40 molecular orbital diagram hf
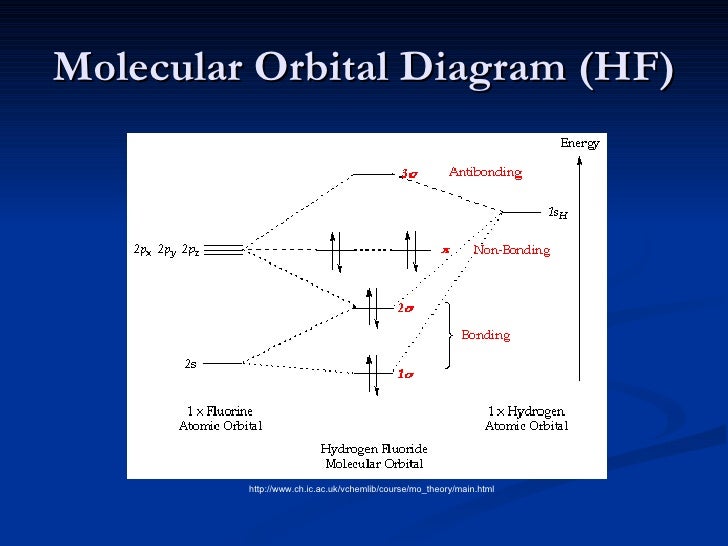
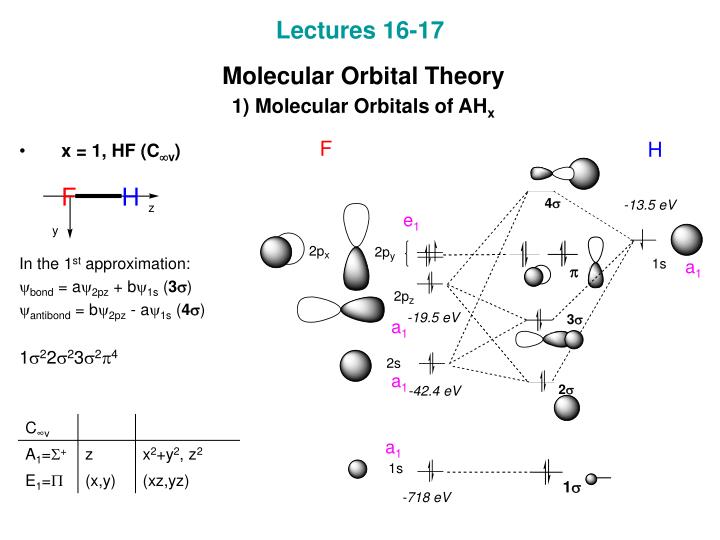
In the LCAO approach, molecular orbitals are constructed by selecting sums and differences of atomic orbitals. For example, for hydrogen fluoride, we start with the H1s, F1s, F2s, F2px, F2py, and Fp2z orbitals. A linear combination of H1s and F2pz orbitals creates a bonding σ orbital and antibonding σ∗ orbital. The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The Is atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding sigma molecular orbital and an antibonding sigma* molecular orbital.
An Introduction to Hartree-Fock Molecular Orbital Theory C. David Sherrill School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Georgia Institute of Technology June 2000 1 Introduction Hartree-Fock theory is fundamental to much of electronic structure theory. It is the basis of molecular orbital (MO) theory, which posits that each electron's motion can be ...

Molecular orbital diagram hf
Construct the molecular orbital diagram for HF. Use only the valence electrons for your diagram. The 2s orbital of F atom has an energy more than 26 eV lower than that of the H 1s, so there is very little interaction between them. The F 2p orbital (-18.65 eV) and the H 1s (-13.61 eV), on the other hand, have similar energies, allowing them to Hartree-Fock Molecular Orbital Theory 1. Invoke the Born-Oppenheimer approximation 2. Express the electronic wavefunction as a single Slater Determinant 3. Solve for those orbitals which minimize the electronic energy (variational method) This winds up being mathematically equivalent to assuming each electron interacts only with the average #MOT #BMO #ABMO #HF #CO #NO #CN #OHHello everyoneThis is shivam here To follow me on instagram search - Sshivam898To join telegram group click on the given l...
Molecular orbital diagram hf. The molecular orbital coefficients describe the contribution of each of the basis functions to a given molecular orbital. The overall electronic wavefunction of the system is constructed as an antisymmetrized product of the molecular orbitals (the Slater determinand) in order to fulfill the Pauli exclusion principle. Since the optimal shape of ... In general, the contribution to MOs is determined by the coefficients in the linear combination. Here, one observes that the 1 s electrons are almost completely localized on the F atom. Also, 1 π electrons are completely localised on the F atom because the 2 p x and 2 p y orbitals on F have a zero net overlap with the 1 s orbital on H. Download scientific diagram | Molecular orbital diagrams for HBr and HF. from publication: Total energy partitioning within a one-electron formalism: A Hamilton population study of surface–CO ... Example 2: hydrogen fluoride When atoms are of different energies, one must be concerned with the relative energies and symmetries of orbitals Orbitals of same symmetry and approximately similar energy combine most effectively Can estimate approximate HF molecular orbitals Energies calculated with Gaussian Gives filling order of orbitals
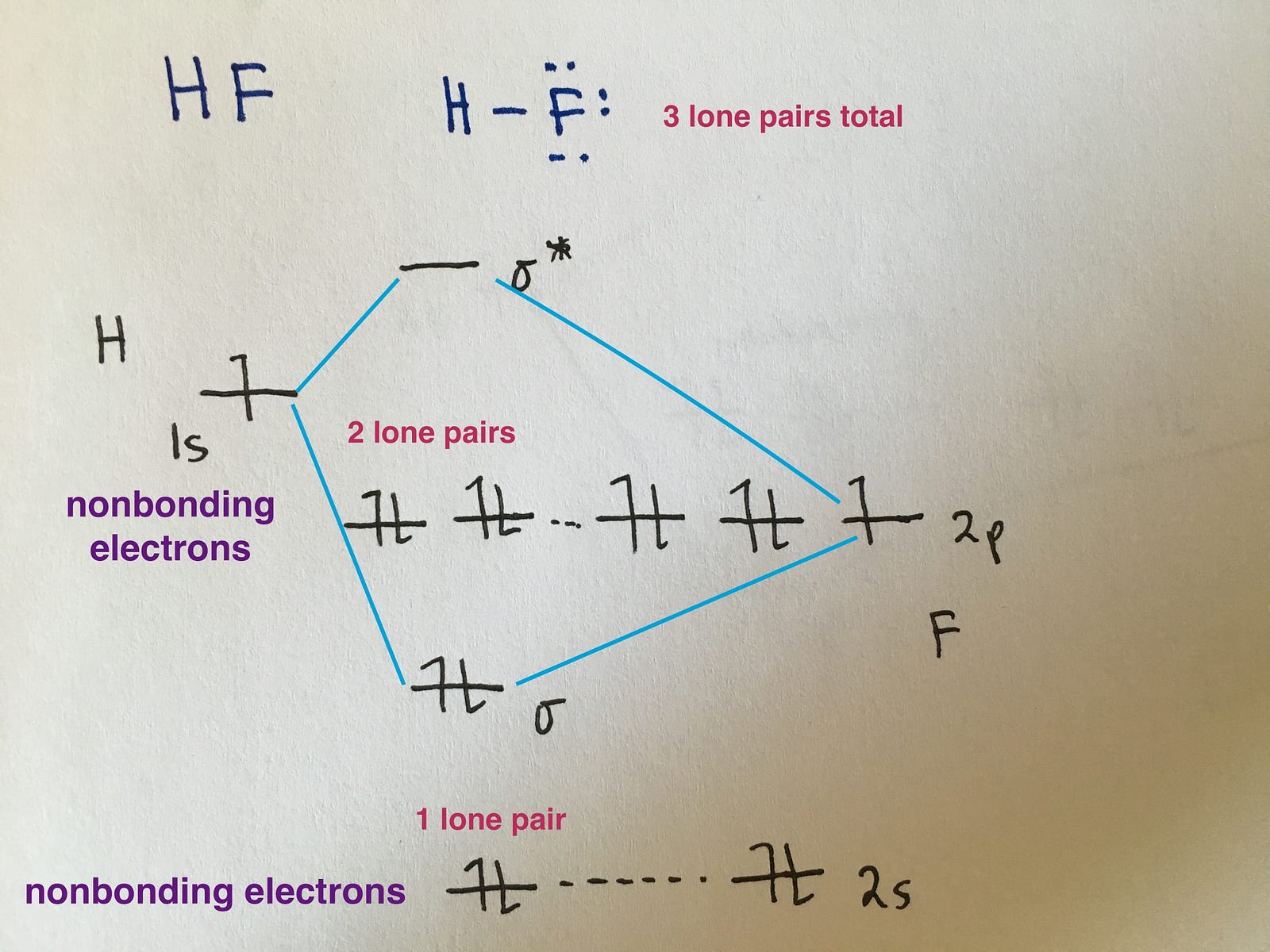
H is easy - it only has the 1 election in the 1s orbital available for bonding. The F atom has the filled 2s and the 5 electrons in the 2p. F's 2s is too low in energy for the H to bond with, so it's down by itself at the bottom as a non-bonding orbital. Next, H's 1s electron will combine with F's 2p electron, to create the bond. Qualitative molecular orbital diagram of HF −. The 2σ orbital, coming from the F 2 s orbital, is nonbonding. The 3σ orbital is a combination of the F 2p z and H 1 s orbitals and is bonding ... Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular… In hydrogen fluoride, HF, symmetry allows for overlap between the H 1s and F 2s orbitals, but the difference in energy between the two atomic orbitals prevents them from interacting to create a molecular orbital.
Home / Structure and Bonding / Atomic Orbitals / Molecular orbitals in Hydrogen Fluoride. Molecular orbitals in Hydrogen Fluoride. CONTROLS . Click on the HF molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. Using Symmetry: Molecular Orbitals One approach to understanding the electronic structure of molecules is called Molecular Orbital Theory. • MO theory assumes that the valence electrons of the atoms within a molecule become the valence electrons of the entire molecule. The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The 1s atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding o molecular orbital and an antibonding o* molecular orbital. Molecular Orbitals for Heterogeneous Diatomic Molecules A simple approach to molecular orbital (MO) theory for heterogeneous diatomic molecules is to show the energy level diagram. The MO energy levels can be worked out following these steps: Recall that the energy E n for the quantum number n is for an element with atomic Z is approximately
much of each atomic coefficient is required to make each of the molecular orbitals. The coefficients for the highest energy MO wavefunction is solved below. Repeat these calculations for determining the coefficients of this molecular orbital, but then go on to calculate the coefficients for the other two MO's in our HF molecule.
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
of the orbitals is specified. b. Molecular Orbital Picture We are now in a position to discuss the basic principles of the molecular orbital (MO) method, which is the foundation of the electronic structure theory of real molecules. The first step in any MO approach requires one to define an effective one electron Hamiltonian, hˆ eff. To this ...
In this screencast, Andrew Burrows walks you through how to construct the MO energy level diagram of HF. http://ukcatalogue.oup.com/product/9780199691852.do#...
Answer (1 of 3): The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. As has been already explained ,only a pz orbital is able to combi...
Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Lih. We shall consider the molecular orbitals in LiH, CH and HF to illustrate how molecular orbital theory describes the bonding in heteronuclear molecules, and to. and 2p orbitals, but that is not how sodium chloride is made. Sodium atoms are Construct an MO diagram for LiH and suggest what type of bond it might have.
Molecular orbital diagram for hf. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form ...
Molecular orbitals of HF. Draw the MO diagram for HBr including energy levels each orbitals shape each orbitals character meaning what atomic orbitals contribute to each MO. H1 is bonded in a linear geometry to two equivalent Br1- atoms. And how much symmetry labels eg. And how much symmetry labels eg.
The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The 1s atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding o molecular orbital and an antibonding o molecular orbital.
Hf Molecular Orbital Diagram - Quantum‐mechanical Condensed Matter Simulations With Crystal Wires molecular orbital diagram a molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular hf the

A female lab technician loading a semiconductor DNA sequencing chip used to identify specific cancer mutations in an individual. Photo taken at the Advanced Technology Research Facility (ATRF) at the Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute.
Which is the molecular orbital diagram for HF? The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. As has been already explained ,only a pz orbital is able to combine with s orbital.
Which is the molecular orbital diagram for HF? The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. As has been already explained ,only a pz orbital is able to combine with s orbital.
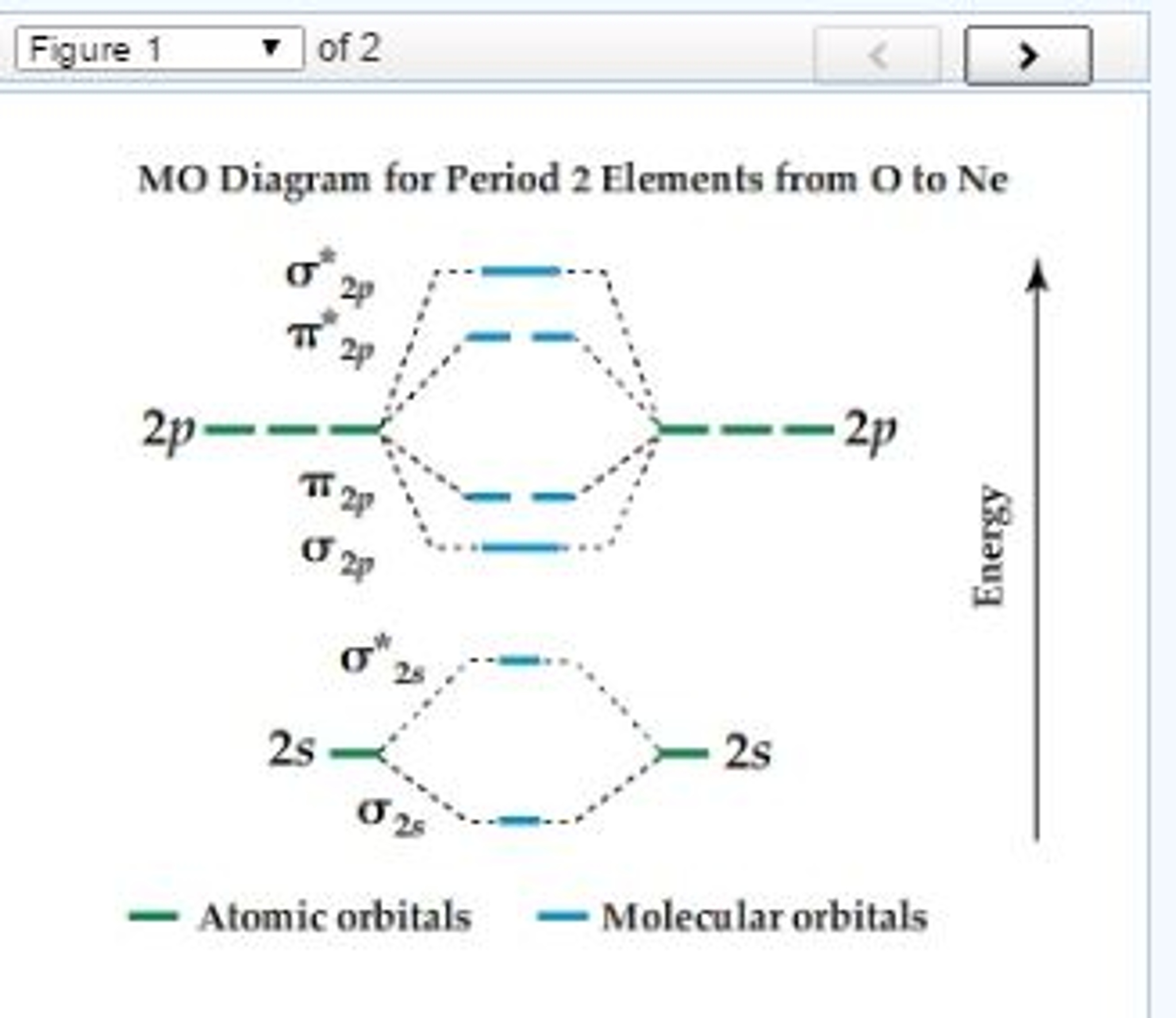
Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
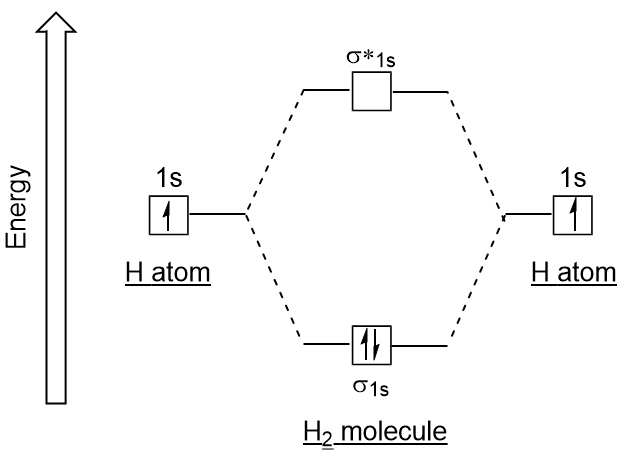
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
#MOT #BMO #ABMO #HF #CO #NO #CN #OHHello everyoneThis is shivam here To follow me on instagram search - Sshivam898To join telegram group click on the given l...
Hartree-Fock Molecular Orbital Theory 1. Invoke the Born-Oppenheimer approximation 2. Express the electronic wavefunction as a single Slater Determinant 3. Solve for those orbitals which minimize the electronic energy (variational method) This winds up being mathematically equivalent to assuming each electron interacts only with the average
Construct the molecular orbital diagram for HF. Use only the valence electrons for your diagram. The 2s orbital of F atom has an energy more than 26 eV lower than that of the H 1s, so there is very little interaction between them. The F 2p orbital (-18.65 eV) and the H 1s (-13.61 eV), on the other hand, have similar energies, allowing them to

The National Cancer Institute's Natural Products Branch at the Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research is the largest program to collect materials worldwide from marine, plant, and microbial sources so they may be studied for possible medical uses.






















0 Response to "40 molecular orbital diagram hf"
Post a Comment