37 diagram of a eukaryotic cell
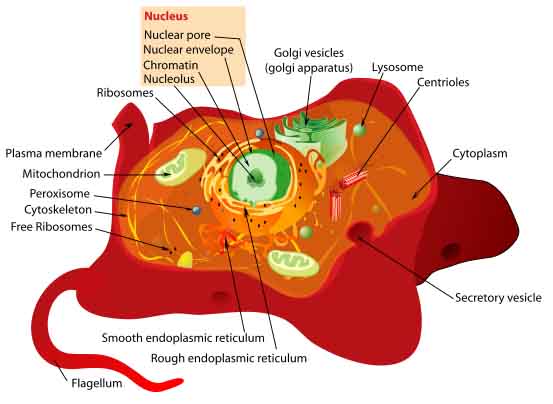
May 15, 2021 · Figure: Diagram of Ribosome, created with biorender.com Structure of Ribosomes. Ribosomes are made up of ribosomal proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). In a eukaryotic cell, ribosomes constitute half ribosomal RNA and half ribosomal proteins. Each ribosome is made up of two subunits i. e large subunit and small subunit with their own distinct shapes. a) Eukaryotic Animal cell b) Eukaryotic Plant cell c) Prokaryotic Bacterial cell d) Eukaryotic Fungal cell 2. In the figure, numbered '4' is the site in the cell which is analogous to “waste bin”. Identify the organelle a) Lysosome b) Nucleus c) Vacuole d) Chloroplast 3. This organelle is the “commanding centre of the cell’’ where ...
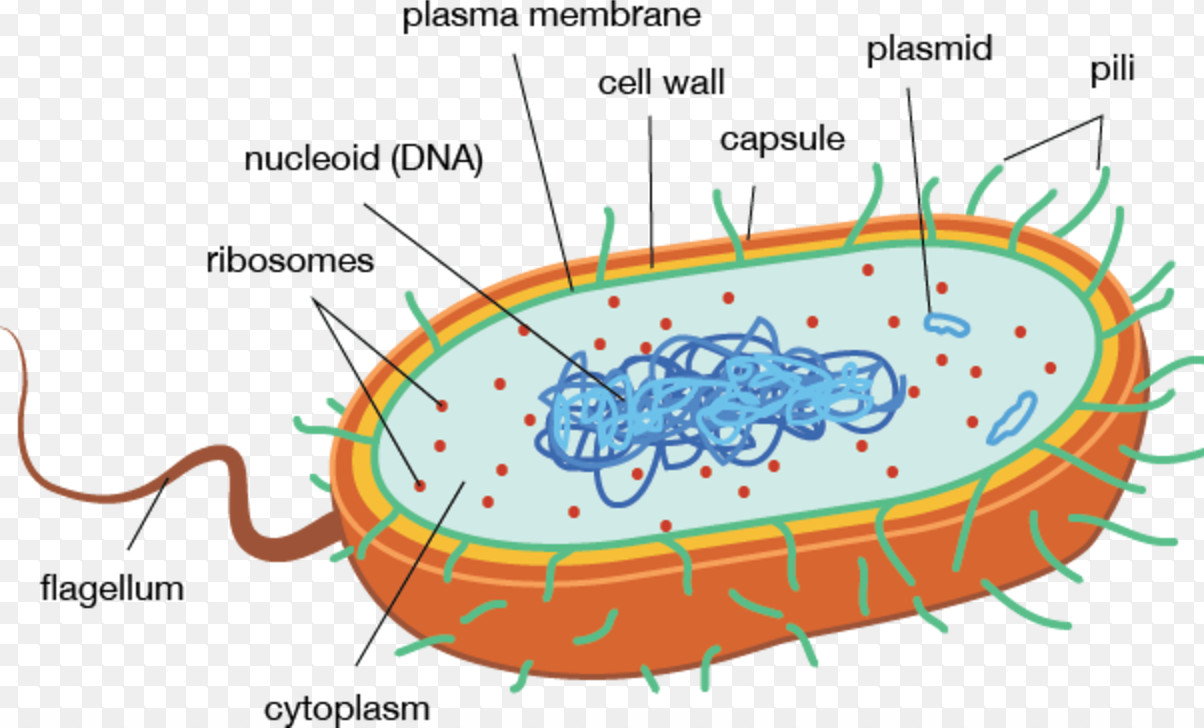
and eukaryotic cells 1. Create a Venn diagram or concept map that clearly distinguishes bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic cells in terms of their genome organization, organelles, cell envelopes, ribosome size and component molecules, and cytoskeleton. 2. Determine the type of microbe when given a description of a newly discovered microbe. 56
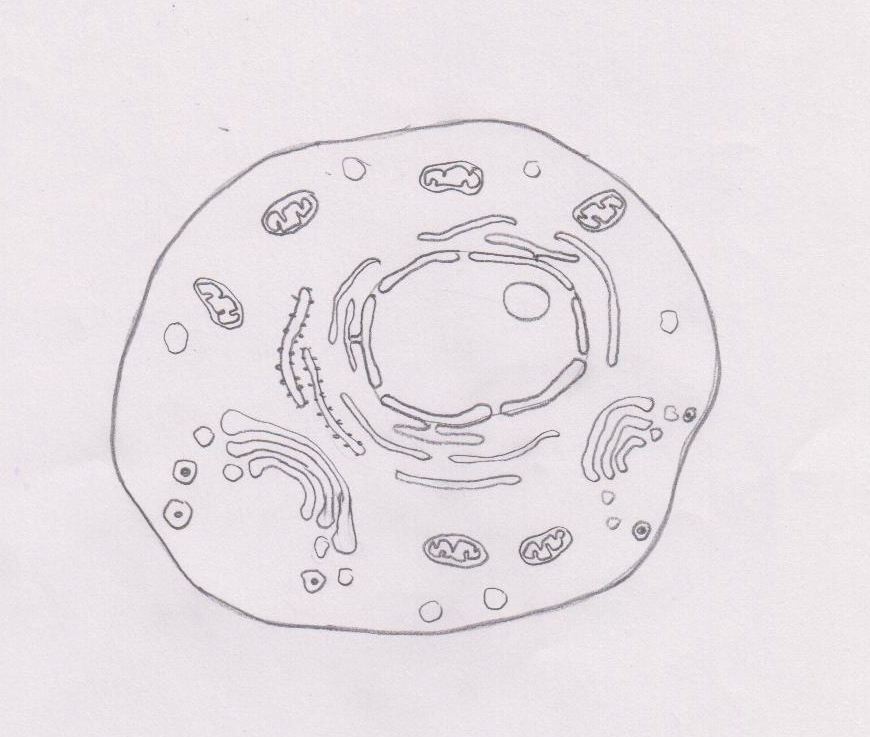
Diagram of a eukaryotic cell
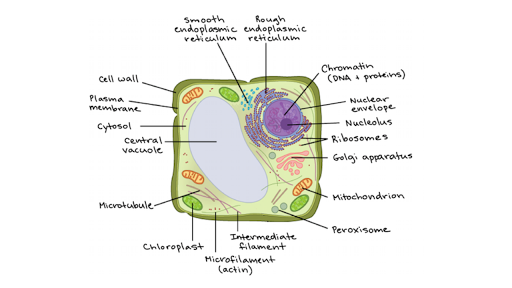
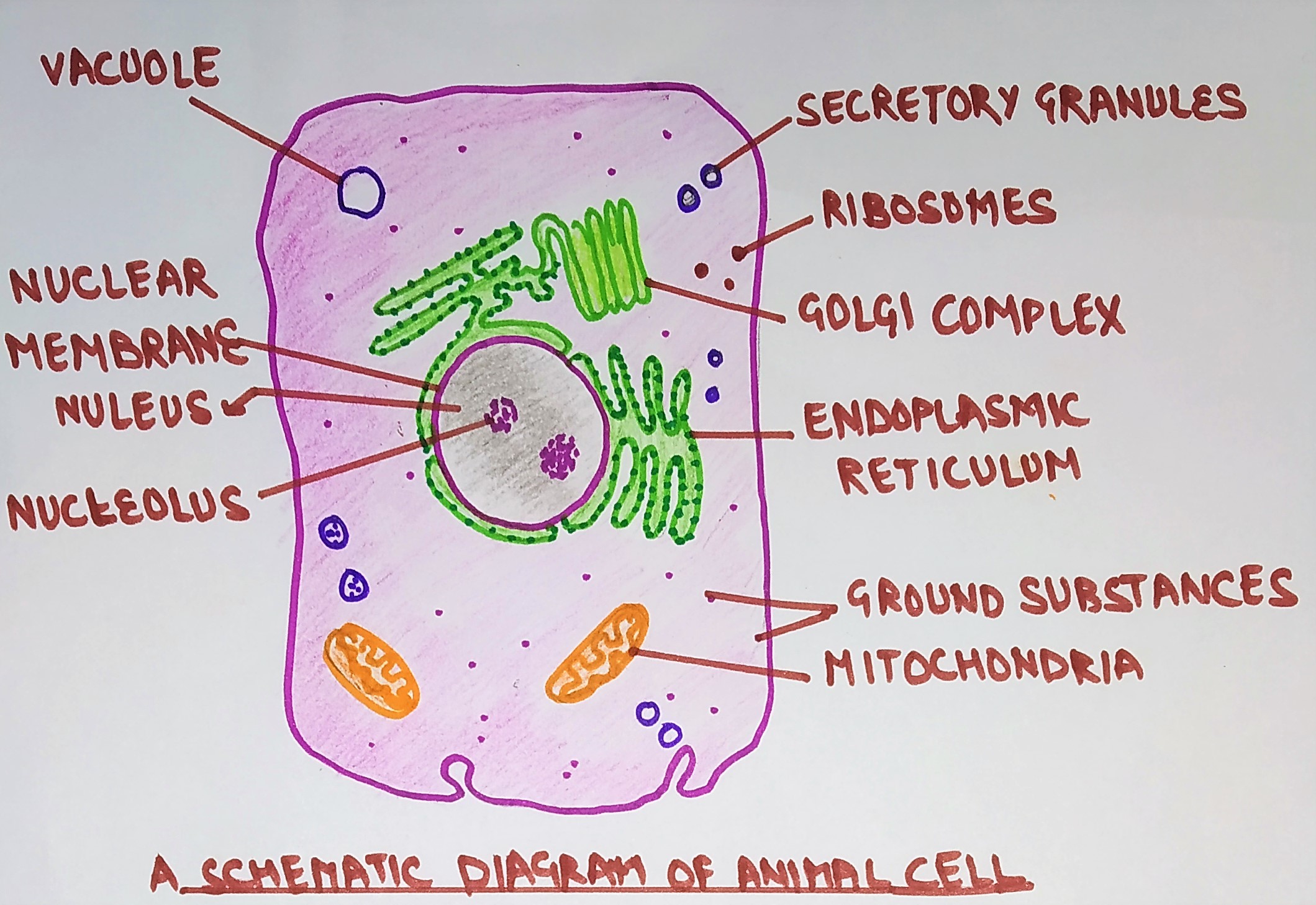
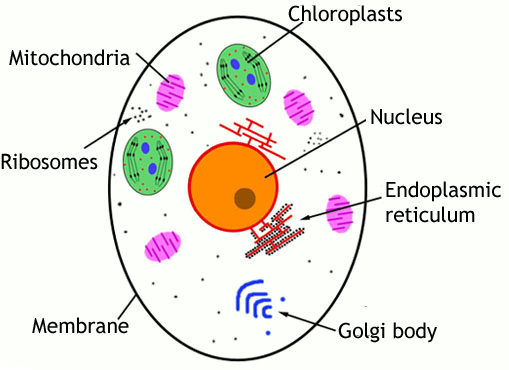
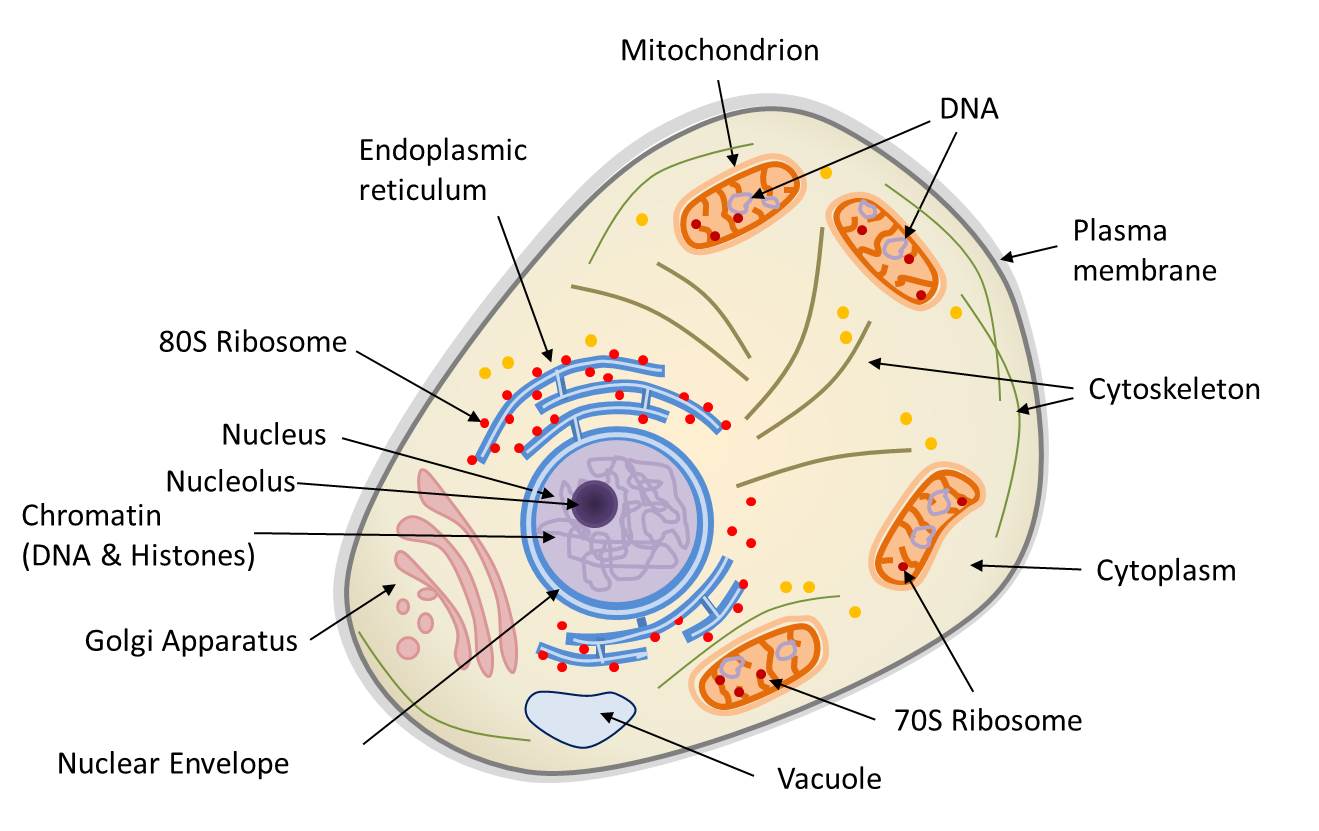
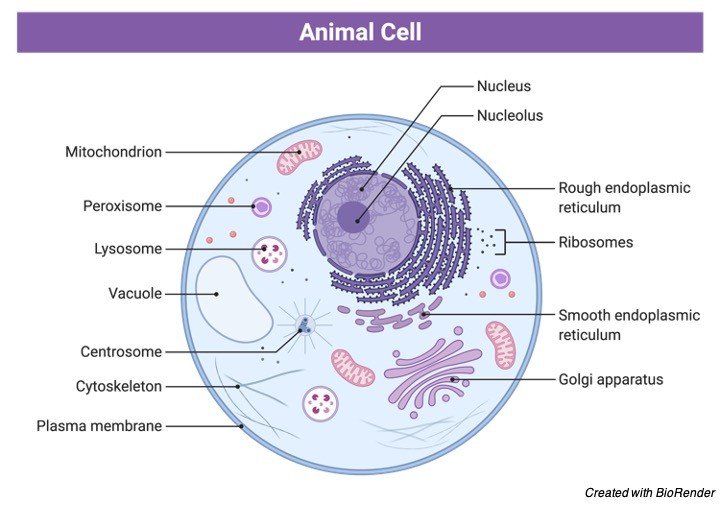
The nucleus is the site of most cellular genetic material, DNA. The Golgi Apparatus processes and packages proteins. The endoplasmic reticulum is the site of protein and lipid production. The mitochondrion is the site where energy stored. The plasma membrane composed of a phospholipid bilayer controls cellular traffic. The Eukaryotic Cell. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum: Throughout the eukaryotic cell, especially those responsible for the production of hormones and other secretory products, is a vast network of membrane-bound vesicles and tubules called the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER for short. The ER is a continuation of the outer nuclear membrane and its varied functions ... Pinocytosis (cell drinking) is a process in which the substances being ingested are in solution form. Cell eating and drinking are both undertaken in association with lysosymes which complete the breakdown of the engulfed material. As you read the information on each organelle, refer to …
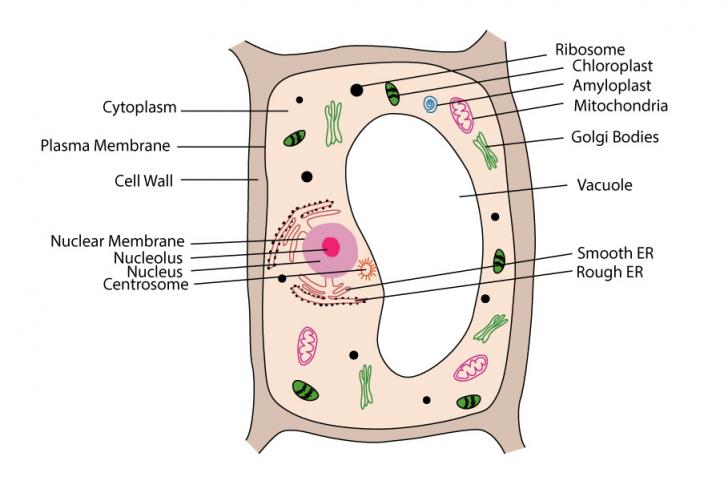
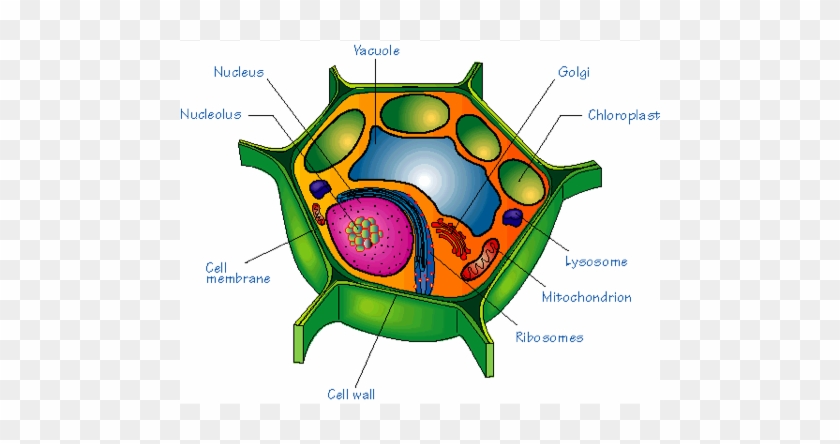
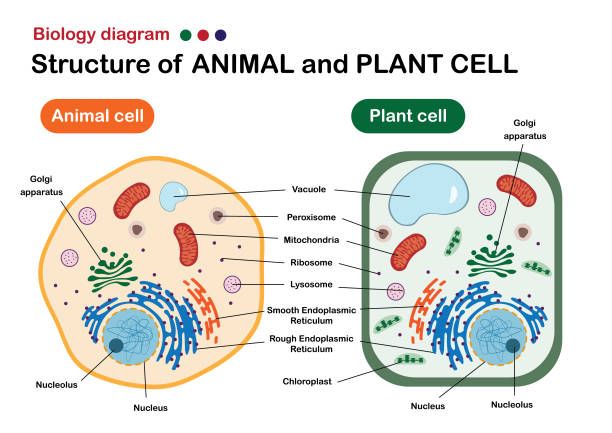
Diagram of a eukaryotic cell. Plant Cell Diagram. The plant cell is rectangular and comparatively larger than the animal cell. Even though plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share a few cell organelles, plant cells are quite distinct when compared to animal cells as they perform different functions. Some of these differences can be clearly understood when the cells ... Jul 05, 2021 · Cell Organelles definition. Cell organelle is a specialized entity present inside a particular type of cell that performs a specific function. There are various cell organelles, out if which, some are common in most types of cells like cell membranes, nucleus, and cytoplasm. Mar 04, 2021 · Cell Membrane Function In Animal Cell. Animal cells are common names for eukaryotic cells that make up animal tissue. Because it does not have a hard cell wall, animal cells vary in shape. A bacteria diagram clearly helps us to learn extra about this single cell organisms that have neither membrane-bounded nucleolus or organelles like […] Eukaryotic Cell Cycle. The cell cycle is described as a series of events that repeat several times and include DNA synthesis or duplication, cell growth, and cell division. Cell division results in the formation of two or four new daughter cells. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle is more complicated than prokaryotes. 4.
Eukaryotic cells have the nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane. The cell has mitochondria. Flagella and cilia are the locomotory organs in a eukaryotic cell. A cell wall is the outermost layer of the eukaryotic cells. The cells divide by a process called mitosis. The eukaryotic cells contain a cytoskeletal structure. The Cell Wall. In Figure 3.8 b, the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. Fungal and protist cells also have cell walls. Jun 24, 2019 · Eukaryotic cells also have organelles, which are membrane-bound structures found within the cell. If you looked at eukaryotic cells under a microscope, you'd see distinct structures of all shapes and sizes. Prokaryotic cells, on the other hand, would look more uniform because they don't have those membrane-bound structures to break up the cell. Feb 04, 2021 · What is a Nucleus. The nucleus is a double membrane-bound organelle located centrally only in a eukaryotic cell, enclosing the DNA, the genetic material. It is the most important and defining feature of all higher organisms, including plant and animal cells, whose main function is to control and coordinate the functioning of the entire cell.. The word ‘nucleus’ (plural: nuclei) is derived ...
Biology questions and answers. Complete the diagram of a eukaryotic gene. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Reset Help 3' UTR stop codon GGU AG CGU CUU start codon GCU 5 UTR CAU UGG Gene Intron 1 Intron 2 Promoter GT AG GT AG GCCTAG Termination CA Exon 1 Exon 2 Exon 3 5" Exon 3 Met-Gly-His-Arg-Leu-Trp-AlaAla. Hello Friends in this video I tell you about how can we draw labelled diagram of eukaryotic cell in easy way so friends if you have problem in any other thin... Feversham College. Q1.The diagram shows a eukaryotic cell. (a) Complete the table by giving the letter labelling the organelle that matches the function. (b) Use the scale bar in the diagram above to calculate the magnification of the drawing. Show your working. The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Eukaryotes have two major types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is used to produce new body cells for growth and healing, while meiosis is used to produce sex cells (eggs and sperm). Meiosis will be discussed in a later chapter.
Eukaryotic Cell Envelope & External Structures Cell Wall: The cells of plants, algae and fungi have thick, protective cell walls, which provide support, help maintain the shape of the cell, and prevent the cell from taking in too much fresh water and bursting.
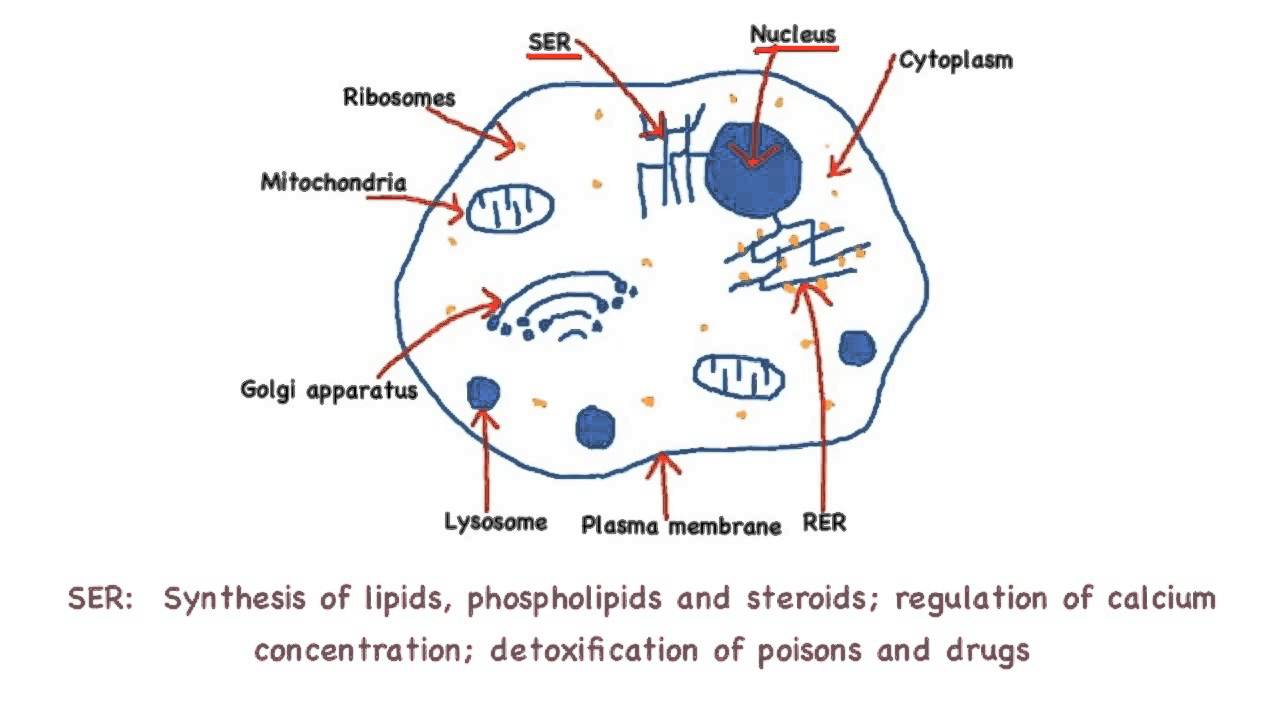
Pinocytosis (cell drinking) is a process in which the substances being ingested are in solution form. Cell eating and drinking are both undertaken in association with lysosymes which complete the breakdown of the engulfed material. As you read the information on each organelle, refer to …
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum: Throughout the eukaryotic cell, especially those responsible for the production of hormones and other secretory products, is a vast network of membrane-bound vesicles and tubules called the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER for short. The ER is a continuation of the outer nuclear membrane and its varied functions ...
The nucleus is the site of most cellular genetic material, DNA. The Golgi Apparatus processes and packages proteins. The endoplasmic reticulum is the site of protein and lipid production. The mitochondrion is the site where energy stored. The plasma membrane composed of a phospholipid bilayer controls cellular traffic. The Eukaryotic Cell.

Cross Section Diagram Of Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Stock Photo Picture And Royalty Free Image Image 2567617

Eukaryotic Vs Prokaryotic Cells Educational Biology Vector Illustration Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Design Eukaryotic 170058733






















0 Response to "37 diagram of a eukaryotic cell"
Post a Comment