37 d orbital energy level diagram
Energy Levels, Orbital Diagrams, Electron Config, Noble Gas - Google Slides. Energy Levels. We know, atoms have energy levels. The periodic table shows us energy levels 1 - 7. Energy Levels. By default electrons are found in the lowest energy level possible, close to the nucleus. This is called the ground state. Molecular Orbital Theory: Energy level diagram for molecular orbitals. Molecular orbital theory was put forward by Hund and Mullikan in 1932. This theory is modern and more rational. This theory assume that in molecules, atomic orbitals lose their identity and the electrons in molecules are present in new orbitals called molecular orbitals.
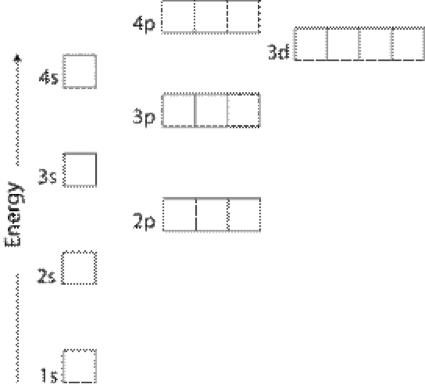
The diagram (not to scale) summarises the energies of the orbitals up to the 4p level. The oddity is the position of the 3d orbitals. They are shown at a slightly higher level than the 4s - and so it is the 4s orbital which will fill first, followed by all the 3d orbitals and then the 4p orbitals.
D orbital energy level diagram
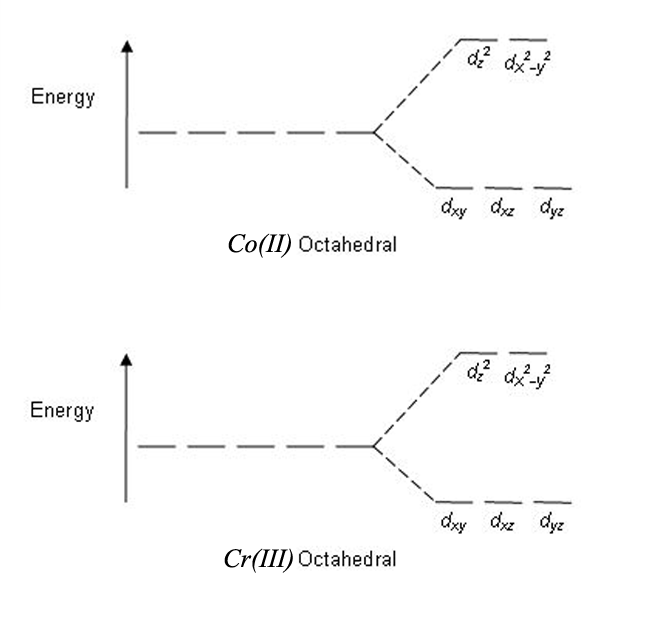
• The energy increase of the e g orbitals and the energy decrease of the t 2g orbitals must be balancedrelative to the energy of the hypotheticalsphericalfield(aka the barycenter).• The energy of each of the two orbitals of the e g set rises by +3/5 o (+6 Dq) while the energy of eachof the three t 2g orbitalsfallsby ‐2/5 o(‐4Dq). • Thisresults inno netenergy changefor the system: The energy of an orbital depends on the shape and size of the orbital. In a multiple-electron system, the shielding effect also influences the orbital's energy. Energies of orbitals are quantized as per quantum mechanics. Thus, there are only selected energy levels available, which an electron can occupy. An electron residing in a particular ... A molecular orbital is a region of space in a covalent species where electrons are likely to be found. The combination of two atomic orbitals always forms two molecular orbitals; the bonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy, and the antibonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy, than the original atomic orbitals.
D orbital energy level diagram. Like all ligand-metal interaction diagrams, the energy levels of the ligands by themselves are shown on one side. The metal's electronic energy levels are shown on the other side. The result of their interaction, a metal-ligand complex, is shown in the middle. The d orbital splitting diagram is shown in a box. The overall molecular orbital energy level diagram for this type of π-bonding in octahedral complexes can be shown as: Figure 21. The generation of π and σ-molecular orbitals in octahedral complexes. Buy the complete book with TOC navigation, high resolution images and Krypton Orbital Diagram. Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of krypton (atomic number: 36), the most common . Box spin diagram of outer electron orbitals for the electron configuration of the atom . 36 Krypton, Kr, [Ar]3ds24p6 = [Kr] (), [Ar]3d 4s 4p v. stable, Kr . Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. ... If N b = Na,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of electron in the bonding molecular orbitals. 2) Stability of molecules in terms of bond order.
A P-Orbital in the second energy level is a 2p orbital ( 2p(x), 2p(y), 2p(z) ) A P-Orbital in the third energy level is a 3p orbital ( 3p(x), 3p(y), 3p(z) ) etc. In addition, the third and subsequent energy levels each contain five D-Orbitals, the fourth and subsequent energy levels contain seven F-Orbitals and so on. The molecular orbital energy- level diagram that results is constructed by putting the molecular orbitals in order of increasing number of internuclear nodal planes, the orbital with no such nodal plane lying at lowest energy and the orbital with nodal planes between all the atoms lying at highest energy. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO ... Your diagram should show the relative energy of each orbital, and the number of electron in each orbital. Question: Using crystal field theory, draw an electron box energy level diagram for the valence d orbital on the cobalt atom in a [CoBr_6]^3- complex. Your diagram should show the relative energy of each orbital, and the number of electron ... with the. d. orbital being one level lower than the energy level it is on. orbital diagram for arsenic see more ideas approximately from diagram electron configuration gallery & create your house design images related to pictures as well help you in locating the solution are seeking about itOrbital diagram for arsenic.
Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels. This video explains s, p, d, and f orbitals, sublevels, and their shapes. It discusses the 4 quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms. n represents the energy leve... Therefore, the electron energy levels of these five d-orbitals in mechanics forming a set five-fold degenerate energy level and the shape diagram dimensions of these orbitals identify by the principal, azimuthal, magnetic, spin quantum number or numbers of the atom for physics or chemistry courses. The overall molecular orbital energy level diagram for σ-bonding in octahedral complexes can be shown as: Figure 10. The formation of σ-molecular orbitals (bonding, antibonding and non-bonding) in octahedral complexes of transition metals. Buy the complete book with TOC navigation,
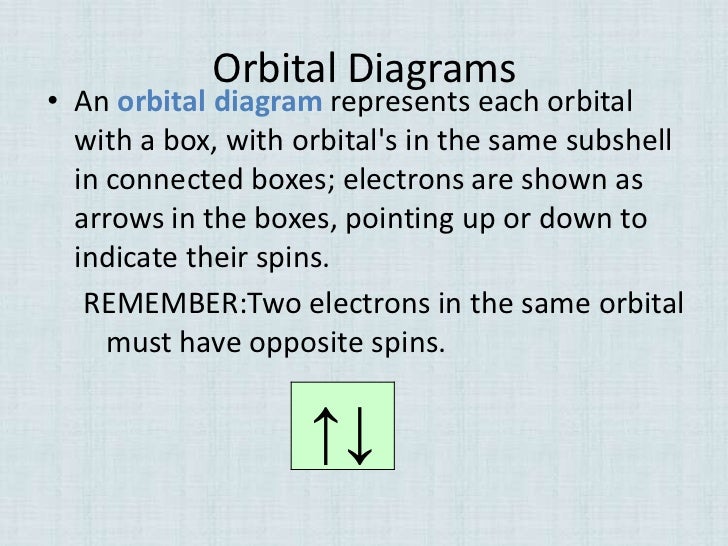
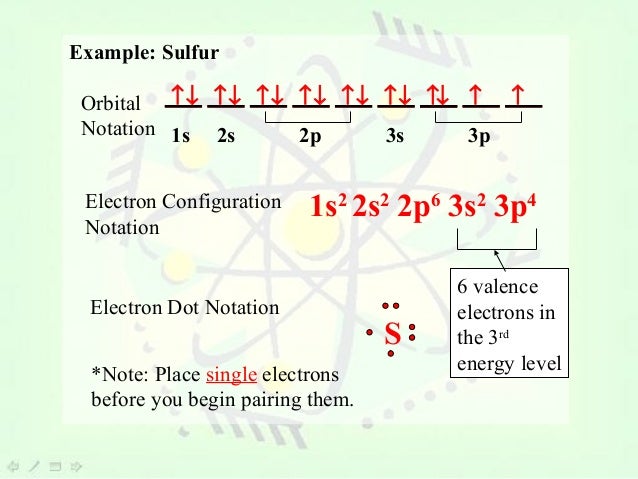
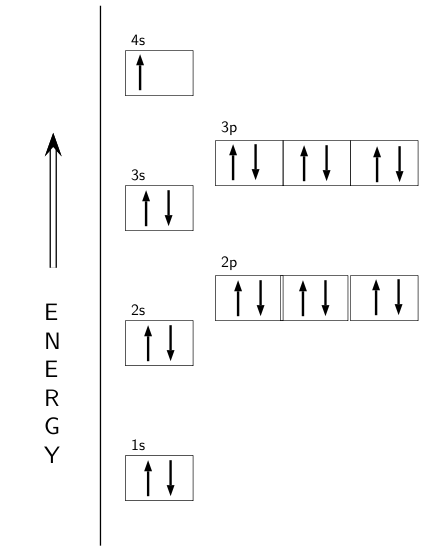
Orbital Diagram 1s ↿⇂ 2s ↿⇂ 2p ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿⇂ 3s ↿⇂ 3p ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿⇂ 3d ↿⇂ ↿ ↿ ↿ ↿ 4s ↿⇂ 4p 4d 4f: ... Two of these are in the lowest energy level, eight are in the second energy level and then one electron is in the third energy level.
The s-orbital has the azimuthal quantum number value of 0, the p-orbital has a value of 1, and the d-orbital has two and f-orbital 3. The orbital energy levels of these are varied, s-orbital having the lowest energy level and f-orbital being the highest, summed up as s < p <; d < f.
All levels except the first have p orbitals. d ORBITALS. In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals which become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels. At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3px, 3py, 3pz). At ...
Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram . For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right.
Figure 6.27 "Orbital Energy Level Diagram for the Hydrogen Atom" shows that the energy levels become closer and closer together as the value of n increases, as expected because of the 1/n 2 dependence of orbital energies. Figure 6.27 Orbital Energy Level Diagram for the Hydrogen Atom.
For example, the orbital 1s (pronounced as the individual numbers and letters: "'one' 'ess'") is the lowest energy level (n = 1) and has an angular quantum number of ℓ = 0, denoted as s. Orbitals with ℓ = 1, 2 and 3 are denoted as p, d and f respectively.
d and f orbitals. In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals which become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels. At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3p x, 3p y, 3p z). At the third level there are a total of ...
another twice-degenerate energy level consisting of $\mathrm{d}_{xy}$ and $\mathrm{d}_{x^2-y^2}$ The first two should be immediately obvious, the third maybe not. ... What is the correct molecular orbital diagram for the d orbitals in platinum for the tetraammineplatinum(II) complex?
Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams: Linear Polyatomic Molecules . This exercise assumes that you are familiar with the "count and sort" algorithm described in Exercise 2.3 (which also contains a table of atomic orbital energies).

Catoptromancy....(or Enoptromancy)..Looking into water's mirror to see the future or contact a supernatural entity...suspended by a thread till its based touched the surface of the water, having first prayed to the goddess and offered incense.
The molecular, sp 3 orbitals are arranged in a tetrahedron, with bond angles of 109.5 o. Each of the 1s orbitals of H will overlap with one of these hybrid orbitals to give the predicted tetrahedral geometry and shape of methane, CH 4. Hybridization also changes the energy levels of the orbitals. The 2s orbital of carbon is lower in energy than the 2p orbitals, since it is more penetrating.
molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the NO molecule. We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2. The bond order is 2.5. Figure 9.42: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure 9.43: A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule.
A molecular orbital is a region of space in a covalent species where electrons are likely to be found. The combination of two atomic orbitals always forms two molecular orbitals; the bonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy, and the antibonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy, than the original atomic orbitals.
The energy of an orbital depends on the shape and size of the orbital. In a multiple-electron system, the shielding effect also influences the orbital's energy. Energies of orbitals are quantized as per quantum mechanics. Thus, there are only selected energy levels available, which an electron can occupy. An electron residing in a particular ...
• The energy increase of the e g orbitals and the energy decrease of the t 2g orbitals must be balancedrelative to the energy of the hypotheticalsphericalfield(aka the barycenter).• The energy of each of the two orbitals of the e g set rises by +3/5 o (+6 Dq) while the energy of eachof the three t 2g orbitalsfallsby ‐2/5 o(‐4Dq). • Thisresults inno netenergy changefor the system:





















0 Response to "37 d orbital energy level diagram"
Post a Comment