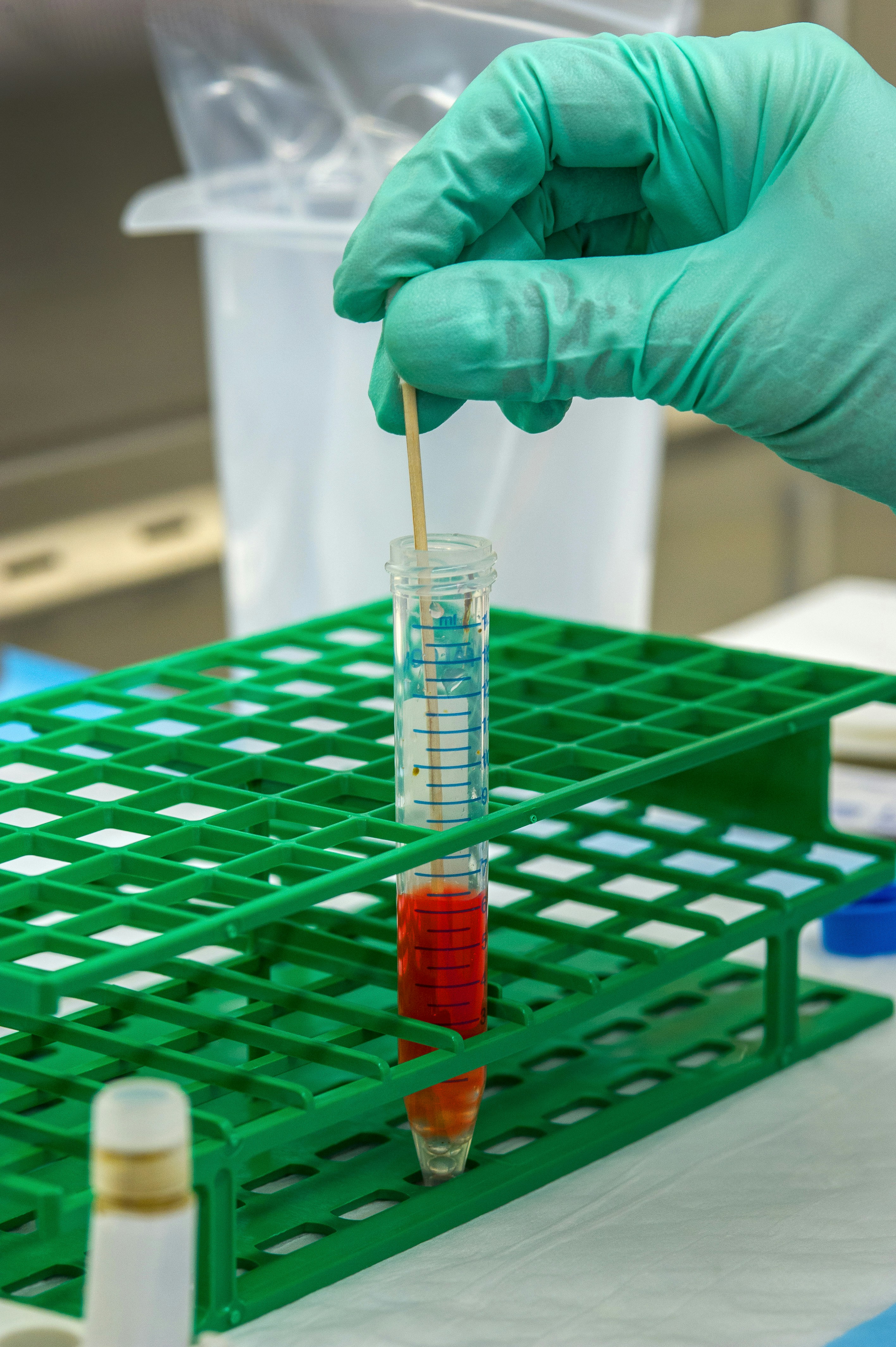
To mix the stool and the chemicals together, this Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) scientist was shown adding a stool sample to the cell culture medium, along with glass beads, which will suspend the stool in the solution.
Once you have an understanding of the parts of the microscope it will be much easier to navigate around and begin observing your specimen, which is the fun part! The 16 core parts of a compound microscope are: Head (Body) Arm Base Eyepiece Eyepiece tube Objective lenses Revolving Nosepiece (Turret) Rack stop Coarse adjustment knobs
Label the parts of the microscope. You can use the word bank below to fill in the blanks or cut and paste the words at the bottom. Microscope Created by Jolanthe @ HomeschoolCreations.net eyepiece head objective lenses arm focusing knob base illuminator stage stage clips nosepiece.
The structure of the microscope is discussed below. There are many functioning parts to the compound light microscope Head/Body The first part of the compound light microscope is the head. This is...
Labeled part diagram of a stereo microscope Major structural parts of a stereo microscope. There are three major structural parts of a stereo microscope. The viewing Head includes the upper part of the microscope, which houses the most critical optical components, including the eyepiece, objective lens, and light source of the microscope.
Image : Labeled Diagram of compound microscope parts. See: Labeled Diagram showing differences between compound and simple microscope parts Structural Components. The three structural components include. 1. Head. This is the upper part of the microscope that houses the optical parts
Microscope Parts and Functions Microscope One or more lenses that makes an enlarged image of an object. 8/7/2018 2 •Simple •Compound •Stereoscopic •Electron Simple Microscope •Similar to a magnifying glass and has only one lens. 8/7/2018 3 Compound Microscope
Microscope Parts and Functions With Labeled Diagram and Functions How does a Compound Microscope Work?. Before exploring microscope parts and functions, you should probably understand that the compound light microscope is more complicated than just a microscope with more than one lens.. First, the purpose of a microscope is to magnify a small object or to magnify the fine details of a larger ...
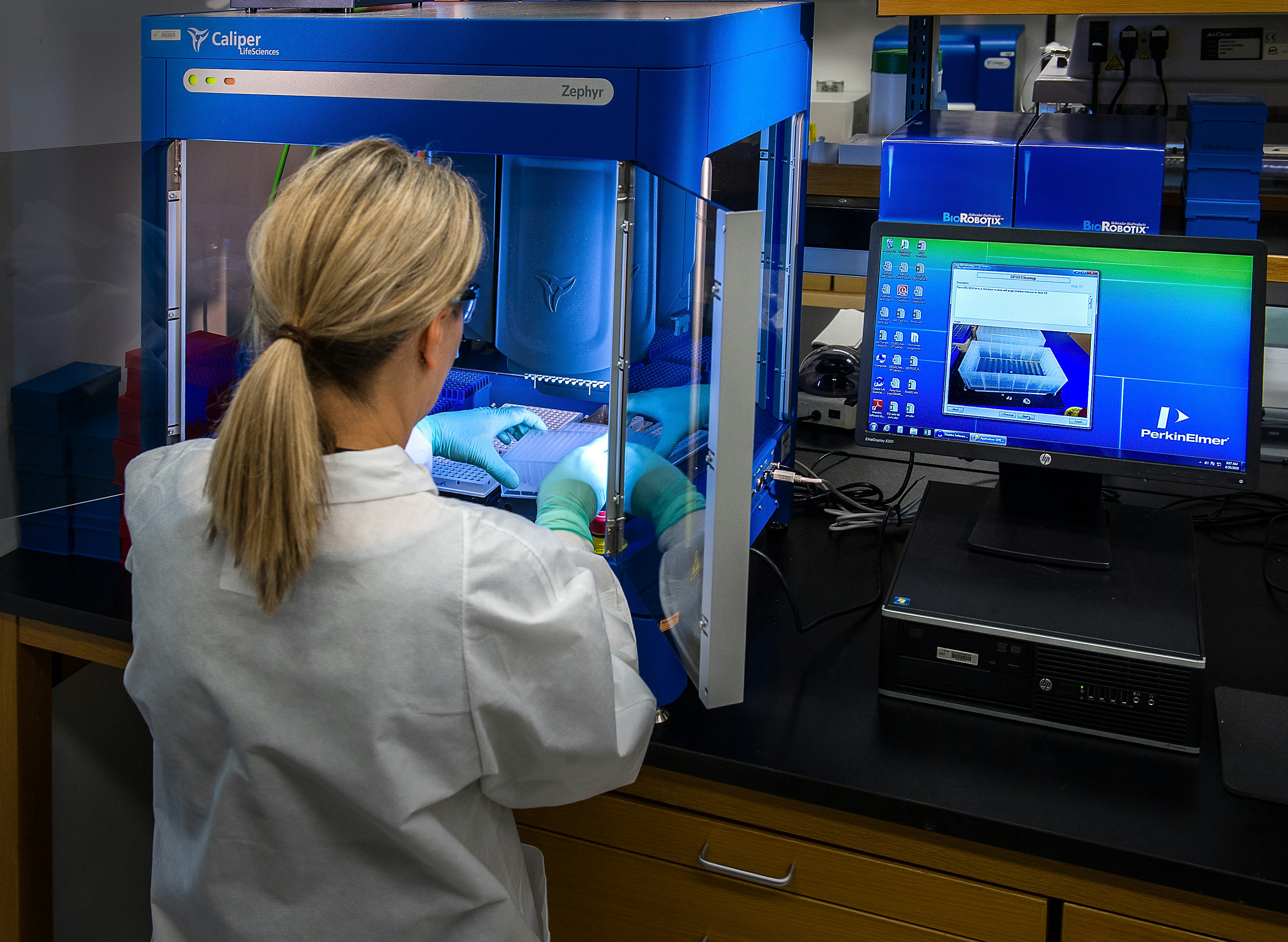

This image depicted a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) scientist interacting with her Caliper LifeSciences’ Zephyr Molecular Biology Workstation, working with samples to be tested using a real-time PCR machine, known as a themocycler (see PHIL 22904), in order to identify the various types of poliovirus contained therein. The data from this analysis is stored in a computer, while the software further analyzes the data before being reviewed by a scientist.

Image from page 67 of "A compendium of astronomy; containing the elements of the science, familiarly explained and illustrated, with the latest discoveries. Adapted to the use of schools and academies, and of the general reader" (1850)

Image from page 369 of "Electron microscopy; proceedings of the Stockholm Conference, September, 1956" (1957)
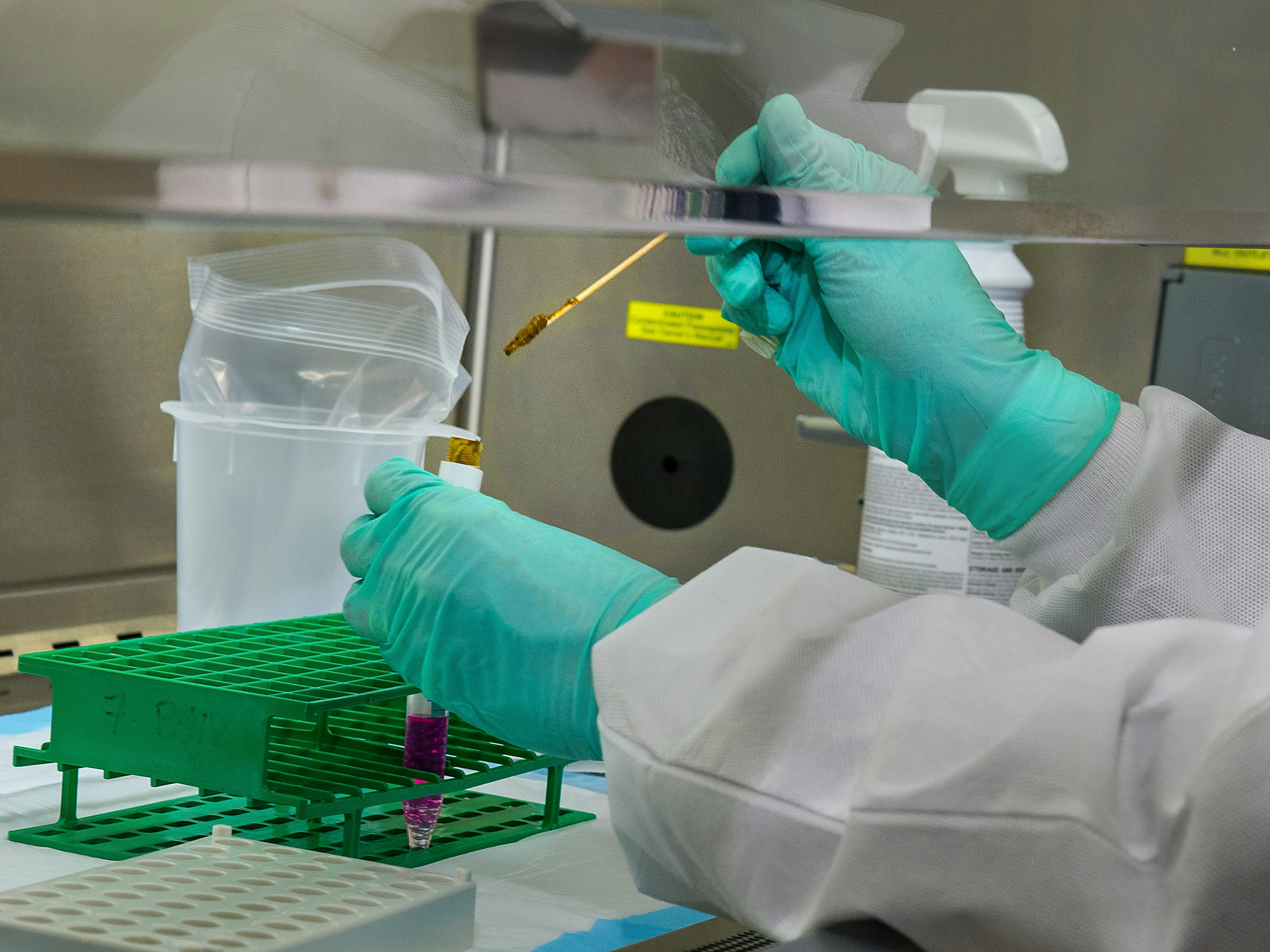

To mix the stool and the chemicals together, this Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) scientist was shown adding a stool sample to the cell culture medium, along with glass beads, which will suspending the stool in the solution. Then the scientist will shake the test tube, in order to get the stool to come off the glass beads, and disperse throughout the liquid.

Image from page 117 of "On epilepsy : anatomo-pathological and clinical notes (with original plates and engravings.)" (1870)

Image from page 214 of "Elements of biology; a practical text-book correlating botany, zoology, and human physiology" ([c1907])
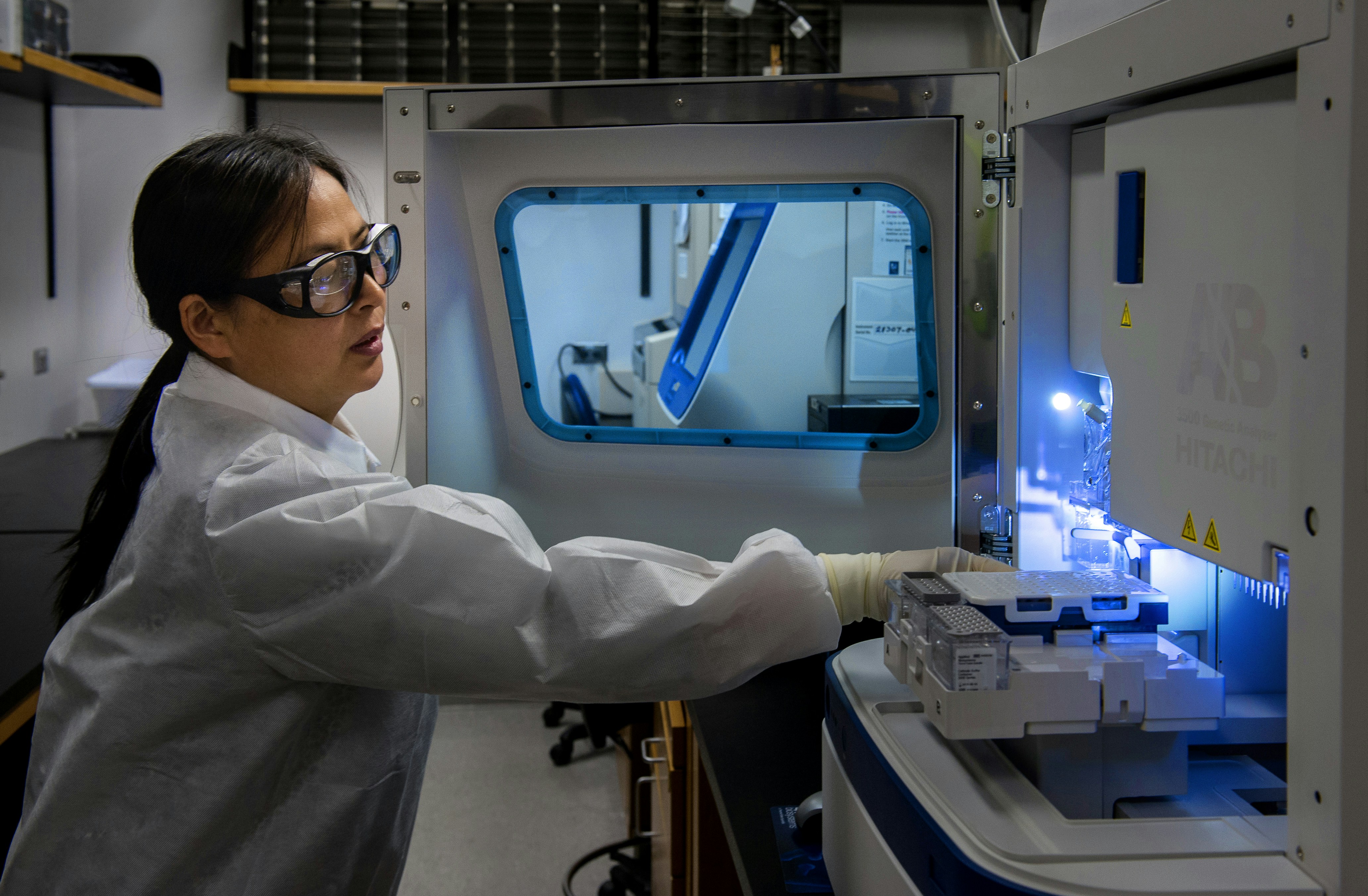

This Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) scientist was performing one of the last steps in a poliovirus testing process. Dyes are used to determine, which of the nucleotides (basis of genetic material) are present in a sequence. The outer coat of the virus (the capsid) is sequenced to find out where the virus has circulated.

(Fang Ruida) Davis. K Coronavirus pneumonia biomarkers and treatment(方瑞达) Davis。K å† çŠ¶åž‹ç—…æ¯’æ€§è‚ºç‚Žç”Ÿç‰©æ ‡å¿—ç‰©åŠæ²»ç–—防治
This photo was made with some experimental liquids as milk, water paint and oil. I’ve made this with a friend and we had so much fun doing it. The surprise of the reactions thought the different material was both charming and changeling. I truly recommend everyone to try something like this, let’s share the different results. Have fun using this picture.

























0 Response to "41 diagram of microscope parts"
Post a Comment