41 free body diagram constant velocity
In physics and engineering, a free body diagram (force diagram, or FBD) is a graphical illustration used to visualize the applied forces, moments, ... A free-body diagram is a diagram that is modified as the problem is solved. Normally, a free body diagram consists of the following components: The number of forces acting on a body depends on the specific problem and the assumptions made. Commonly, air resistance and friction are neglected.
Level 3: Drawing Free Body Diagrams When we are working with forces, we often need to find the net force acting on an object. To do this, we first start by sketching a picture of the forces acting on it. We call this picture a free body diagram. There are a few rules we should follow when drawing a free body diagram. 1.
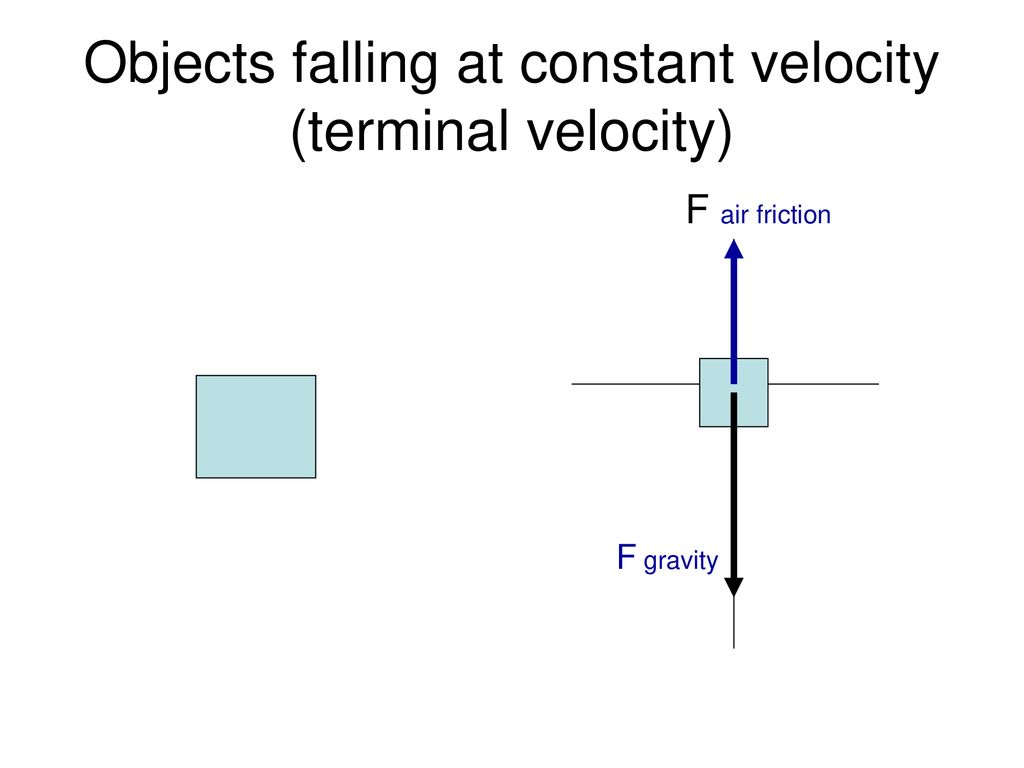
Free body diagram constant velocity
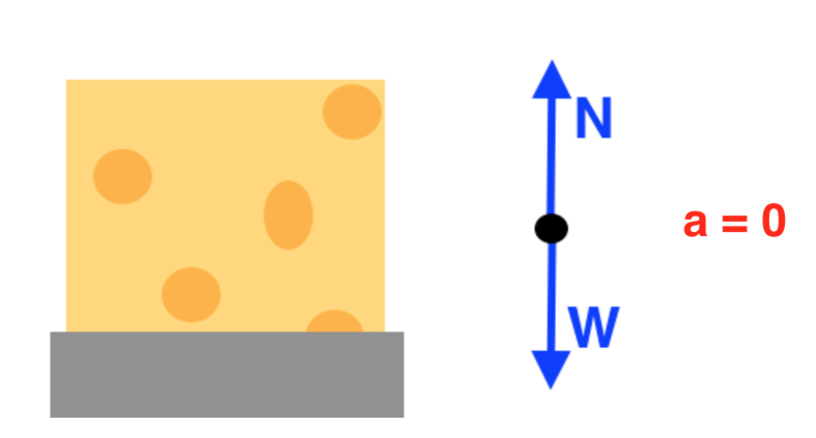
So, the free-body diagram of the object will look something like this: ... Remember that whenever an object is either at rest or moving at constant velocity, the resultant force acting on the object is 0. When you have two independent equations with two unknowns, you can solve them in different ways. Usually we tend to solve one of the two equations for one unknown, and substitute the result ... Free Body Diagrams a.k.a. Force Diagrams ... Constant Velocity Balanced forces. Could be at rest or moving left, right, up or down. Experiencing an Acceleration Unbalanced forces Can't tell which way it is moving, can only say which way it is experiencing an acceleration. Accelerating to the right. free body diagrams. used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting on an object. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. A flying squirrel is gliding (no wing flaps) from a tree to the ground at constant velocity. Consider air resistance.
Free body diagram constant velocity. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram reflects the magnitude of the force. The direction of the arrow shows the direction that the force is acting. Each force arrow in the diagram is labeled to indicate the exact type of ... 39. A 2-kg box is free-falling from the table to the ground. ("Free-falling" indicates that the only force that influences the motion is the force of gravity.) 40. A 2-kg box equipped with a parachute is falling at a terminal velocity after being dropped from a plane. (A "terminal velocity" indicates a constant velocity and a balance of forces.) Drawing the normal force on an free body diagram. On a free body diagram, "fbd," the normal force, "η," is ALWAYS drawn normal to the surface of contact. Free-body Diagram. Not sure about the correct wording for this question! A brick of mass M sits on a rubber pillow of mass m . Together they are sliding to the right at constant velocity on an ice-covered parking lot. (a) Draw a free-body diagram of the brick and identify each force acting on it. (b) Draw a free-body diagram of the pillow and ...
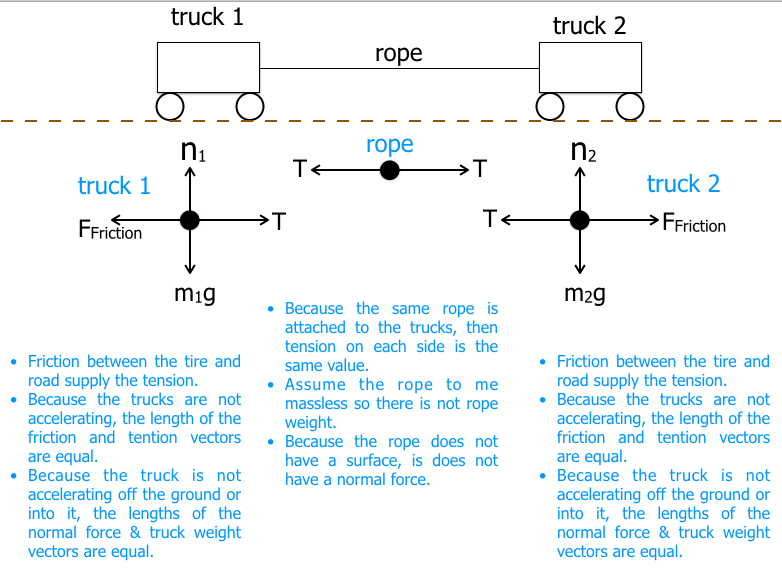
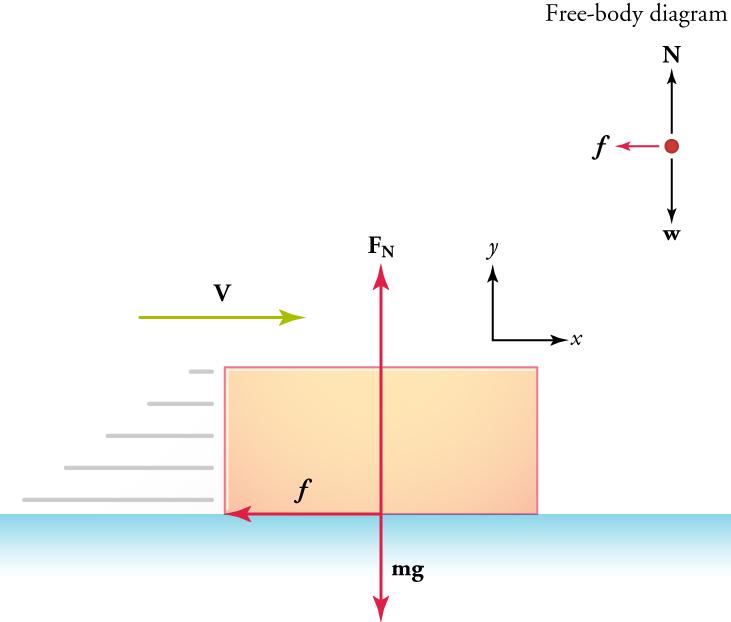
A person pushes a 16.0-kg shopping cart at a constant velocity for a distance of 22.0 m. ... Free Body Diagram. Since the shopping cart is not moving up and down. Since the cart is pushed at constant speed, a x is zero. PH 201 Homework Chapter 6 Solutions . Dr. Donovan's PH 201 Homework Page ... A car moving at a constant speed (uniform motion) has all forces acting on it balanced. In this case, the two backward forces (air resistance and friction) ... Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation, A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector ... travel at constant velocity. Do force diagrams for each block separately 9/23/2009 . 3. 5. Name Date Worksheet 2, Drawing Force Diagrams Sketch separate free-body diagrams for you, the elevator by itself, and the combined system of you plus the elevator for these three situations: the elevator has no acceleration (standing still or moving with constant velocity) the elevator has an upward acceleration (accelerating upward, or decelerating while on the way down) ...
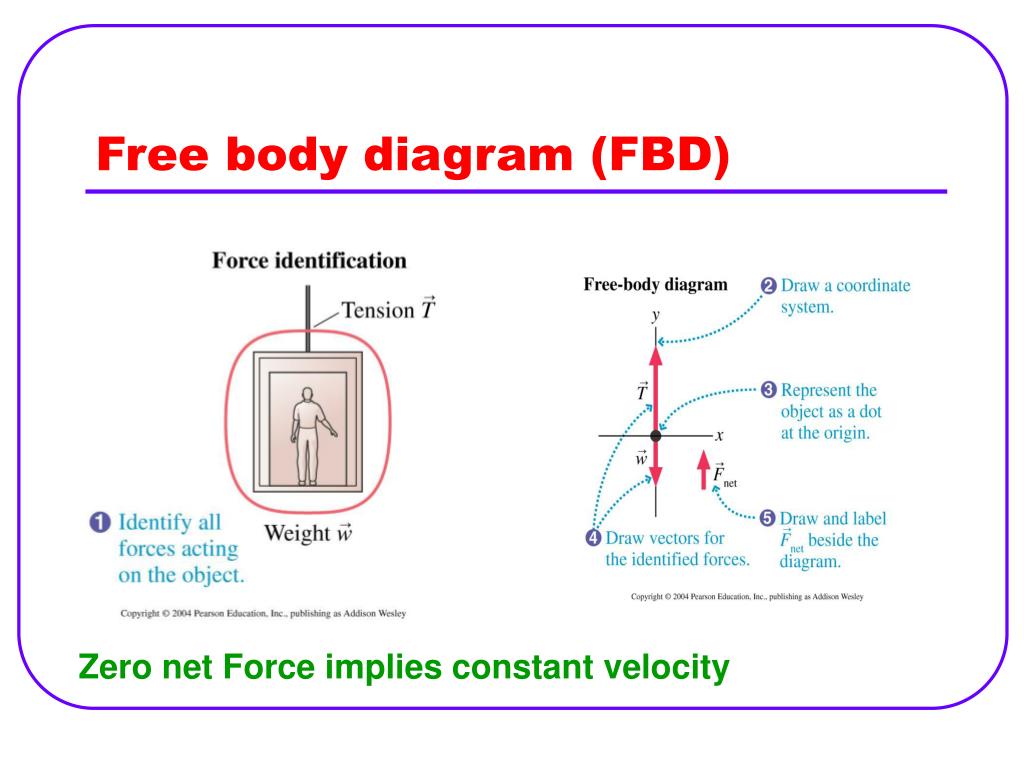
Using Free Body Diagrams to Develop a Math Model: ... If the body is moving at a constant velocity then the summation will equal zero. (Recall that a body at rest is moving at a constant velocity of zero.) If the body is accelerating, then the summation will equal F net or as it is sometimes written, ma net. 1. Draw a free body diagram of a parachutist who . a. has just stepped out of the airplane, and is accelerating toward the ground. b. has opened her parachute and is traveling downward with constant velocity. 2. Draw a free body diagram of a brick. a. at rest on a table. b. being pushed with constant velocity along a rough horizontal surface. The free body diagram of a car traveling at a constant speed consists mainly of five forces, when considered in an actual situation. These vectors are that of friction, gravity, normal force, air resistance, and engine driving force. In a hypothetical situation without external forces (friction and air resistance), only the three remaining forces will act on the vehicle. To draw a free-body diagram, we draw the object of interest, draw all forces acting on that object, and resolve all force vectors into x– and y-components. We ...Net external force: →Fnet=∑→F=→F1+→F2+...Definition of weight, vector form: →w=m→gw...Newton’s second law, vector form: →Fnet=∑...Newton’s second law, component form: ∑→Fx...
A free body diagram models the forces acting on an object. The object or 'body' is usually shown as a box or a dot. The forces are shown as thin arrows pointing away from the centre of the box or ...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
by W Moebs · 2016 — The first step in describing and analyzing most phenomena in physics involves the careful drawing of a free-body diagram. Free-body diagrams have been used ...
Answer (1 of 5): What do you mean by 'constant velocity'? Everything in the universe is in the constant velocity. You take a glass of water and spill it on the floor. It looks at rest to you, but are at motion wrt the birds flying over your head. The birds are at rest wrt to each other and are at...
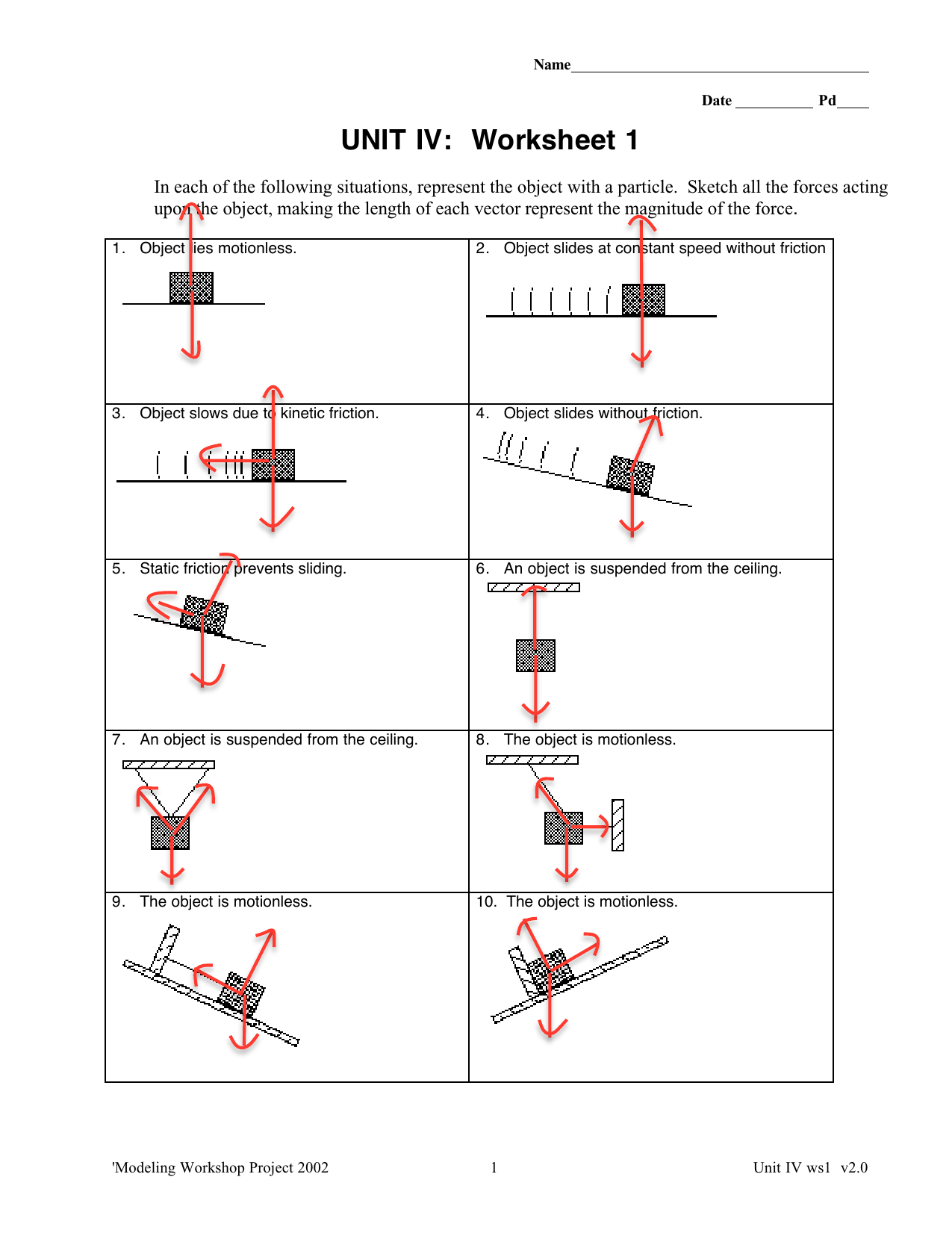
Construct free-body diagrams for the following physical situations. Label all forces (e.g, Fgrav, Fnorm, Fapp, Ffrict, Fair, Ftens, etc. ). a. A physics book rests upon a level table. b. A skydiver is falling and has reached a terminal velocity. c. A large crate is being pushed leftward at a constant velocity. d. A sledder has reached
Free body diagram. Weight, reaction force and friction for an object moving at constant speed down a hill. Drawing of situation. Free body diagram. Weight, upthrust, thrust and air resistance for ...
consistent with your constant velocity (of zero). The free-body diagram of the elevator is a bit more challenging. Let’s start by drawing a downward force of gravity and an upward tension force, which are the only forces that act on the elevator when the elevator is empty. Even though we draw what looks like an empty elevator, to construct the free-body diagram we have to remember that, in ...
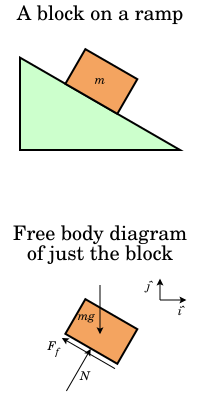
Finding Forces Acting Upon Objects On An Inclined Plane Or Ramp With Free Body Diagrams The Crafty Canvas Learning Library
Free Body Diagram - 941 Words | Cram. Show More. Check Writing Quality. Register to read the introduction…. Move the ramp to an angle of zero (horizontal) and draw a free body diagram of the cabinet here: On a horizontal plane, the normal force is _Perpendicular_______ to the weight. The cabinet has a mass of 100kg.
Why It Is Said That The Force Is Zero When Two Men Pushing A Box To Move In Contant Velocity Those Men Obviously Applying Force To Move It But It Iis Said
Free body diagram of a mountain biker up hill (5% grade) Biking up a hill over rugged terrain is strenuous on the body because of the change in forces due to the angle of the surface. As you increase the slope being traveled up, this significantly decreases the normal force which produces more of a pulling force.
A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: 6. A rightward force is applied to a book in order to move it across a desk at constant velocity. Consider frictional forces. Neglect air resistance. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: motionless by one strap from one shoulder. A free-body diagram for this situation ...
Explain the effects with the help of a free-body diagram. Use free-body diagrams to draw position, velocity, acceleration, and force graphs, and vice versa. Explain how the graphs relate to one another. Given a scenario or a graph, sketch all four graphs.
ball is the force of gravity, so the free-body diagram would be the same as in Figure 3.6. The successive locations of the ball on the motion diagram would also be the same, with the times increasing from bottom to top instead of from top to bottom. 3-3 Constant Velocity, Acceleration, and Force If an object is moving at constant velocity, is there a net force acting in the direction of motion ...
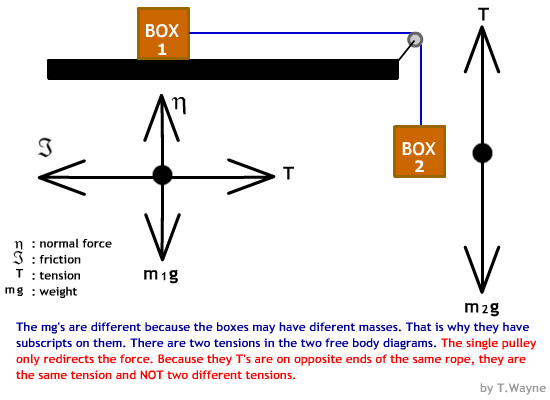
Example 8 : A system with two blocks, an inclined plane and a pulley. A) free body diagram for block m 1 (left of figure below) 1) The weight W1 exerted by the earth on the box. 2) The normal force N. 3) The force of friction Fk. 4) The tension force T exerted by the string on the block m1. B) free body diagram of block m 2 (right of figure below)
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
The constant velocity horizontal component of its projectile motion can be explained by drawing the free body diagram so that: there are no forces to the left or right OTHER SETS BY THIS CREATOR

The Physics Classroom New At The Physics Classroom Match That Free Body Diagram We Re Pleased To Announce That We Just Completed Another Concept Builder Titled Match That Free Body Diagram The Match
11. Free-Body Diagram Draw a free-body dia-gram of a bag of sugar being lifted by your hand at a constant speed. Specifically identify the system. Label all forces with their agents and make the arrows the correct lengths. 12. Direction of Velocity If you push a book in the forward direction, does this mean its velocity has to be forward?
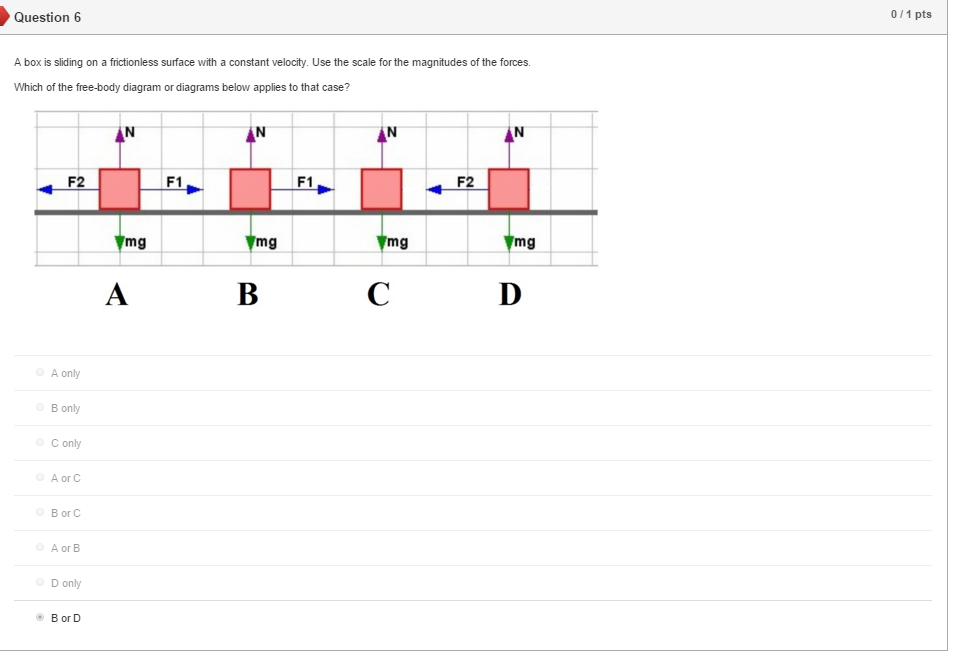
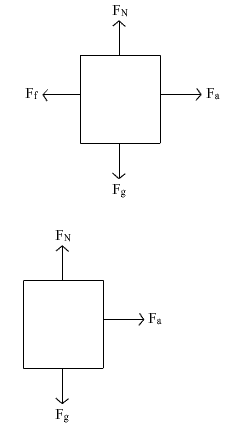
A free-body diagram is a sketch showing an object and all of the forces being exerted on it. ... Constant Velocity: A box is moving at constant velocity to the right. Which free-body diagram is correct? mg down and N up mg down, N up, some other force F to the right mg down, N up, equal-and-opposite forces left and right could be 1 or 3 In both cases above, mg and N are equal in magnitude and ...
Free Body Diagrams Practice Problems Construct free-body diagrams for the various situations described below. Use the following forces. 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. 2. A girl is suspended motionless from a bar which hangs from the ceiling by two ropes. Diagram the forces acting on the girl. 3.
free body diagrams. used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting on an object. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. A flying squirrel is gliding (no wing flaps) from a tree to the ground at constant velocity. Consider air resistance.

A Person Pushes A Crate So That It Moves At Constant Velocity Towards The Right A Free Body Diagram For The Crate Is Shown Below The Picture The Arrows Are Not Necessarily
Free Body Diagrams a.k.a. Force Diagrams ... Constant Velocity Balanced forces. Could be at rest or moving left, right, up or down. Experiencing an Acceleration Unbalanced forces Can't tell which way it is moving, can only say which way it is experiencing an acceleration. Accelerating to the right.

Force Problems A Car Is Traveling At Constant Velocity With A Frictional Force Of 2000 N Acting Opposite The Motion Of The Car The Force Acting On The Ppt Download
So, the free-body diagram of the object will look something like this: ... Remember that whenever an object is either at rest or moving at constant velocity, the resultant force acting on the object is 0. When you have two independent equations with two unknowns, you can solve them in different ways. Usually we tend to solve one of the two equations for one unknown, and substitute the result ...
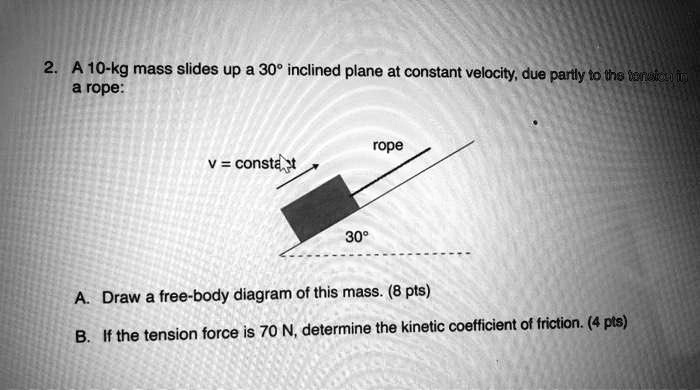
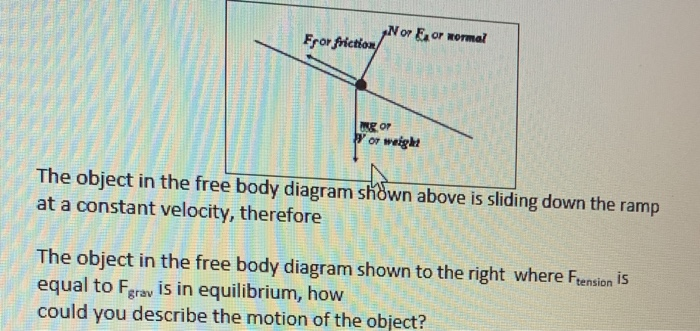
Solved A 10 Kg Mass Slides Up A 30 Inclined Plane At Constant Velocity Due Parlly To Tho Tersae Rope Rope Consta U 309 Draw A Free Body Diagram Of This Mass 8 Pts If
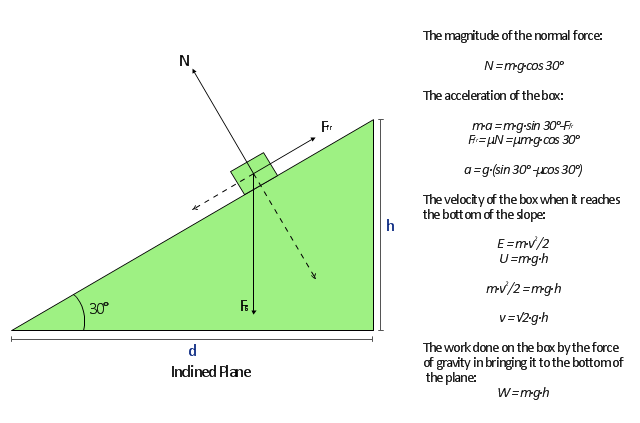
Free Body Diagram How To Draw Physics Diagrams In Conceptdraw Pro Physics Concept Of Free Body Diagram
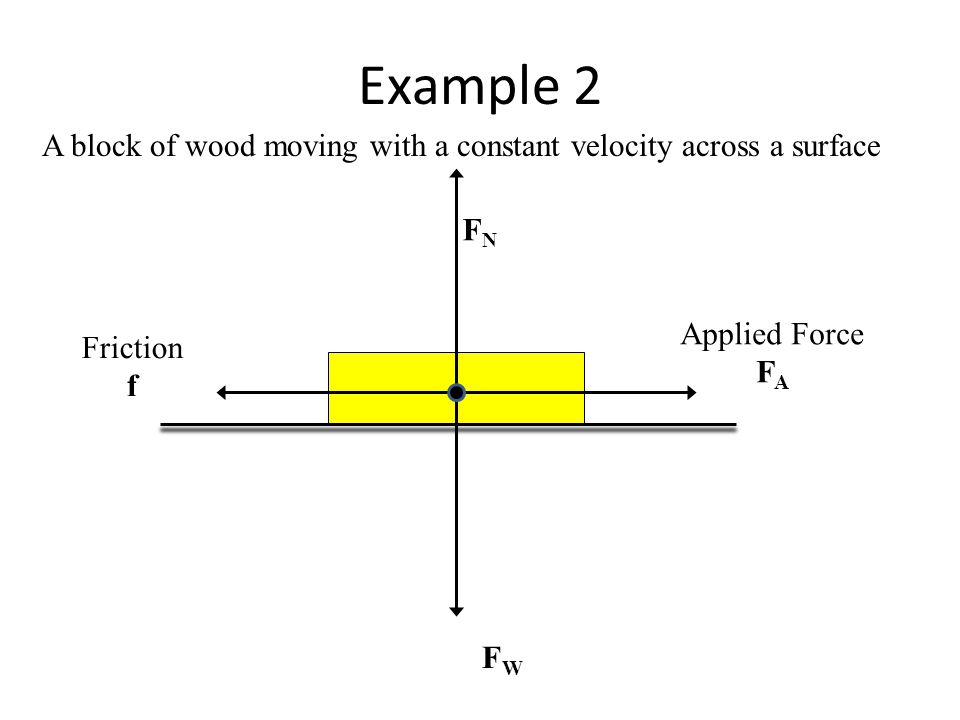
Free Body Diagrams A Free Body Diagram Fbd Is A Visual Representation Of All The Forces Acting On A Single Object Fbds Are Extremely Powerful Problem Ppt Video Online Download
6 A Person Pushes A 16 0 Kg Shopping Cart At A Constant Velocity For A Distance Of 22 0 M She Pushes In A Direction 29 0 Below The Horizontal A 48 0 N Frictional Force Opposes The Motion Of The Cart A What Is The Magnitude Of The Force That The Shopper












0 Response to "41 free body diagram constant velocity"
Post a Comment