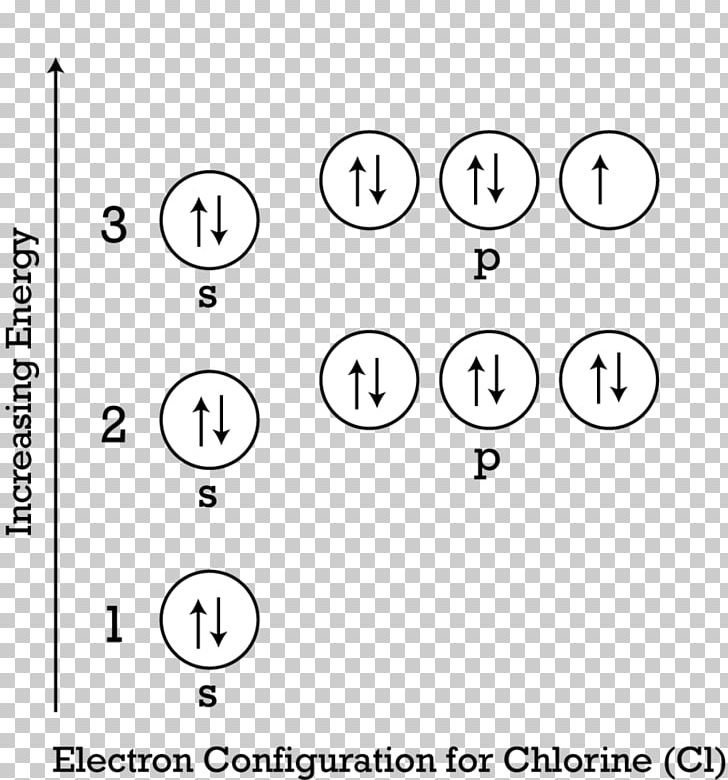
37 orbital diagram for chlorine
Draw the atomic orbital diagram for chlorine. Learn this topic by watching The Electron Configuration Concept Videos All Chemistry Practice Problems The Electron Configuration Practice Problems Q. Construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion.TiTi2+Ti4+ Q. Write the corresponding electron configuration for the following pictorial ... orbital and energy match, therefore very low HOMO and high LUMO energy! σ C-Cl! σ* C-Cl! C (sp3)! In a C-Cl bond, an sp3 orbital from carbon is still being mixed so same energy level! It is mixed, however, with a p orbital on chlorine which is much lower in energy (more electronegative)! Cl (p)! Poor energy match means orbitals do not
Orbital diagram of chlorine 17 1 Know the formula. In molecular orbital theory, the binding order is defined as half the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. Binding order = [(Number of electrons in binding molecules) - (Number of electrons in antibonding molecules)]/2. 2 Know that the larger the binding order ...

Orbital diagram for chlorine
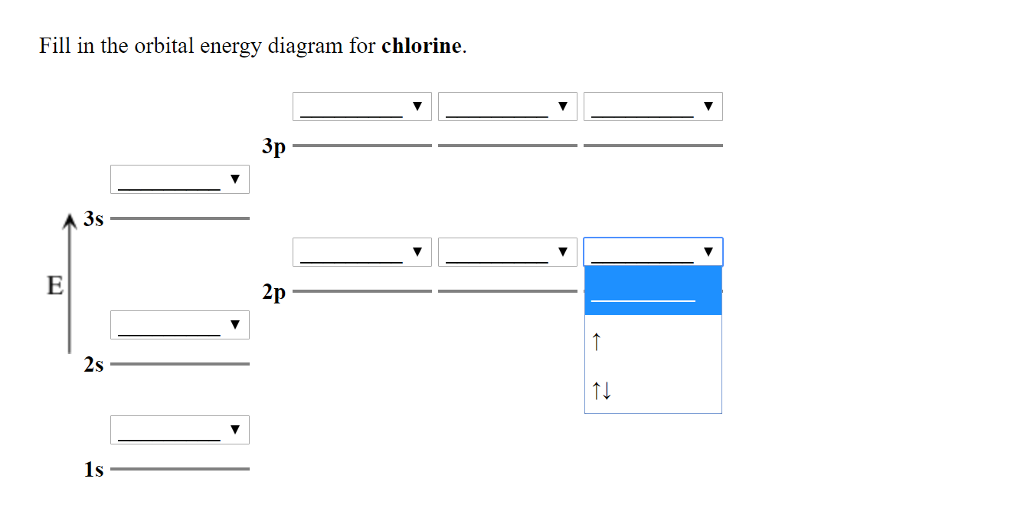
An orbital is a region of space that an electron can exist in. For the diagram you start with the 1 s orbital and then 2s, 2p, and so on. Each orbital can hold 2 electrons and each arrow ... Solved 4p 3d Draw the orbital energy diagram for Cl | Chegg.com. Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. 4p 3d Draw the orbital energy diagram for Cl (chlorine) -4s 3p Represent electrons as arrows (with up or down spin) What is the [core] valence electron configuration? (type in the box below) 2pL LU 2s -1s ×Reset Draw Erase. The hydrogen element is exceptional compared to the other elements in the periodic table. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of hydrogen and orbital diagram, period and group, valency and valence electrons, bond formation, hydrogen compound formation, application of different principles. FAQ. 1.
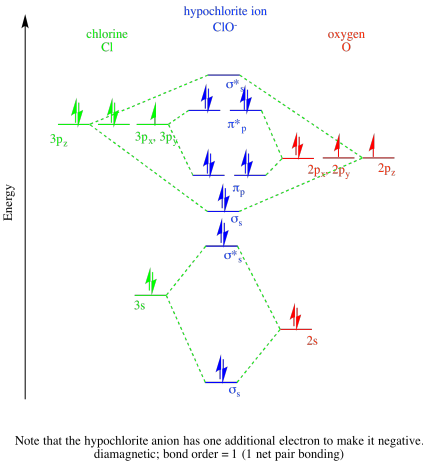
Orbital diagram for chlorine. Molecular Orbital Diagram - Cl2, Br2, I2 3s & 3p and higher atomic orbitals are not so widely separated in energy and allow significant mixing (hybridization) to occur. This mixing causes the inversion of the σσand πmolecular orbitals' energy. σσσ ππ σ* π* 3,4,5 p 3, 4,5 s σ* σ 3,4,5 s 3,4,5 p Interhalogens Br Br F F Br F F F F. ... In gaseous BeCl 2, these half-filled hybrid orbitals will overlap with orbitals from the chlorine atoms to form two identical σ bonds. Figure 3. Hybridization of an s orbital (blue) and a p orbital (red) of the same atom produces two sp hybrid orbitals (purple). Each hybrid orbital is oriented primarily in just one direction. The atomic orbital diagram of chlorine is as given below, Become a member and unlock all Study Answers. Try it risk-free for 30 days Try it risk-free Ask a question. Our experts can answer your ... 2. The molecular geometry of chlorine dioxide is bent and the bond angle is slightly less than 109 degrees. 3. The hybridization of chlorine dioxide is sp2 and its ion is sp3. 4. The hybridization can further be studied in detail with the help of a molecular orbital diagram. 5. The formal charge distribution on chlorine dioxide is -1. 6.
Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer 03/07/2016 · Finally, the last electron to be added will be placed in the 3p_z orbital, once again having spin-down. Here's a diagram showing the electron configuration of chlorine, with the last electron added highlighted So, the magnetic quantum number, m_l, tells you the specific orbital in which the electron is located. Click to visit. Orbital diagram of Chlorine (Cl) 18: Orbital diagram of Argon (Ar) 19: Orbital diagram of Potassium (K) 20: Orbital diagram of Calcium (Ca) 21: Orbital diagram of Scandium (Sc) 22: Orbital diagram of Titanium (Ti) 23: Orbital diagram of Vanadium (V) 24: Orbital diagram of Chromium (Cr) 25: The electron configuration of fluorine(F) and the orbital diagram is the main topic of this article. This article gives an idea about the fluorine orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of fluorine, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles.
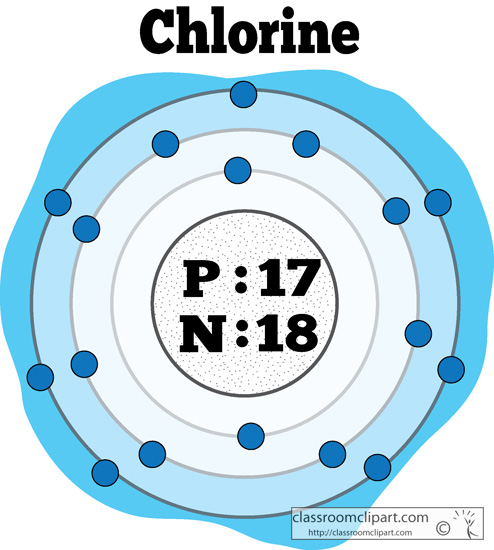
Jan 03, 2022 · The premise of molecular orbital (MO) theory is that all the constituent atoms contribute towards the formation of molecular orbitals, which are a linear combination of the atomic orbitals. As per this theory, the electrons in a molecule are not individually assigned to atomic orbitals but to molecular orbitals. Check out the MO diagram for CH2Cl2. Dec 28, 2021 · In a molecular orbital diagram of PCl3, we can see 3 bonding orbitals, which will be occupied. And 3 anti-bonding orbitals which will be empty. We can see from the hybridization that 3 Sp3 hybrid orbitals of phosphorus will be occupied by 3 Cl atoms. The remaining one is a non-bonding orbital but doubly field, which denotes the lone pair of ... Orbital Diagram 1s ↿⇂ 2s ↿⇂ 2p ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿⇂ 3s ↿⇂ 3p ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿ 3d What is the Valency of chlorine? The electronic configuration of chlorine can be written as 2, 8, 7. 2, 8, 7 electrons are distributed in the shells K, L, M respectively. Chlorine(Cl) is the 17th element in the periodic table and its symbol is 'Cl'. The electron configuration of chlorine and the orbital diagram is the main topic in this article. Also, valency and valence electrons of chlorine, and compound formation, bond formation have been discussed. Hopefully, after reading this article you will know in ...
Three rules are useful in forming orbital diagrams. According to the Auf Bau Principle, each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital. You jump up a little bit in energy and we get the 2s orbital that make it the 2p sublevel. What is the orbital diagram for chlorine? In writing the electron configuration for Chlorine the first two electrons ...
Bromine(Br) is the 35th element in the periodic table and its symbol is 'Br'. The electron configuration of bromine and the orbital diagram is the main topic in this article. Also, valency and valence electrons of bromine, and compound formation, bond formation have been discussed. Hopefully, after reading this article you will know in ...
Mar 15, 2018 · Periodic trends predict differences between elemental characteristics as you move across the periodic table. Trends are based on Coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. Atomic size measured the distance between the nucleus of an atom and the outermost non-valence electrons of the atom. Atomic size decreases from …
Write the full electron configuration, noble gas electron configuration, and fill in the orbital diagrams, for the following elements. 1. Nitro en 3s B 2. Chlorine Is 3. Sodium a øan a as ap 4. Neon Is 23 5. Nickel 6 Vanadium Is 7 Cop er
In writing the electron configuration for Chlorine the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Chlorine go in the 2s orbital. The next six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two ...
Abbreviated orbital diagram of chlorine Description Greenish-yellow, disagreeable gas. Never found in free form in nature. Uses Used in water purification, bleaches, acids and many, many other compounds such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFC). Sources Salt (sodium chloride, NaCl) is its most common compound.
To write the orbital diagram for the Chlorine atom (Cl) first we need to write the electron configuration for just Cl. To do that we need to find the number...
Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration.
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics.
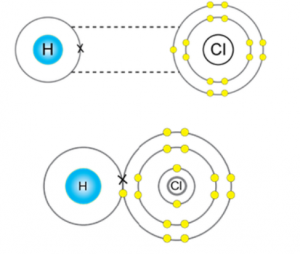
Answer (1 of 2): Here is a useful MO diagram of HCL found on the internet: The Cl electrons residing up to 3s orbital (1s, 2s, 2px,2py,2pz,3s) are largely stabilized than H electron in 1s orbital and therefore they cannot mix and form bond. The 3p electrons of Cl have comparable energy with the ...
An orbital drawing of the anti-transition state is shown on the right. Note that the base attacks the alkyl halide from the side opposite the halogen, just as in the S N 2 mechanism. In this drawing the α and β carbon atoms are undergoing a rehybridization from sp 3 to sp 2 and the developing π-bond is drawn as dashed light blue lines.
Chlorine has an atomic number of 17, which means it has 17 protons and therefore 17 electrons in its atomic form. We'll need to know how many sublevel is present in each energy level, and in turn, how many electrons each sublevel can accommodate. From the given table, for energy level 1, there's only 1 sublevel, which is called 1s.
Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration.
Cl2 molecular orbital diagram. In contrast to crystal field theory, molecular orbital included the covalent nature of the metal-ligand bond interaction. Energy of. Cl atom has 17 electrons, so chlorine molecule has (Cl2) has 34 electrons. so, bond order of chlorine molecule is 1.
Boron (atomic number 5) has five electrons. Four electrons fill both the 1s and 2s orbitals. The fifth electron is added to a 2p orbital, the sublevel next higher in energy (Figure 5.9). The electron configuration of boron is: B: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1. Table 5.2 shows the electron configurations of the elements with atomic numbers 1 through 18.
Give the orbital diagram for an atom of {eq}Cl {/eq}. Electron Configuration: We use three rules to help determine how to draw the orbital diagrams (and thus get the electron configuration) for atoms:
An orbital box diagram can be written as well. Boxes, or horizontal lines represent the orbitals, arrows represent the electrons, and if an orbital is full, the electrons must be of opposite spin–one arrow pointing up and the other one pointing down. The orbital box diagrams are listed for the first 20 elements in the figure below.
The hydrogen element is exceptional compared to the other elements in the periodic table. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of hydrogen and orbital diagram, period and group, valency and valence electrons, bond formation, hydrogen compound formation, application of different principles. FAQ. 1.
Solved 4p 3d Draw the orbital energy diagram for Cl | Chegg.com. Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. 4p 3d Draw the orbital energy diagram for Cl (chlorine) -4s 3p Represent electrons as arrows (with up or down spin) What is the [core] valence electron configuration? (type in the box below) 2pL LU 2s -1s ×Reset Draw Erase.
An orbital is a region of space that an electron can exist in. For the diagram you start with the 1 s orbital and then 2s, 2p, and so on. Each orbital can hold 2 electrons and each arrow ...








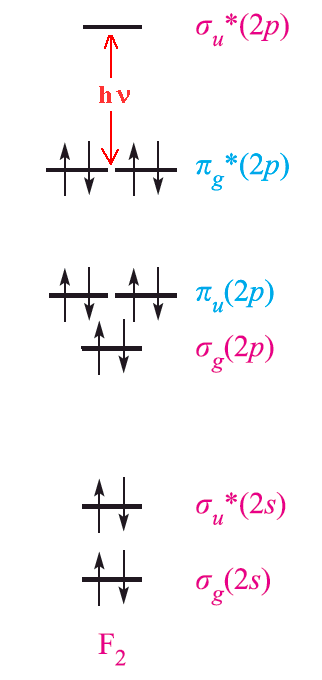










0 Response to "37 orbital diagram for chlorine"
Post a Comment