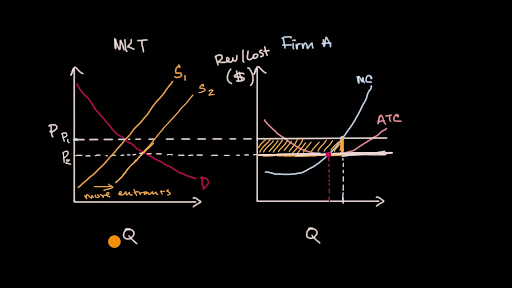
40 if the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will
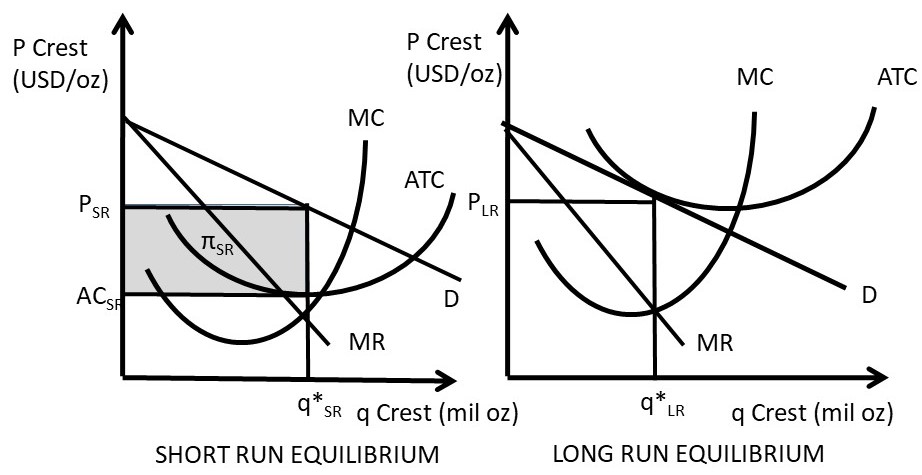
2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Which of the following is ...
in the provided diagram, the short run supply curve for this firm is the ... if the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will.

If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will
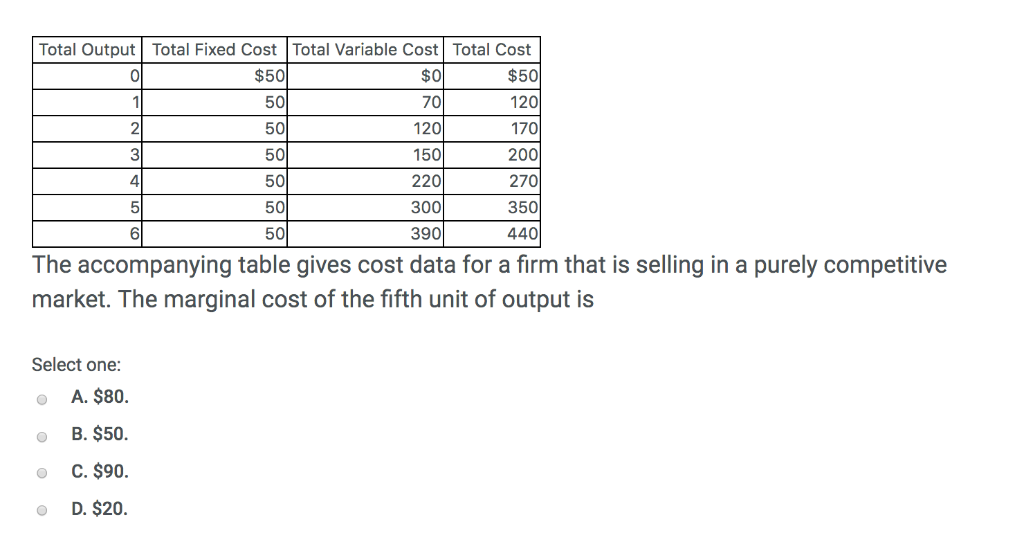
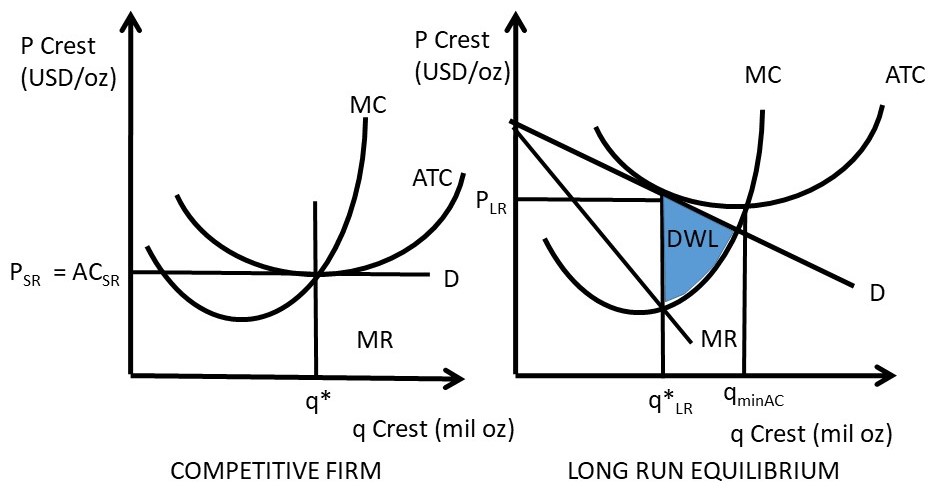
26) Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is P1, the profit-maximizing firm in the short run should A) produce output A. B) produce output B. C) produce output C. D) produce output D or shut down as it doesnʹt really matter which. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: a. suffer an economic loss. b. earn a normal profit. c. earn an economic profit. d. achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: a. suffer an economic loss. b. earn a normal profit. c. earn an economic profit. d. achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. b. earn a normal profit. Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q: a. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved.
If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: A. suffer an economic loss.B. earn a normal profit. C. earn an economic profit.D. achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency. Chapter 09 - Pure Competition in the Long Run 55. If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will suffer an economic loss. earn a normal profit. earn an economic profit. achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, ... If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents ... If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will:. Rating: 5 · 1 review
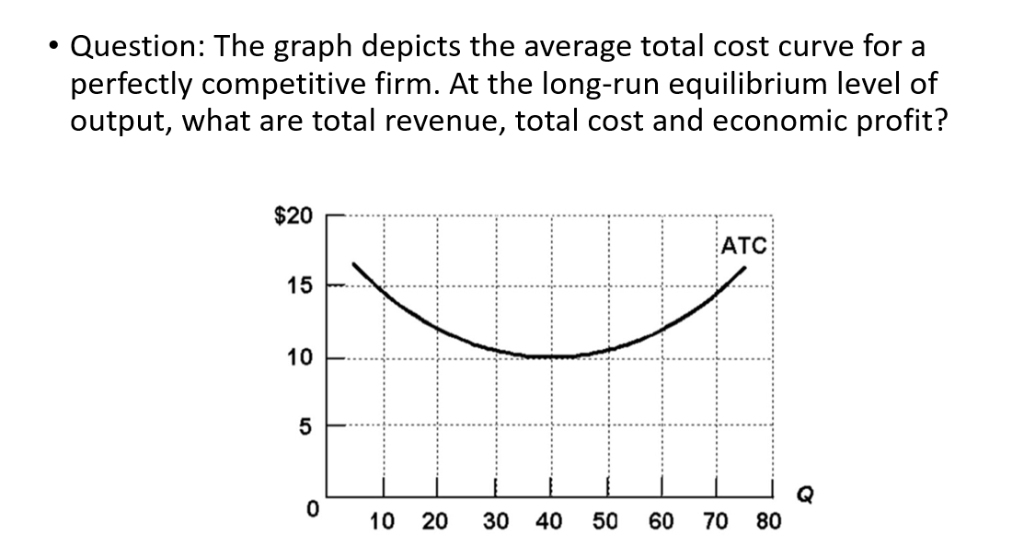
Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. In the long run we should expect. firms to leave the industry, market supply to fall, and product price to rise. ... If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will. earn a normal profit. If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will. earn a normal profit. Marginal cost is _____. (TVC+TFC)/Q. The diagram shows the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue ... Refer to the provided graph for a purely competitive firm ... In the competitive firm, the firm sets… View the full answer Transcribed image text : 6 MC ATC Price MR 00:45:49 Q, Q Quantity If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will Multiple Choice suffer an economic loss. achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. earn an economic profit. View Homework Help - ECONHW12Sols19.pdf from ECOP 1003 at The University of Sydney. 60. Award: 1.00 point If the competitive rm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will suffer an economic
If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: a. suffer an economic loss. b. earn a normal profit. c. earn an economic profit. d. achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. b. earn a normal profit. Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q: a. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: a. suffer an economic loss. b. earn a normal profit. c. earn an economic profit. d. achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency. 26) Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is P1, the profit-maximizing firm in the short run should A) produce output A. B) produce output B. C) produce output C. D) produce output D or shut down as it doesnʹt really matter which.

The Dynamics Of Green Supply Chain Management Within The Framework Of Renewable Energy Gawusu International Journal Of Energy Research Wiley Online Library

Wages Profitability And Growth In A Small Open Economy In Imf Staff Papers Volume 1991 Issue 004 1991

Education Sciences Free Full Text The Index Number Problem With Dea Insights From European University Efficiency Data Html
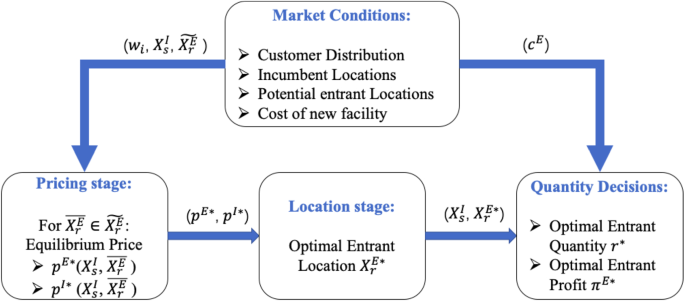
Quantity Decisions Of Two Stage Competitive Location Model Based On Different Location Modes Springerlink

Wages Profitability And Growth In A Small Open Economy In Imf Staff Papers Volume 1991 Issue 004 1991
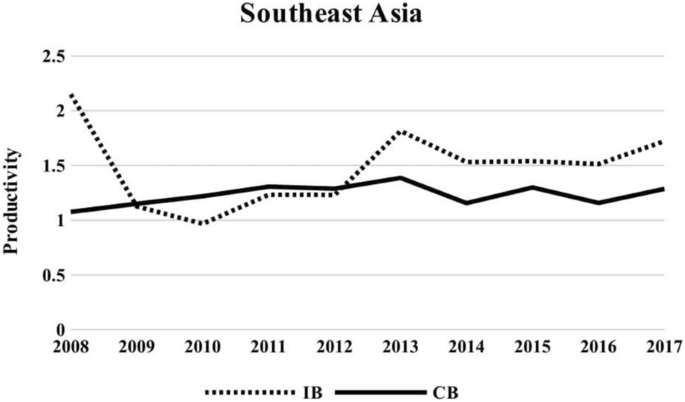
Do Islamic Versus Conventional Banks Progress Or Regress In Productivity Level Future Business Journal Full Text
Value Co Creation In Firm Sponsored Online Communities What Enables Constrains And Shapes Value Emerald Insight

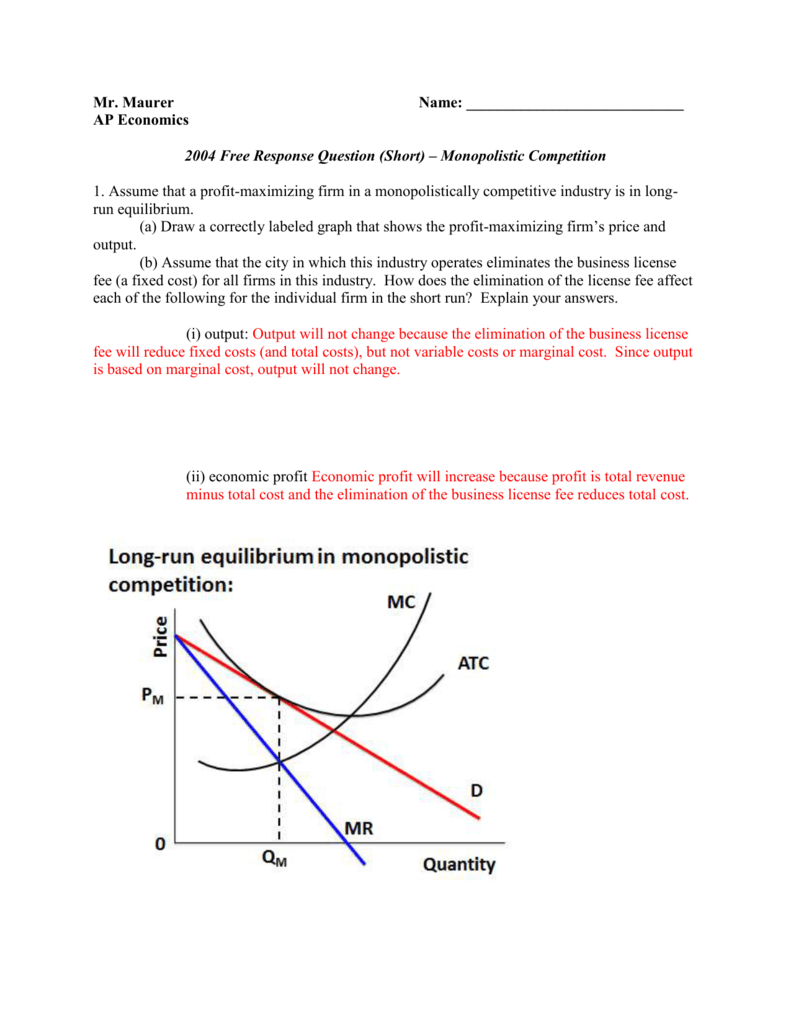

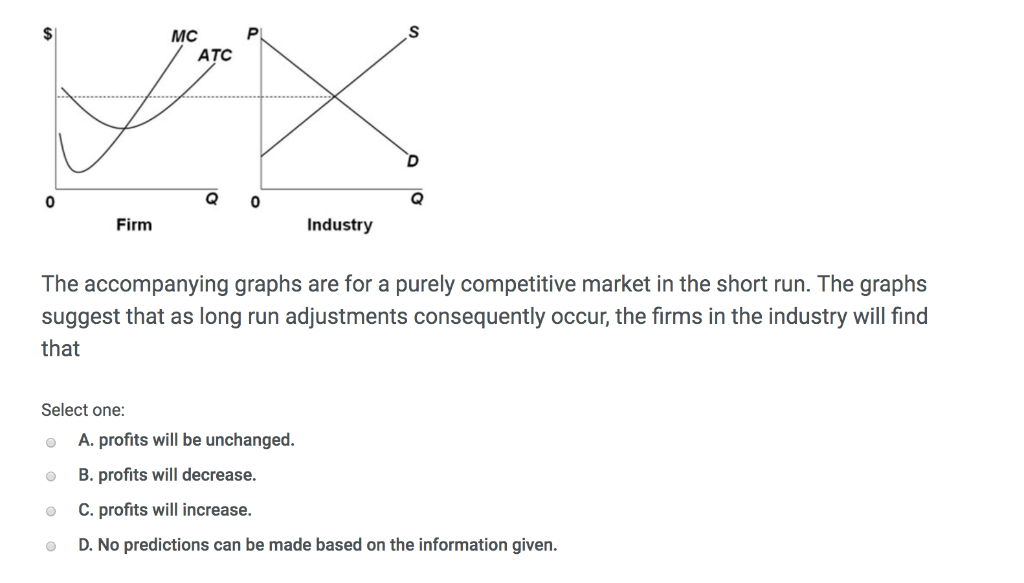













0 Response to "40 if the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will"
Post a Comment