38 earth moon sun diagram
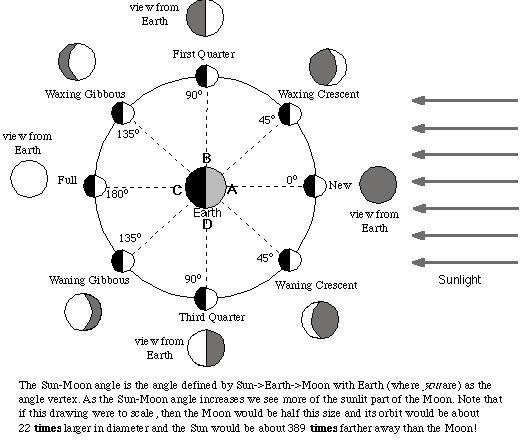
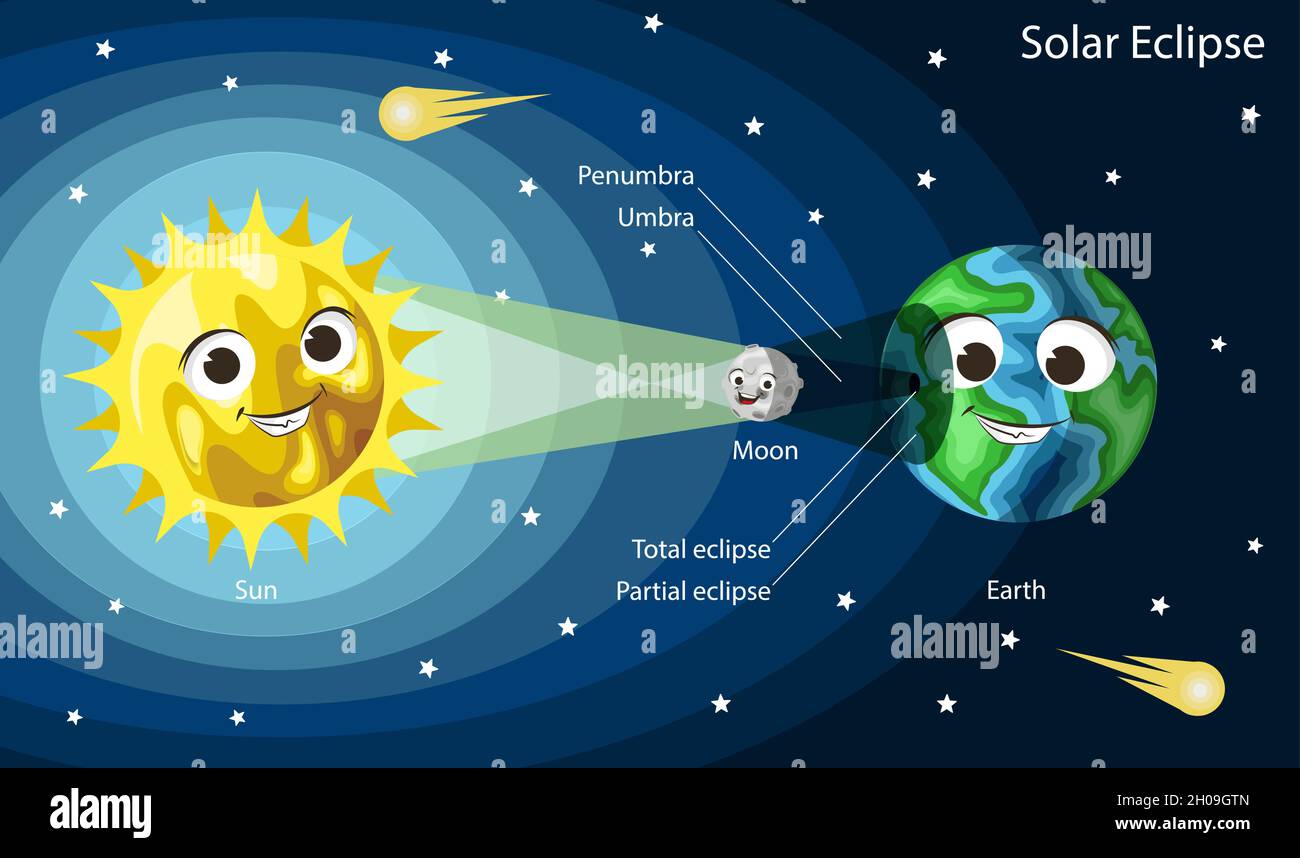
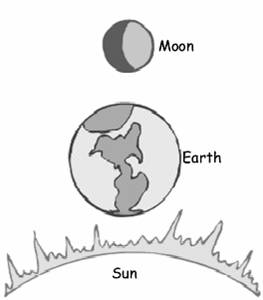
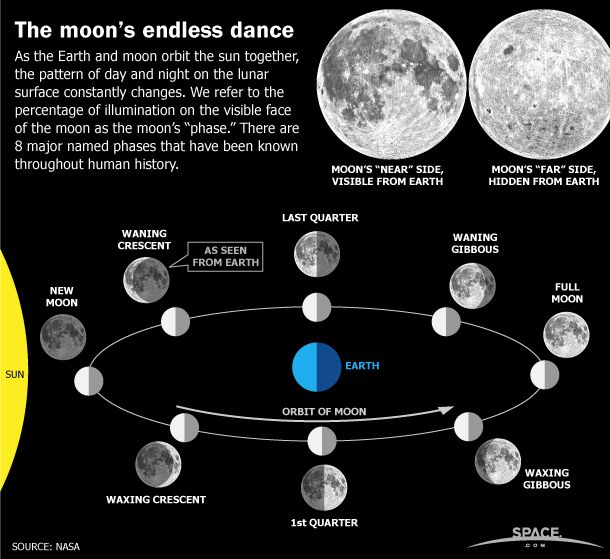
Moon phases diagram. Moon phases diagram/image credits: StarChild team at Nasa. As seen in the diagram, when the earth is between the moon and the sun, then we see a full moon. When the moon is between the earth and the sun, we have a new moon. If they are perfectly aligned, then we have a solar eclipse. Lunar Eclipse Diagram. This shows the geometry of a lunar eclipse. When the Sun, Earth, and Moon, are precisely aligned, a lunar eclipse will occur. During an eclipse the Earth blocks sunlight from reaching the Moon. Earth creates two shadows: the outer, pale shadow called the penumbra, and the dark, inner shadow called the umbra.
Annotated Earth, Sun and Moon Diagram Teaching Resource 5th Grade Science, Science Biology,. teachstarter. Teach Starter. 42k followers.

Earth moon sun diagram
Sun, Earth and Moon Position - 3D Simulator. With this simulator of the local solar system, with data from the earth, the sun and the moon, you can know the exact position of the moon and the sun with respect to the earth for any date. On earth, the area where it is night is drawn in darker color. Current simulation date Teaching Science. Science Activities. Science Ideas. The Sun, the Moon and the Earth Display. I created this for a Year 5/6 classroom when studying the sun, moon and earth. The red section contains a lift the flap quiz, together with some of the children's work. chelseameans21. C. Chelsea Means. A poster showing the interplay of the Sun, Earth and Moon. Use this annotated diagram when studying the movements of the Sun, Earth and Moon.
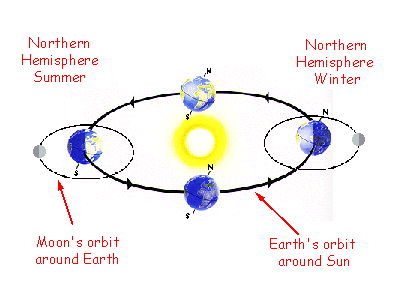
Earth moon sun diagram. Simple animation of the earth and moon moving about the sun. This animation is a follow-up to this one: http://youtu.be/W47Wa7onrIQ, dedicated to the many hu... The motions of the Moon around the Earth and of the Earth around the Sun are complex. The motions involved in revolutions are superimposed on the movements involved in rotations. The Earth and the Moon both turn on their own axis (rotation), but both also move around another object (revolution). The rotation of the Earth (24 hours) explains the alternation of day and night. The portion of the moon phases where you see less and less of the lit side of the moon each day/night. Lunar Eclipse. When the sun's rays are bent to reflect red light onto the moon. Sun and moon have to be on opposite sides of Earth. Solar Eclipse. When the moon is in perfect position to block out the sun's light. Have you ever wondered about the scale of the Solar System? The relative sizes of the planets, their Moons and the Sun are difficult to comprehend due to the...
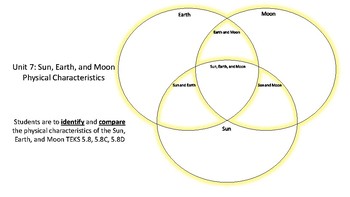
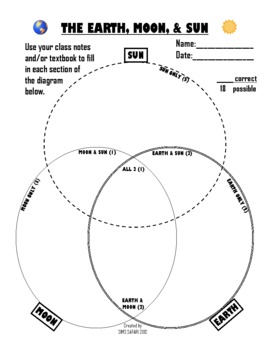
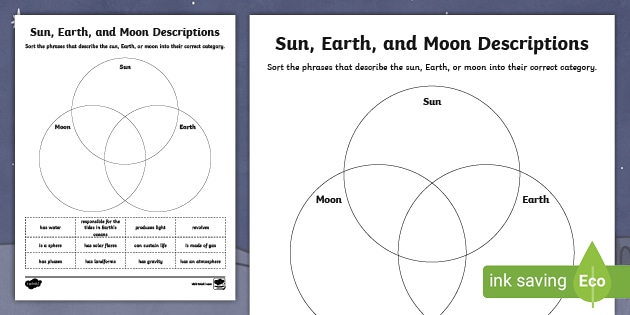
The Earth and Moon. Although the whole solar system is fascinating, the other planets don't play a role in eclipses. For our purposes, we're interested in the Sun, the Earth, and the Moon, and how they relate to each other. This diagram shows the Sun, Earth, and Moon, and how their orbits work. Challenge students to sort the characteristics of the Sun, Earth, and Moon, using a Venn diagram. Students will cut and glue characteristics into the three-way Venn diagram. This is a great partner activity or assessment. Check out this Venn Diagram Worksheet to get started with this amazing data and organization topic.This resource addresses the following standard: TEKS Science 5.8.D. At that point, the far side of the Moon is facing the Sun. This phase is called a new moon. During the new moon, the side facing Earth is dark. The eight Moon phases: 🌑 New: We cannot see the Moon when it is a new moon. 🌒 Waxing Crescent: In the Northern Hemisphere, we see the waxing crescent phase as a thin crescent of light on the right. Also, looking at the diagram (and imagining it to scale), you may have wondered why, at a new moon, the moon doesn't block the sun, and at a full moon, why the earth doesn't block sunlight from reaching the moon. The reason is because the moon's orbit about the earth is about 5 degrees off from the earth-sun orbital plane.
Yes, always in Diagram 2 and sometimes in Diagram 3. Could the half of the Moon that faces Earth ever be completely dark in any of these diagrams? The Moon is always moving around Earth in a circle. Diagram C is accurate because the Moon is almost as far as it can be from the sun, and so almost none of the Moon is lit by the sun. All three diagrams are sometimes accurate because the Moon has some lighter-colored rock and some darker-colored rock, and the half of the Moon with the lighter-colored rock rotates to face different directions. The Moon rotates on its axis and revolves around the Earth as the Earth revolves around the Sun. It takes about 27 Earth days for the Moon to rotate on its axis and about 29 ½ Earth days (month) for it to revolve around the Earth.; Because the Moon's period (time) of rotation on its axis and period of revolution around the Earth are nearly the same, the same side of the Moon always faces Earth. Because of the Earth's axial tilt, the Sun's assumed location shifts up and down slightly over the course of the year in this animation, appearing on the same horizontal plane as the Earth solely during the March and September equinoxes. The circle shows the Moon's anticipated path in the upcoming weeks, including the next 3 or 4 Moon phases ...
ANSWER KEY Moon, Earth, and Sun Model CER Claim (Write a sentence stating what causes moon phases after working with your model.) - Moon phases are caused by the moon's position around the earth, and the earth's position around the sun. Evidence (Provide examples from using your model to support your claim.)
Map of A diagram from 1891 showing position of the earth, moon, and sun during spring and neap tide. "When the sun and moon act simultaneously, on the same hemisphere of the earth, as shown in Fig. 74, the tidal wave is higher than usual. The flood tides are then highest, and the ebb tides lowest. These are called spring tides. They occur twice during every revolution of the moon — once at ...
This diagram features pictures of the Sun, Earth and Moon, as well as circular lines denoting Earth and the Moon's orbits around the Sun and Earth respectively. To complete the activity, students must identify and label each of the three bodies and two orbits. This would be a good activity to give pupils at the start of a series of lessons on ...
Phases of the Moon are caused by a shadow from the Earth. Different countries see different phases of the Moon on the same day. The Moon goes around the earth in a single day. The Moon makes light the same way the Sun does. Lunar and solar eclipses occur every month somewhere on Earth.
Play this game to review Science. The diagrams above show Earth and the Moon in different positions, as seen from above (top view). Sunlight is coming from the left, but these diagrams do not show what parts of Earth or the Moon are light or dark. 3. Could the half of the Moon that faces Earth ever be completely dark in any of these diagrams?</p>
Facts about the Moon for KS2. Here are some interesting facts about the Moon that you can teach to your KS2 students: - The Moon orbits the Earth once every 28 days. - The Moon doesn't change shape; it is the Sun's light that makes it appear to wax and wane. - The Moon is only held in place by the gravitational pull of the Earth.
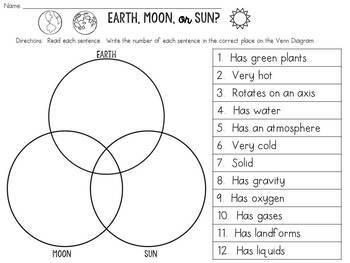
Distance from sun: 92,000,000. Both are spheres. Both orbited by a planet. Both have atmospheres. Is made out of hot gases. Is at the center of the solar system. Surface temp. 5,788 K. Is a sphere.
More Astronomy Crafts: EnchantedLearning.com Sun, Earth, and Moon Model More Crafts. This is a model of the Sun, Earth, and Moon, that shows how the Earth orbits the Sun, and the Moon goes around the Earth.. Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543) was a Polish astronomer who developed the Copernican system, a model of the solar system in which the Earth and the other planets orbit the Sun.
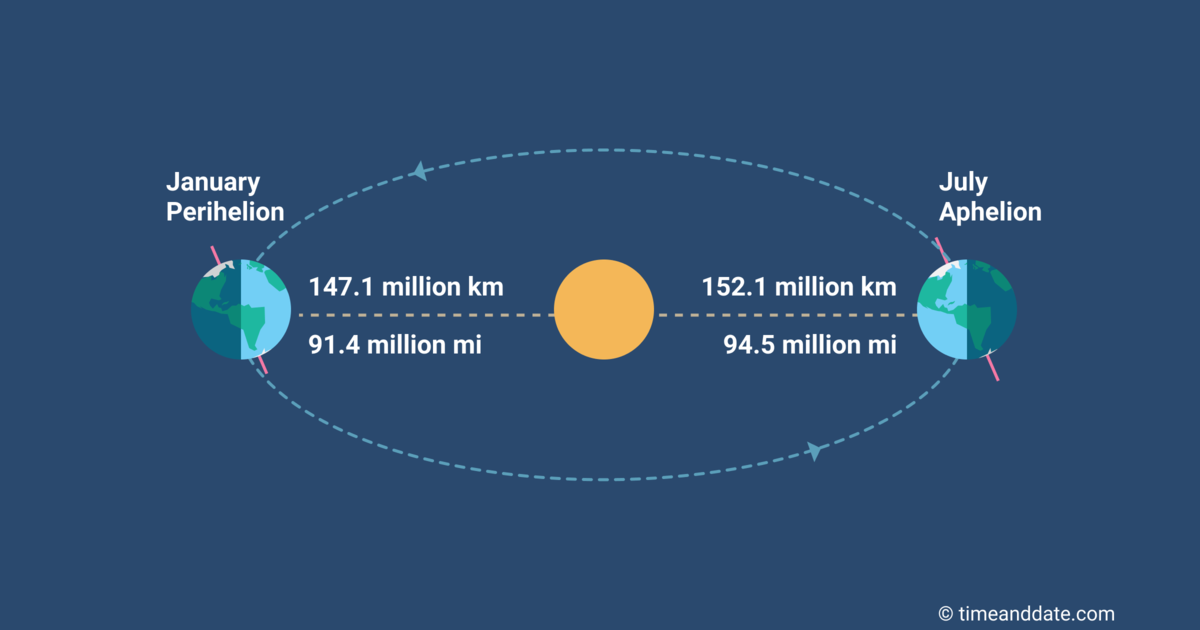
Distance Between the Sun, Moon, and Earth. This image depicts the distance from the Earth to the Moon and Sun, and the width of the Moon and the Sun. Not to scale.
The Moon's path around Earth is tilted compared to Earth's orbit around the Sun. The Moon can be behind Earth but still get hit by light from the Sun. In this diagram, you can see that the Moon's orbit around Earth is at a tilt. This is why we don't get a lunar eclipse every month. This diagram is not to scale: the Moon is much farther ...
Earth, Sun and Moon [classic] by Karissa Martinez. Edit this Template. Use Creately's easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. You can edit this template and create your own diagram. Creately diagrams can be exported and added to Word, PPT (powerpoint), Excel, Visio ...
Describe how Earth's movements affect seasons and cause day and night. Explain solar and lunar eclipses. Describe the phases of the Moon and explain why they ...
The amount of Moon we see changes over the month — lunar phases — because the Moon orbits Earth and Earth orbits the Sun. Everything is moving. During a lunar eclipse, Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon, blocking the sunlight falling on the Moon. Earth's shadow covers all or part of the lunar surface.
A poster showing the interplay of the Sun, Earth and Moon. Use this annotated diagram when studying the movements of the Sun, Earth and Moon.
Teaching Science. Science Activities. Science Ideas. The Sun, the Moon and the Earth Display. I created this for a Year 5/6 classroom when studying the sun, moon and earth. The red section contains a lift the flap quiz, together with some of the children's work. chelseameans21. C. Chelsea Means.
Sun, Earth and Moon Position - 3D Simulator. With this simulator of the local solar system, with data from the earth, the sun and the moon, you can know the exact position of the moon and the sun with respect to the earth for any date. On earth, the area where it is night is drawn in darker color. Current simulation date





















0 Response to "38 earth moon sun diagram"
Post a Comment