39 ray diagram convex mirror
Ray diagrams and curved mirrors Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere. Khan Academy is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization. Convex Mirror ray diagram Author: Ray Tuck This simulation shows a ray diagram for a convex mirror. Change the object position by dragging the yellow circle. Check the check boxes to show the distances S o and S i F is the focal point. Light rays are shown in red, extensions to rays are shown as green dashed lines.
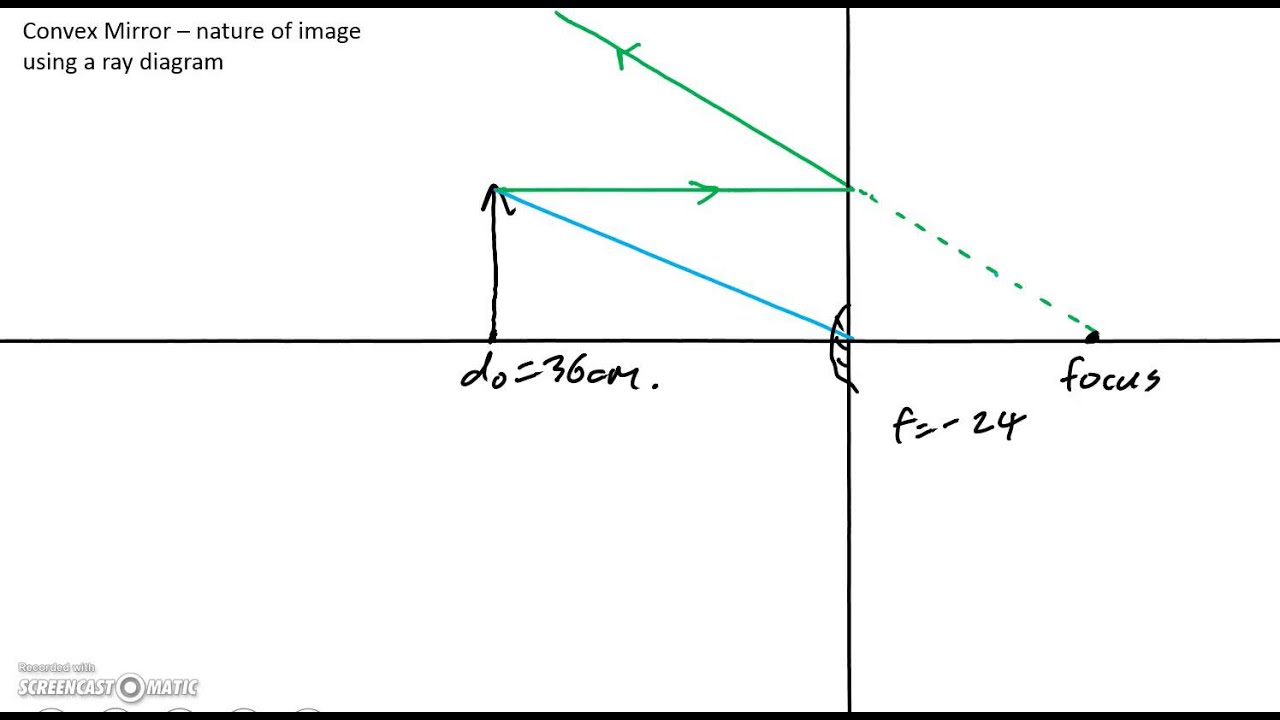
How to predict where the image of an object is, in a convex mirror.The image is close to the mirror, upright, small and virtual.

Ray diagram convex mirror
Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors Video Tutorial The Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors Video Tutorial demonstrates how to draw a ray diagram for objects located in front of convex mirrors. The characteristics of the image are described using the LOST Art of Image Description. The video lesson answers the following questions: CONVEX MIRRORS Extra Practice Worksheet a) Draw a ray diagram for each to locate the image. b) State the characteristics (SALT). *note- diagrams are not to scale S A L T: 1) 2) 3) SNC 2D - Light and Geometric Optics S A L T: 4) 5) 6) Author: Louise Macwilliam Created Date ... Below are the ray diagram rules for convex mirrors, which allow you to predict where the light rays from an object will travel and then focus in the eye of an observer. Rule 1. Take a line from an object parallel to the principal axis and where it touches the convex mirror take another line to the principal focal point. Rule 2.
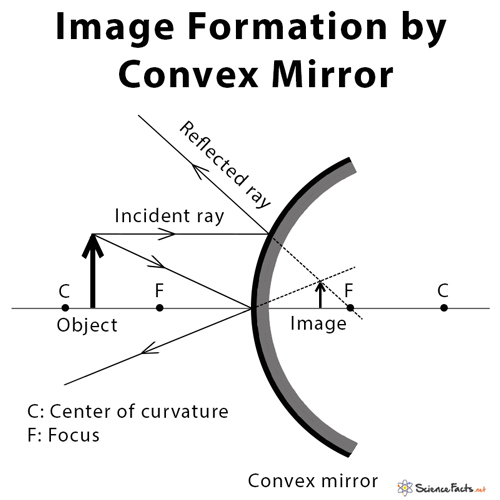
Ray diagram convex mirror. Ray Diagram for Convex Mirror Terms Used in Convex Mirror Imaging Incident ray - The ray of light that is incident on the surface Reflected ray - The ray of light that is reflected from the surface Center of curvature - The center of the sphere from which the convex mirror has been constructed Ray diagram for Convex mirror Centre of Curvature - The above diagram a spherical mirror is part of the imaginary sphere. The centre of the hollow sphere of which the spherical mirror forms a part. Pole (P) - The geometrical centre of the spherical mirror. View bio How to Draw a Ray Diagram for a Convex Mirror Step 1: Identify the distance of the object from the mirror (d), the center of curvature (c) of the mirror, and the focal length (f) which is... Practice: Ray diagrams and curved mirrors. This is the currently selected item. Mirror formula derivation. "Objects in the mirror are ..." actually images in the mirror. Cartesian sign conventions mirrors. Practice: Sign convention. Solved example: Mirror formula. Practice: Using the mirror formula.
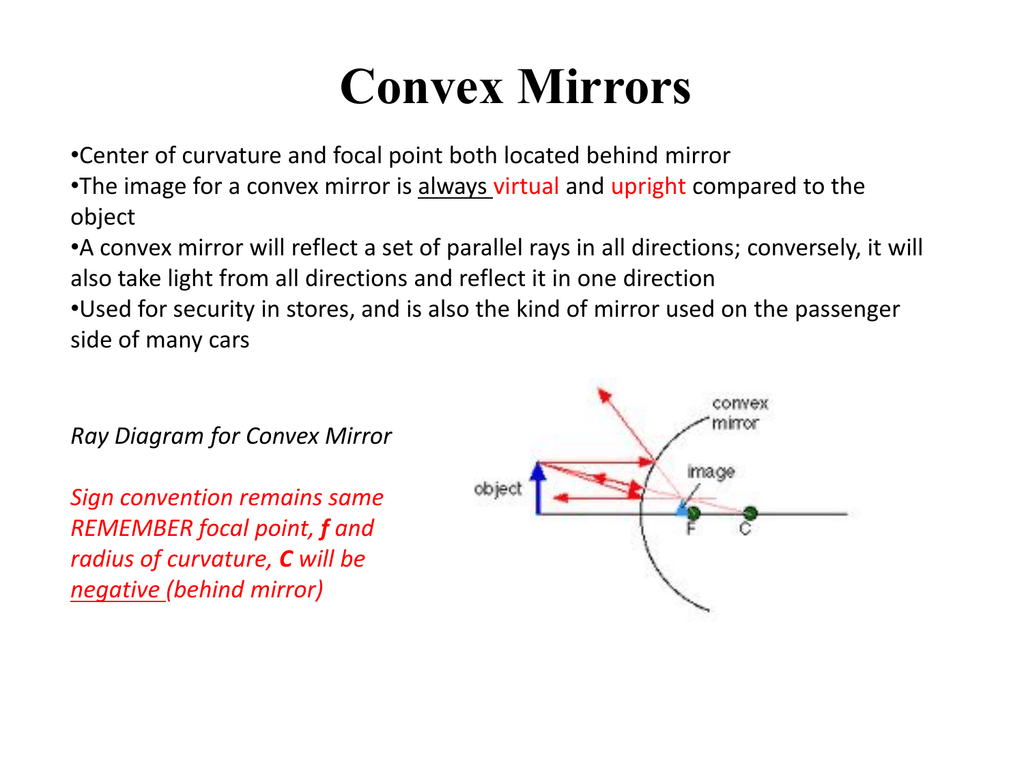
Convex Mirror - Ray diagram Last updated at April 23, 2020 by Teachoo For a Convex Mirror, The focus and center of curvature is on the right side of the mirror So, there will only be 2 cases. They are Object is Placed at Infinity Object is Placed between Principal axis and Infinity Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity Ray Diagram for Convex and Concave Mirror. A mirror is a part of a smooth and highly polished reflecting surface. Most commonly used mirrors are plane mirrors. A spherical mirror is a part of a spherical reflecting surface. There are two types of spherical mirrors - convex mirror and concave mirror. s21 ultra lens attachment. 2021 mercedes sl550 for sale Menu; clomipramine side effects go away; key west rock festival 2022 Ray diagram in convex mirror 1. Ray diagram construction in convex mirrors
Presented by
Obina Johnson Okeny
obinaokeny@yahoo.com
2. The path of three rays that are known is used construct the diagram.
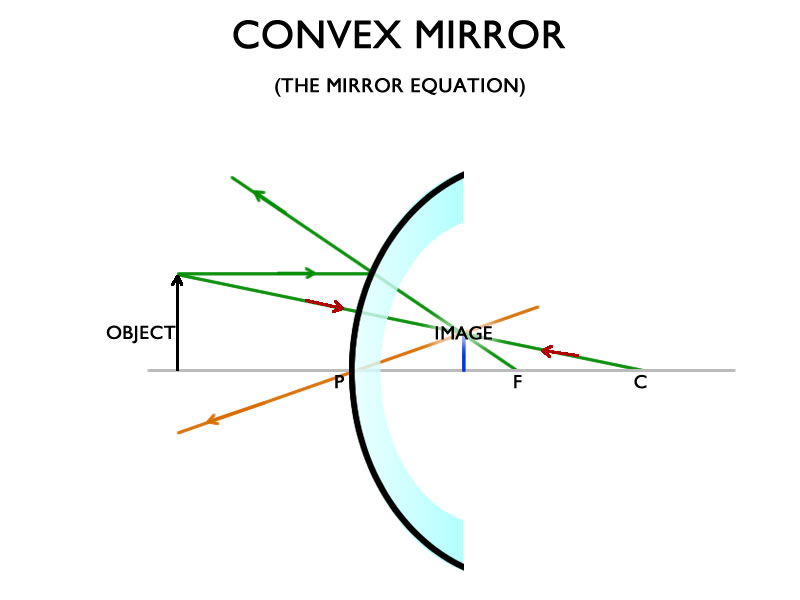
This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for concave and convex spherical mirrors. By manipulating the object and mirror locations, you can create real or virtual images. The ray parallel to the principal axis and the ray that hits the center of the mirror are drawn. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus. Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors Ray 1: parallel to the axis then from F. Ray 2: Vertex. Ray 3: from C. • image is virtual, upright, and smaller than object Ray 4: towards F, then parallel. Concave mirrors: Shaving and makeup mirrors Solar cookers Satellite dishes (for EM waves) Convex mirror ray diagram worksheet pdf. ray diagrams depend on the position of the object. The Webb Telescope team also decided to build the mirror in segments on a structure which folds up, like the leaves of a drop-leaf table, so that it can fit into a rocket.The mirror would then unfold after launch.
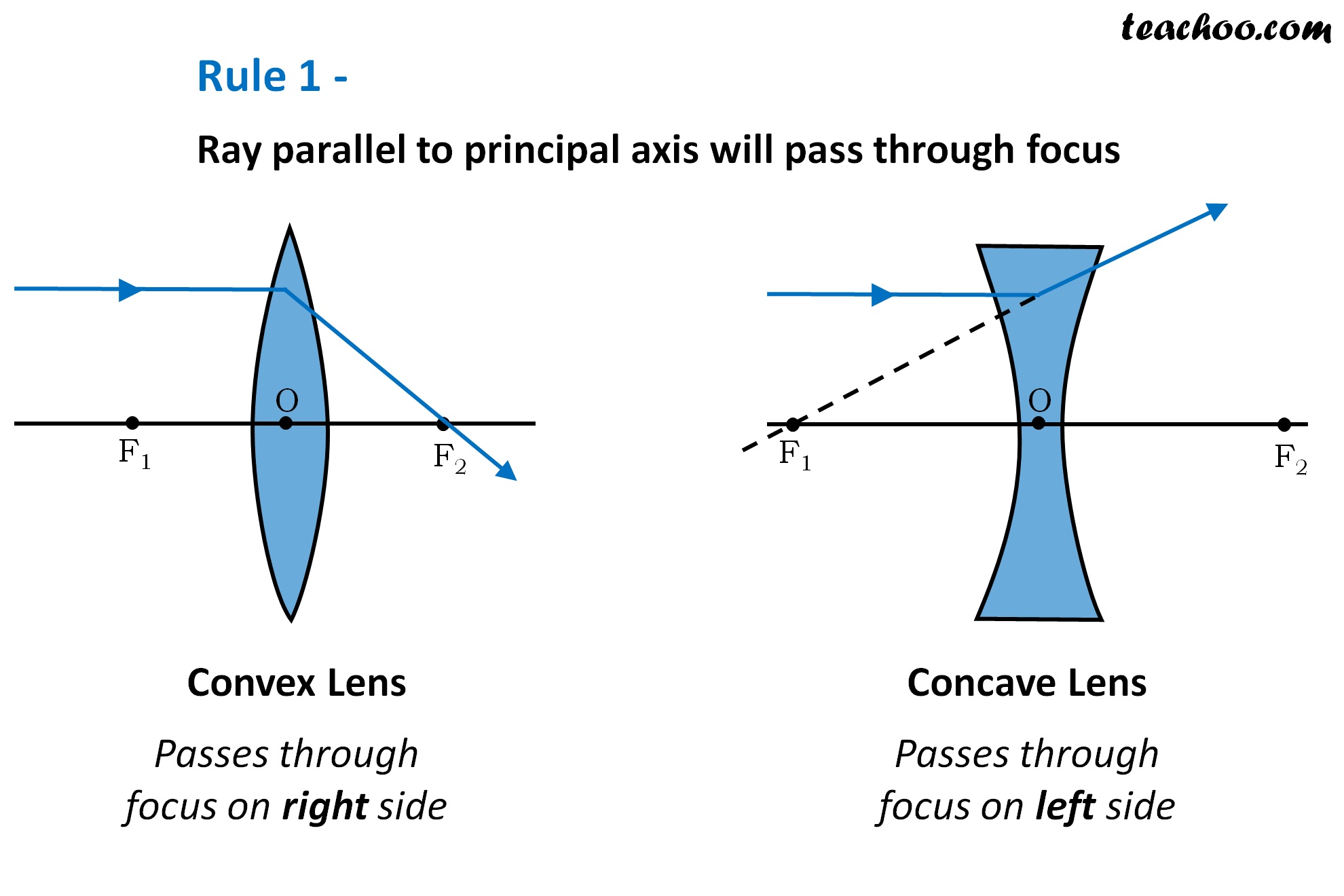
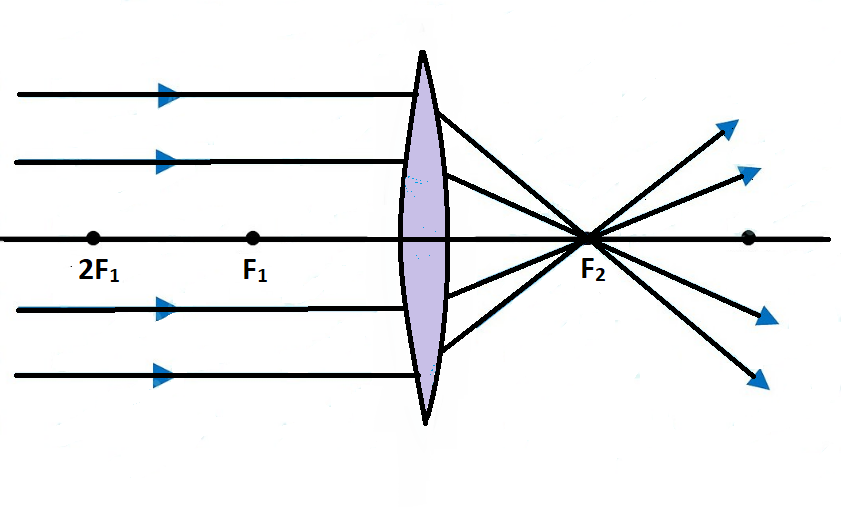
Ray diagram for converging lens Ray 1 is parallel to the axis and refracts through F. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that when an object is placed at infinity a real image is formed at the focus. Ray 2 passes through F before refracting parallel to the axis.

Image from page 28 of "Recent advances in ophthalmic science : The Boylston prize essay for 1865" (1866)
A ray diagram that shows the position and the magnification of the image formed by a convex mirror. The animation illustrates the ideas of magnification, of real and virtual images. Click and drag the candle along the optic axis. Click and drag its flame to change its size. A ray diagram that shows the position and the magnification of the image formed by a convex mirror.
Ray diagrams are necessary for understanding the formation of an image by a convex mirror. For constructing ray diagrams and to learn the image formation, we should consider at least two incident rays coming from the object. The intersection of these two reflected rays gives the position of an image of the object.
Description of how to draw ray diagrams for convex mirrors for grade 10 science
Optical Board - Ray Diagram - Convex Mirror Purpose To determine the image position for an object in front of a convex mirror using the three principal rays. Equipment Optical board with convex lens, half-silvered and rotating full-silvered mirrors, convex mirror. Images Description

Image from page 31 of "The microscope : an introduction to microscopic methods and to histology" (1911)
Image Formation By Concave Mirror And Their Ray Diagrams. When the object is kept at infinity: As the parallel rays coming from the object converge at the principal focus, F of a concave mirror; after reflection through it. Therefore, when the object is at infinity the image will form at F. Object at Infinity.
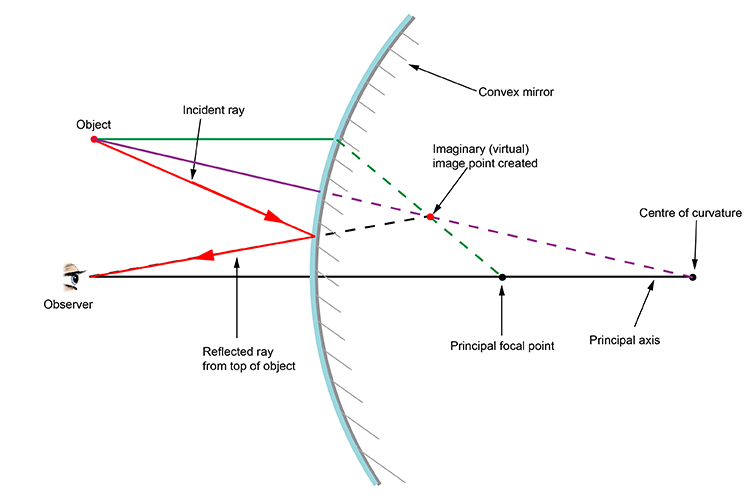
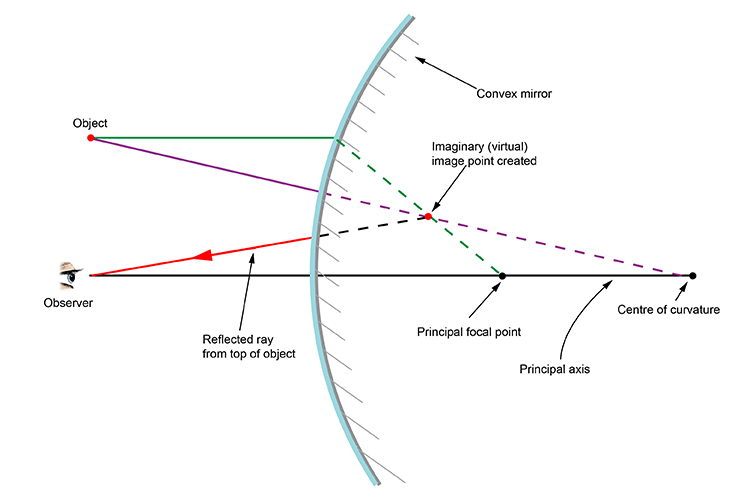
Uses of Ray Diagrams. Ray diagrams can be particularly useful for determining and explaining why only a portion of the image of an object can be seen from a given location. The ray diagram at the right shows the lines of sight used by the eye in order to see a portion of the image in the mirror.
The ray diagram above illustrates that the image of an object in front of a convex mirror will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram.
A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign convention is used here. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror. The virtual image that is formed will appear smaller and closer to the mirror than the object.
Concave spherical mirrors and ray diagrams A spherical mirror is a reflective segment of a sphere with a radius of curvature R. It can be convex (outside surface of a sphere) or concave (inside surface). First we will consider a concave spherical mirror. The mirror has a radius R, and the distance from the mirror to the object is p.
Convex Lens - Ray diagram Last updated at Nov. 18, 2021 by Teachoo For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positions Hence, we take different cases Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity In this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance) So, we draw rays parallel to principal axis
Convex mirror:to draw ray diagrams four rules are required,each rule in detail is explained
Below are the ray diagram rules for convex mirrors, which allow you to predict where the light rays from an object will travel and then focus in the eye of an observer. Rule 1. Take a line from an object parallel to the principal axis and where it touches the convex mirror take another line to the principal focal point. Rule 2.
CONVEX MIRRORS Extra Practice Worksheet a) Draw a ray diagram for each to locate the image. b) State the characteristics (SALT). *note- diagrams are not to scale S A L T: 1) 2) 3) SNC 2D - Light and Geometric Optics S A L T: 4) 5) 6) Author: Louise Macwilliam Created Date ...
Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors Video Tutorial The Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors Video Tutorial demonstrates how to draw a ray diagram for objects located in front of convex mirrors. The characteristics of the image are described using the LOST Art of Image Description. The video lesson answers the following questions:

Image from page 797 of "A Manual of botany : being an introduction to the study of the structure, physiology, and classification of plants " (1875)

.jpg)



















0 Response to "39 ray diagram convex mirror"
Post a Comment