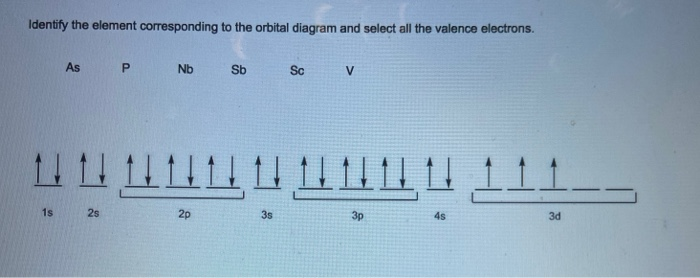
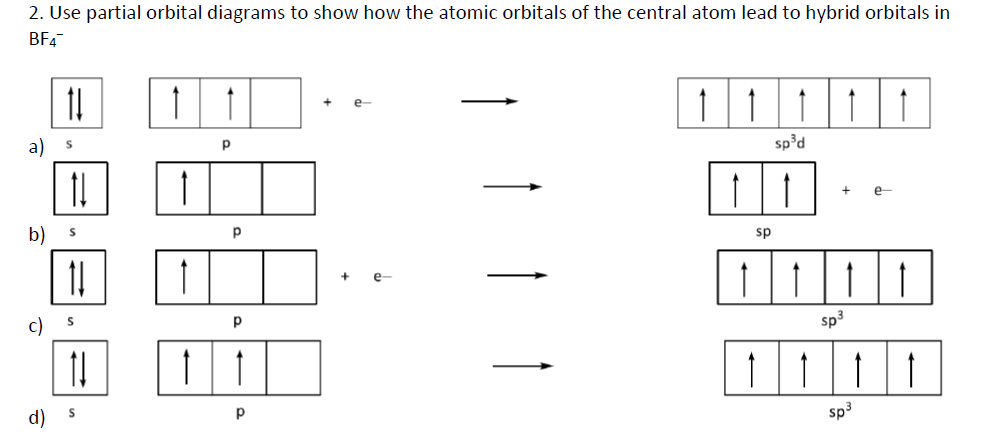
40 orbital diagram for as
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine What is the orbital diagram of CO 27? What is the electronic configuration of 27? Which of the following is the electron configuration for the element with the atomic number 27? What is the approximate mass of an atom that contains 27 protons 27 electrons and 32 neutrons? What is the charge of Al 27? How many electrons does al 27 have?
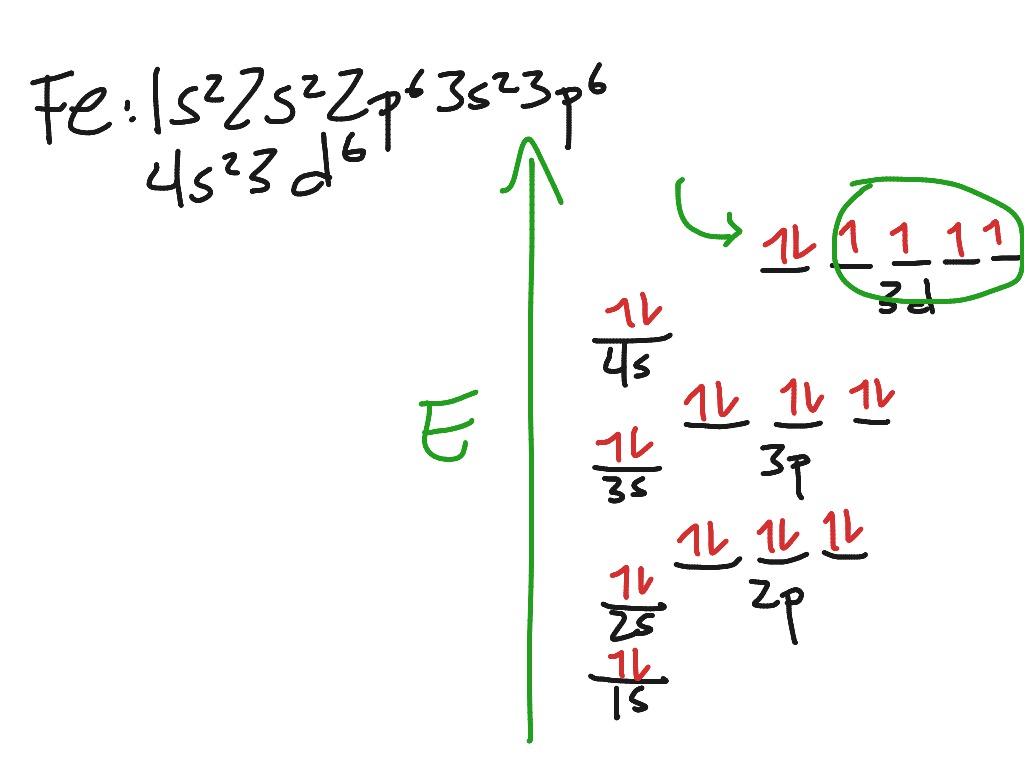
Table 8.3 Partial Orbital Diagrams and Electron Configurations * for the Elements in Period 4. * Colored type indicates the sublevel to which the last electron is added. 8-26. Figure 8.10 A periodic table of partial ground- state electron configurations. 8-27. Figure 8.11.
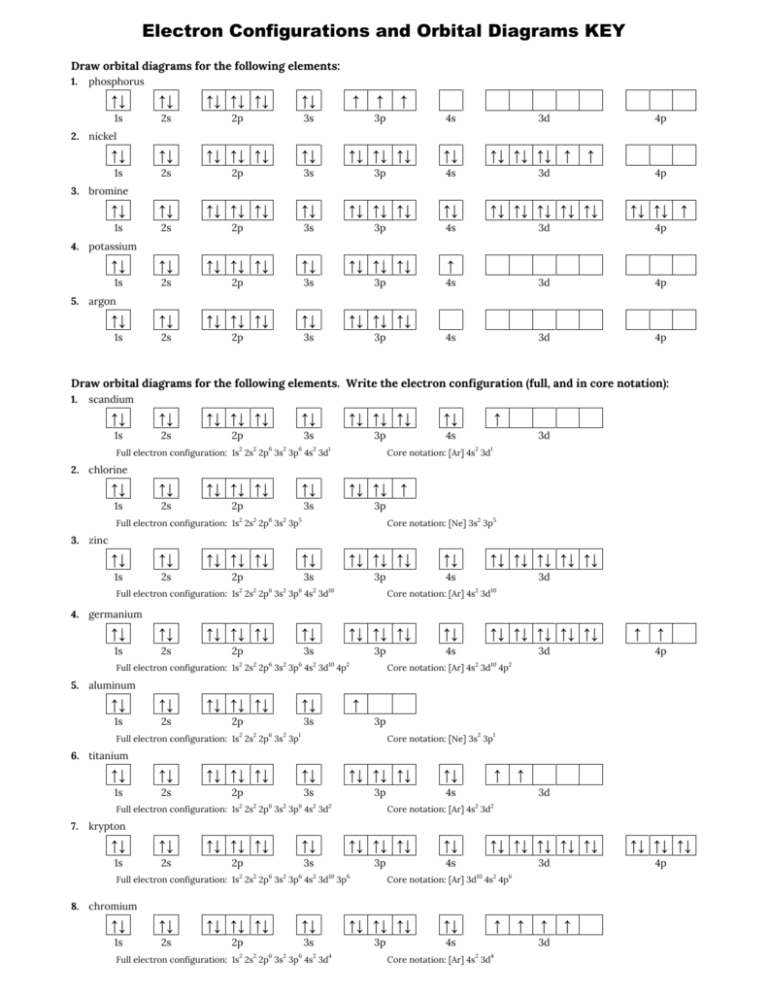
Orbital diagram for as
An orbital box diagram can be written as well. Boxes, or horizontal lines represent the orbitals, arrows represent the electrons, and if an orbital is full, the electrons must be of opposite spin-one arrow pointing up and the other one pointing down. The orbital box diagrams are listed for the first 20 elements in the figure below. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... The orbital diagram for hydrogen can be represented in the following way. This notation uses a box to represent the orbital, the label for the orbital and an arrow to represent the electron. The electronic configuration for hydrogen can be written as 1s 1. This is a short-hand notation which identifies the level, the sublevel and the number of ...
Orbital diagram for as. Simple pictures showing orbital shapes are intended to describe the angular forms of regions in space where the electrons occupying the orbital are likely to be found. The diagrams cannot show the entire region where an electron can be found, since according to quantum mechanics there is a non-zero probability of finding the electron (almost ... Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: The Aufbau principle, the Pau... An orbital filling diagram is the more visual way to represent the arrangement of all the electrons in a particular atom. In an orbital filling diagram, the individual orbitals are shown as circles (or squares) and orbitals within a sublevel are drawn next to each other horizontally. In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for ...
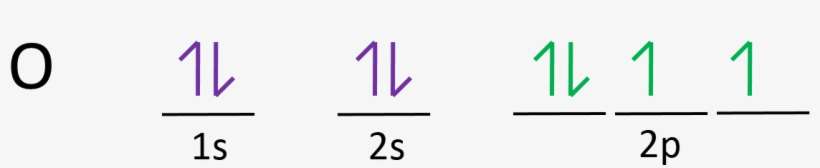
Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 7.7.9). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. What is the correct orbital diagram for arsenic? Electrons & Oxidation. Oxidation States. ±3,+5. Electrons Per Shell. 2 8 18 5. Electron Configuration. [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3. Energy-Level Diagrams. Because electrons in the σ 1 s orbital interact simultaneously with both nuclei, they have a lower energy than electrons that interact with only one nucleus. This means that the σ 1 s molecular orbital has a lower energy than either of the hydrogen 1s atomic orbitals. Conversely, electrons in the \( \sigma _{1s}^{\star } \) orbital interact with only one hydrogen ... The electron configuration for oxygen is: 1s^2 2s^2 2p^4 This video will walk you through the step of writing orbital diagram. The video uses Kr as an example, but the process is exactly as the same as what you need to do for oxygen. Hope this helps!
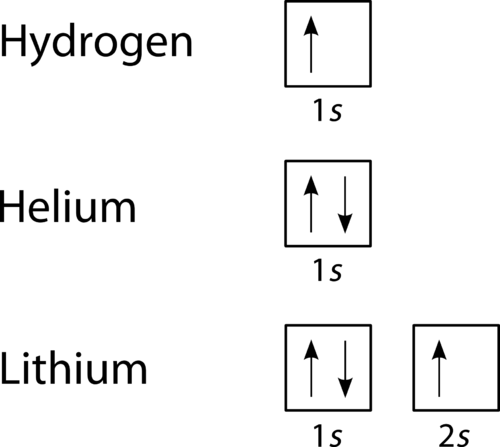
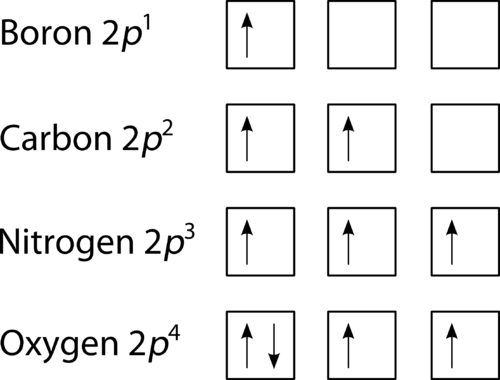
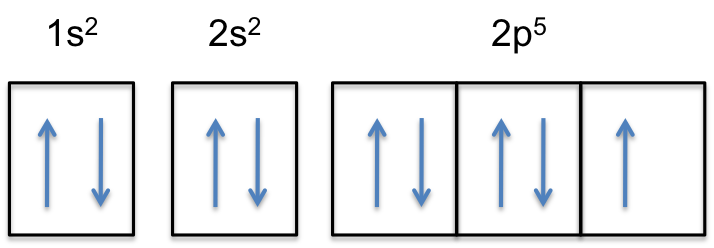
The orbital filling diagram for helium. The electron configuration for helium is 1s². This means that we have two electrons in the 1s orbital, which looks like this: This diagram is exactly the same as the one for hydrogen, except that there's a second arrow added to the 1s orbital. This represents the second electron in the 1s orbital, and ... Construct the orbital diagram for As. First, we need to determine the electron configuration for As (arsenic). The electron configuration depends on the number of electrons an atom or ion has. Since As is neutral (uncharged), we can say that Z (atomic number) = number of protons = number of electrons. Arsenic has an atomic number of 33, so it ... Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8. Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9. Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10. Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11. Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na) Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom
It is common to omit the core electrons from molecular orbital diagrams and configurations and include only the valence electrons. Figure 8. This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be 2 +, showing the molecular orbitals of the valence shell only. The molecular orbitals are filled in the same manner as atomic orbitals ...

Woodward Hoffmann Rules Molecular Orbital Diagram Atomic Orbital Cycloaddition Molecular Orbital Diagram Angle Text Png Pngegg
Molecular Orbital Diagrams This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 + . Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic ...
Part C Electron configurations are a shorthand form of an orbital diagram, describing which orbitals are occupied for a given element. For example, 1s22s22p1 is the electron configuration of boron. Use this tool to generate the electron configuration of arsenic (As).
An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration. (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s. →. 2s.
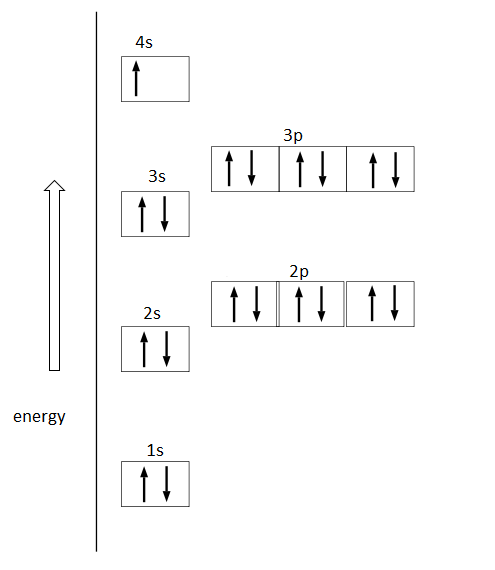
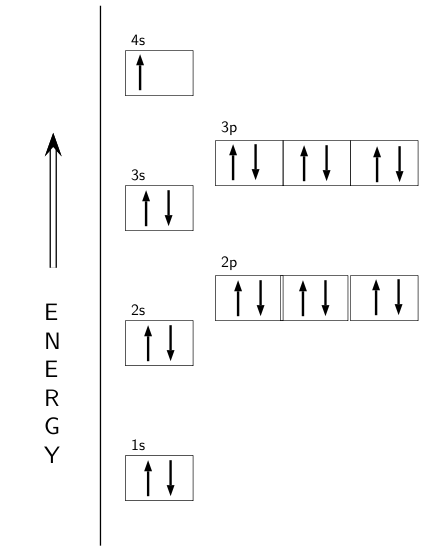
So the electron configuration of potassium will involve 19 electrons. The full electron configuration of potassium is "1s"^2"2s"^2"2p"^6"3s"^2"3p"^6"4s"^1". The noble gas notation is "[Ar]4s"^1". The following orbital diagram shows the increase in energy from one energy sublevel to the next, but you can write them on the same level horizontally,
Orbital Diagram For Arsenic. Because the 4p section has 3 orbitals, but Arsenic ends with 4p3. It'll want to leave as few orbitals empty, so you have three arrows pointing up. The orbital diagram of arsenic can be written as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 4s2 3d10 4p3. Arsenic has 33 electrons, including 3 in itsoutermost shell. schematron.org!
An orbital diagram is similar What is the orbital diagram for. For example, write the electron configuration of scandium, Sc: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 1. So for scandium the 1 st and 2 nd electron must be in 1s orbital, the 3 rd and 4 th in the 2s, the 5 th through 10 th in the 2p orbitals, etc. 6/14/ Ch 8 4/18 Correct Part B Complete ...
The molecular orbital diagrams of , and are drawn in the attached image. There is no unpaired electron present in the MO diagram of and all the electrons are paired up so it is diamagnetic in nature. There is one unpaired electron present in the MO diagram of and therefore it is paramagnetic in nature.
Answer (1 of 3): Orbital Diagrams Many times it is necessary to see all the quantum numbers in an electron configuration, this the purpose of the orbital diagram. In addition to listing the principle quantum number, n, and the subshell, ℓℓ, the orbital diagram shows all the different orientation...
In an orbital diagram, such as the one below, each small box represents which of the following? Select the correct answer below: a shell a subshell an individual orbital an individual electron. an individual orbital. The electrons in the outermost shell of an atom are called:
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. It explains how to write the orbital diagram n...

Difference Between Orbital Diagram And Electron Configuration Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
The orbital diagram for hydrogen can be represented in the following way. This notation uses a box to represent the orbital, the label for the orbital and an arrow to represent the electron. The electronic configuration for hydrogen can be written as 1s 1. This is a short-hand notation which identifies the level, the sublevel and the number of ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
An orbital box diagram can be written as well. Boxes, or horizontal lines represent the orbitals, arrows represent the electrons, and if an orbital is full, the electrons must be of opposite spin-one arrow pointing up and the other one pointing down. The orbital box diagrams are listed for the first 20 elements in the figure below.

Solved Draw A Partial Valence Level Orbital Diagram And Write The Condensed Ground State Electron Configuration For Each Begin Array Ll Text A Mathrm Mn Text B Mathrm P Text C Fe End Array
The Orbital Diagram In Which The Aufbau Principle Is Violated Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




















0 Response to "40 orbital diagram for as"
Post a Comment