39 free body diagram of block on incline
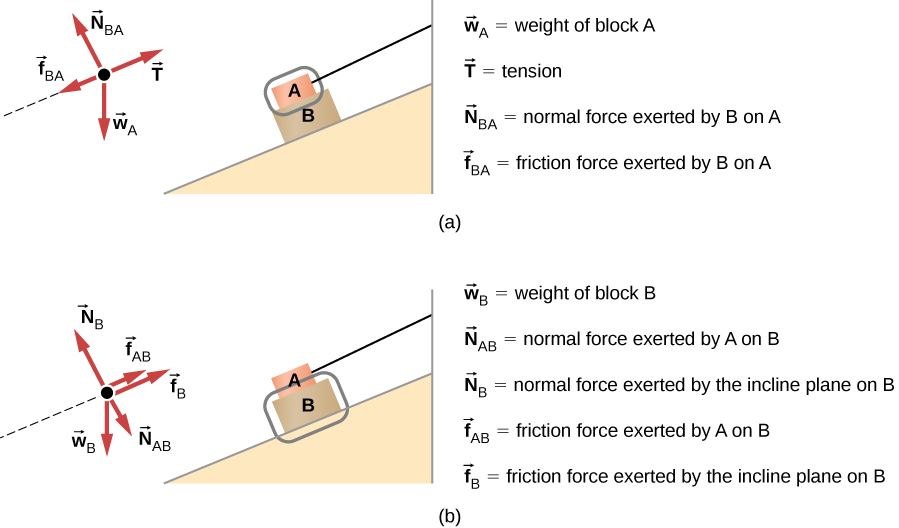
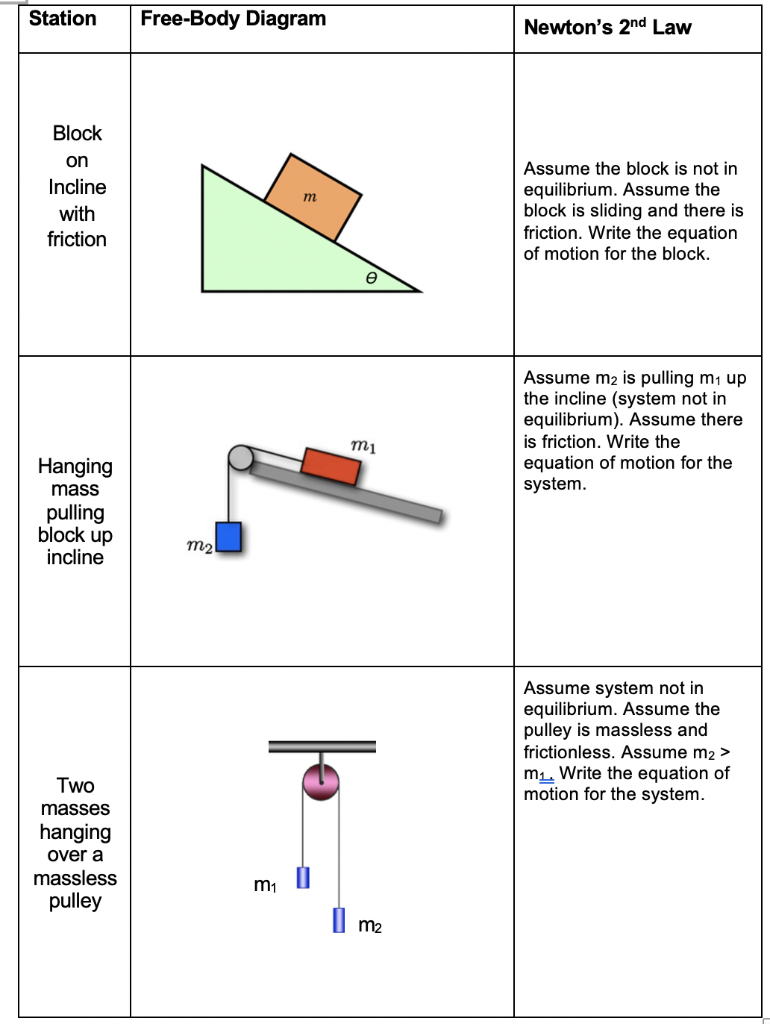
by W Moebs · 2016 — Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane. Construct the free-body diagram for object A and object B in (Figure). Strategy. We follow the four steps listed in ... Free-body diagram s are diagram s used to show the rel at ive magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situ at ion. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagram s th at were d is cussed in an earlier unit. The se diagram s will be used throughout our study of physics.
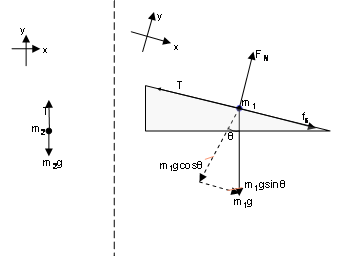
Solution: First of all, draw a free-body diagram and specify all forces acting on the block. The object does not move in the vertical direction so Newton's second law gives us the magnitude of the normal force exerted by the surface \[F_N-mg=0 \Rightarrow F_N=mg=20\,{\rm N}\] We don't know whether the block moves or not.
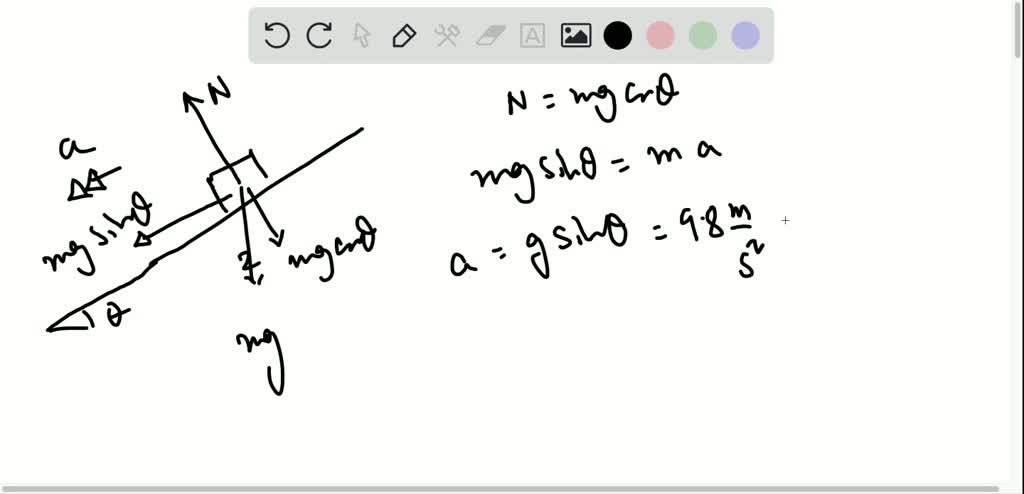
Free body diagram of block on incline
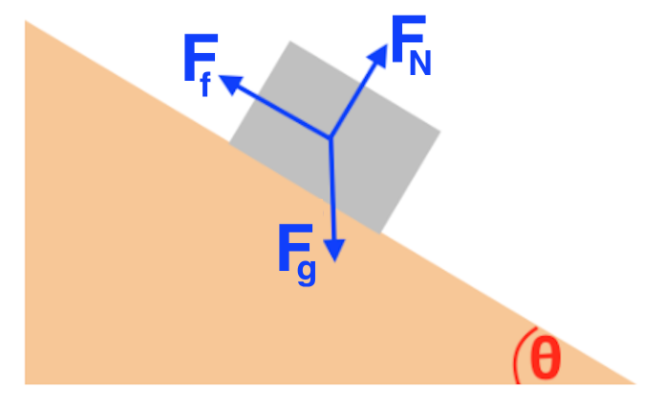
A block slides down a rough ramp with a 30-degree incline as shown. A diagram of a block on a 30 degree incline. Which diagram represents the forces acting on the block? A free body diagram with three forces: a force vector northeast labeled F Subscript N Baseline, a force vector southeast labeled F Subscript … Continue reading "A block slides down a rough ramp with a 30-degree incline as shown. There is a free body diagram drawn on a block on a 50-degree incline with 3 force vectors. The first vector is pointing away from the surface of the incline and perpendicular to the surface, labeled F Subscript N Baseline. The second vector is pointing into and perpendicular to the surface of the incline, labeled … In a free-body diagram (FBD), you have to decide what the "body" is. In any physical situation, you can draw many free-body diagrams... some are more useful to answering questions you may have. ... Blocks stacked on an incline connected by rope around pulley. 1. Rotating platform with pulleys and stacked blocks. 2. Free body diagram of this ...
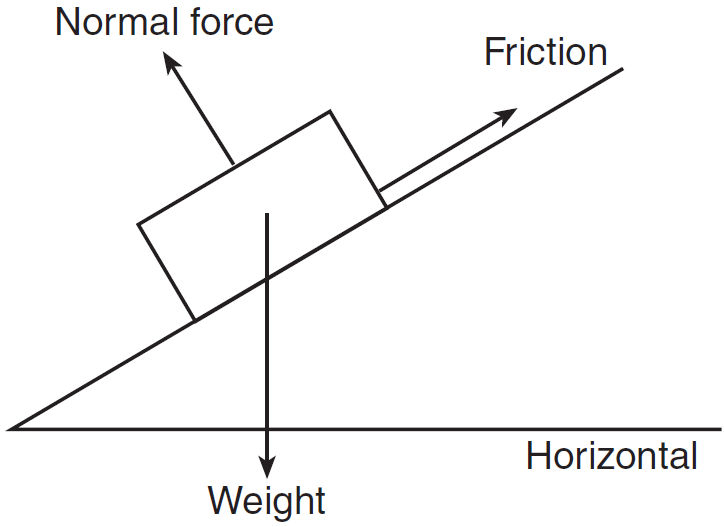
Free body diagram of block on incline. FIGURE 1 Step 1 of 19 (a) The figure below shows the free-body diagram of the block on the inclined. Coordinate axes are shown in red, along and perpendicular to the plane. The sine component of the weight of the block provides the pulling force on the block down the incline, and the cosine component of the weight gives rise to the normal force ... There is a free body diagram drawing on a block on a 22 degree incline with 5 force vectors. The first force is pointing up and parallel to the surface of the incline, labeled F Subscript T Baseline. The second force is pointing down and parallel to the surface of the incline, labeled F Subscript f Baseline = 14.8 N. The free body diagram of a car traveling at a constant speed consists mainly of five forces, when considered in an actual situation. The se vectors are that of friction, gravity, normal force, air resistance, and engine driving force. Draw a free-body diagram. (Neglect air friction) The force of gravity is the only force described. (no air ... Aug 19, 2015 — c. has two vector forces directed down the incline, but only of which is is cancelled. d. is tricky. There is a unbalanced force going into the ...2 answers · Top answer: In (d), the net force on the object is into the plane, and so it should be accelerating through ...
For T₂, its free-body diagram shows us it is only responsible for the mass of m₂, we can say that T₂ = a * m₂. With that said, T₂ = (2.4 m/s²) * (2 kg) = 4.8 N . On the other hand, T₁ is the tension force that pulls both the weight of m₁ and m₂. There is a free body diagram drawn on a block on a 50-degree incline with 3 force vectors. The first vector is pointing away from the surface of the incline and perpendicular to the surface, labeled F Subscript N Baseline. The second vector is pointing into and perpendicular to the surface of the incline, labeled F Subscript g y Baseline. A block lies on a smooth inclined plane tilted at an angle of 35 to the horizontal. a) Draw the free-body diagram for the block. b) Determine the block's acceleration as it slides down the inclined plane. Math/Physics2. The block has mass m=8.5 kg and lies on a fixed smooth frictionless plane tilted at an angle theta=20.0 degrees to the ... 14+ Free Body Diagram Examples. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of. A box is pushed up an incline with friction which makes an angle of 20° with the horizontal. This makes it easier to understand the forces, and allows us to analyse the stresses within the object.
We can see how this presents a problem by using a free-body diagram to illustrate the forces. ... so 3465 N down the incline. ... A block of mass m1=22kg is at rest on a plane inclined at \theta ... Block on a ramp. A 5.0 kg block slides down an incline of 22° at a constant velocity. Show a free body diagram of the block and determine the coefficient of kinetic friction. A box is pulled up a rough ramp that makes an angle of 22 degrees with the horizontal surface. The surface of the ramp is the x-plane.There is a free body diagram drawing on a block on a 22 degree incline with 5 force vectors. The first force is pointing up and parallel to the surface of the incline, labeled F Subscript T Baseline. How to write Newton's second law for forces on an incline. 1) Draw a free body diagram for the object (see Figure 3). Remember to rotate the coordinate axes to ...
A block lies on a smooth inclined plane tilted at an angle of 35 to the horizontal. a) Draw the free-body diagram for the block. b) Determine the block's acceleration as it slides down the inclined plane. 👍.
Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane. Construct the free-body diagram for object A and object B in (Figure). Strategy. We follow the four steps listed in ...
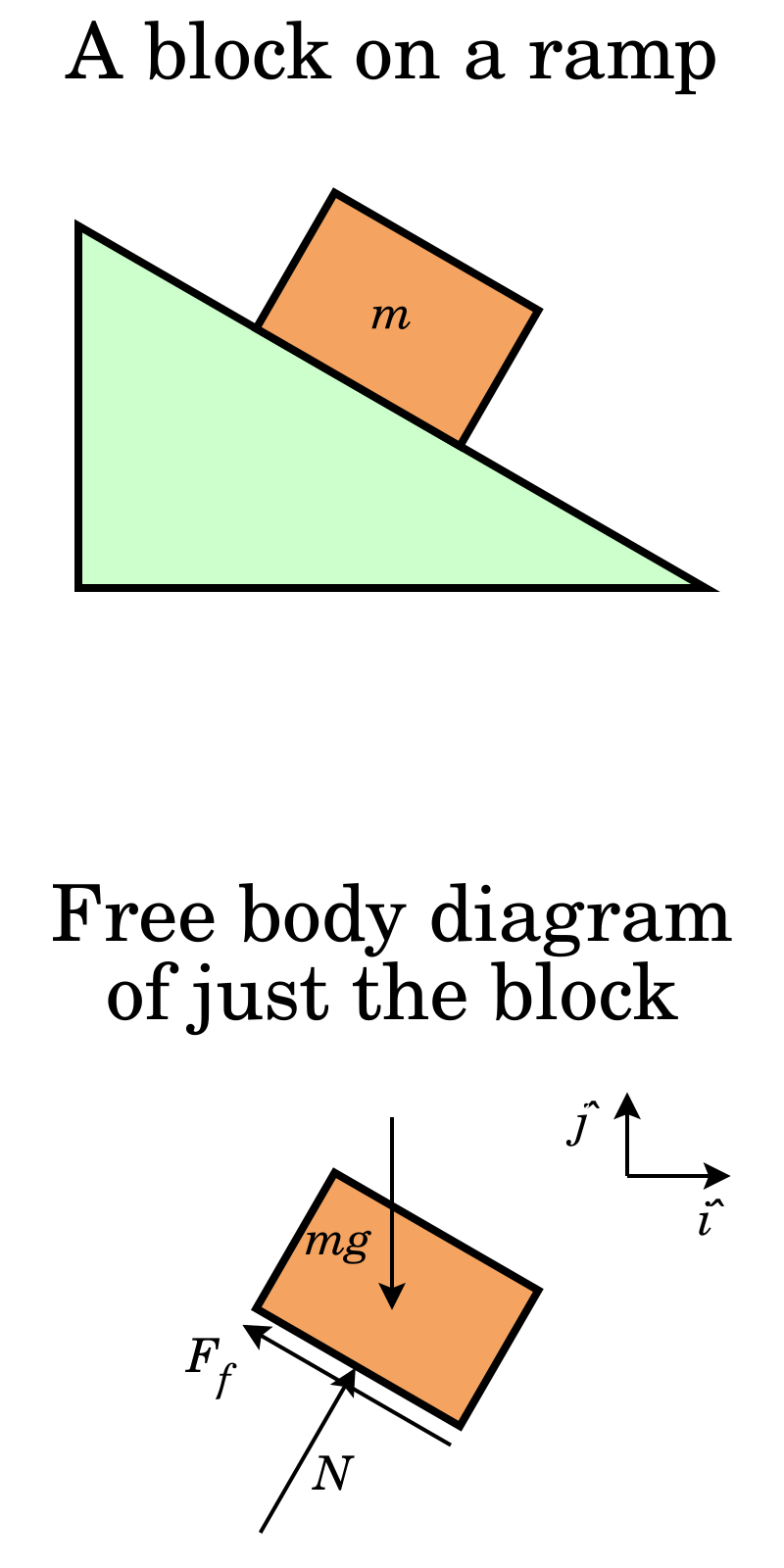
Day #: Free-body diagrams of an object on an incline. By the end of this unit students should be able to draw complex free body diagrams of objects on an incline. Demo: Inclined plane and block. Whenever you have an object sitting on a surface you always have two forces acting on it.
I have attached a picture file and a free-body diagram file for this problem. Determine the friction force acting on the block shown when the angle is 30 degrees and P=200N. us=0.3 (static friction) uk=0.2 (kinetic friction) The free-body diagram is how I started this solution. My equations became: Fx=0=200-Ncos(60)-fcos(30) Fy=0=-1000-fsin(30 ...
Its free body diagram is as shown below. Assume that the force applied on the incline and surface produces an acceleration 'a' so that there is a pseudo force (of magnitude 'ma') acting on the smaller block. The magnitude of normal reaction is equal to the total force acting normally at the contact surface between two solids. Share. Cite.
Question #267690. For the system of two blocks on a frictionless double incline where the blocks are linked by an inextensible massless string over a frictionless pulley (see figure), (a). Draw the free body diagram for m 1 and m 2. (b). Express the equations of motion of the two blocks using Newton's Laws. (c).
As shown in the diagram, there are always at least two forces acting upon any object that is positioned on an inclined plane - the force of gravity and the ...
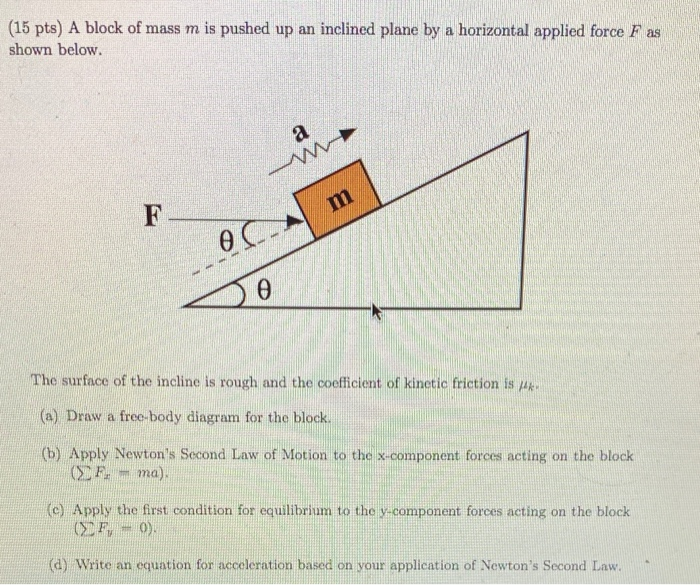
Answers: 2 on a question: A block of mass m = 5.8 kg is pulled up 37 incline as in Figure with a force of magnitude F = 32 N. (a) Draw a free-body diagram. (b) Find the acceleration of the block if the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and incline is 0.1.
A 5 N force is applied to the 5 kg block at 30° to the horizontal as shown in the diagram below. 2.1 Write down Newton's Second Law of motion in words. (2) 2.2 Draw a free-body diagram of all forces acting on the 5 kg block. (5) 2.3 The coefficient of kinetic friction (µk) between the 5 kg block and the surface is 0,2.
Free-Body Diagrams 4:34 ... Given the coefficient of static friction between the box and the incline, Two blocks of mass M = 10 kg and m = 8 kg and a spring with spring constant k = 150 N/m are ...
The forces acting on the lower block (1) Its weight W1 = 50 lbs (2) Normal reaction of the surface N1 (3) Tension of the strut T (4) Applied force P (5) The limiting friction force F1 = N1 The free body diagram is shown in the figure. As the block is in limiting equilibrium, net force in horizontal direction should be zero.
Answer: To create constant velocity through an inclined plane, force acting on the body should be zero. In presence of gravity only, if the upward frictional force between the surface & body is equal to the downward pull & object is pushed downwards initially, then it will continue to move down ...
A diagram of a block on a 30 degree incline. Which diagram represents the forces acting on the block? A free body diagram with three forces: a force vector northeast labeled F Subscript N Baseline, a force vector southeast labeled F Subscript f Baseline, and a force vector south labeled F Subscript g Baseline.
Let's apply the problem-solving strategy in drawing a free-body diagram for a sled. In Figure 6.8. 1 a, a sled is pulled by force P → at an angle of 30°. In part (b), we show a free-body diagram for this situation, as described by steps 1 and 2 of the problem-solving strategy. In part (c), we show all forces in terms of their x- and y ...
A body of mass 2 kg is lying on a rough inclined plane of inclination 30°. Find the magnitude of the force parallel to the incline needed to make the block move (a) up the incline (b) down the incline. Coefficient of static friction = 0.2.
A 3.0 kg block is pushed 3.0 m at a constant velocity up a vertical wall by a constant force applied at an angle of 29.0 degrees with the horizontal, … as shown in the figure. The acceleration of gravity is 9.81 m/s^2 Part A: If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the wall is 0.20, find the work done by the force on the ...
In a free-body diagram (FBD), you have to decide what the "body" is. In any physical situation, you can draw many free-body diagrams... some are more useful to answering questions you may have. ... Blocks stacked on an incline connected by rope around pulley. 1. Rotating platform with pulleys and stacked blocks. 2. Free body diagram of this ...
There is a free body diagram drawn on a block on a 50-degree incline with 3 force vectors. The first vector is pointing away from the surface of the incline and perpendicular to the surface, labeled F Subscript N Baseline. The second vector is pointing into and perpendicular to the surface of the incline, labeled …
A block slides down a rough ramp with a 30-degree incline as shown. A diagram of a block on a 30 degree incline. Which diagram represents the forces acting on the block? A free body diagram with three forces: a force vector northeast labeled F Subscript N Baseline, a force vector southeast labeled F Subscript … Continue reading "A block slides down a rough ramp with a 30-degree incline as shown.






















0 Response to "39 free body diagram of block on incline"
Post a Comment