37 brain diagram reticular formation
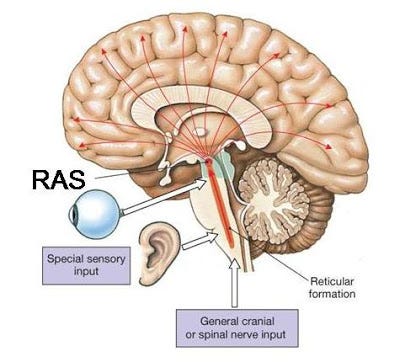
The reticular formation is found bilaterally in the brain and is therefore able to provide motor control to both sides of the brain when a person laughs or smiles. Since these fibers do not integrate with the corticobulbar fibers (also involved in facial expression), a patient may still smile symmetrically even if they have suffered a ... Reticular formation nuclei that modulate activity of the cerebral cortex are part of the reticular activating system. Effects of Damage. Mass lesions in the ...
Definition. The reticular formation is a neuron network in the brainstem that enables consciousness, sensory and motor function, and endocrine and neurotransmitter regulation. This part of the central nervous system, spread in three main columns from one end of the brainstem to the other, is a core relay point that connects the nerves of the spinal cord with the brain via efferent and afferent ...
Brain diagram reticular formation
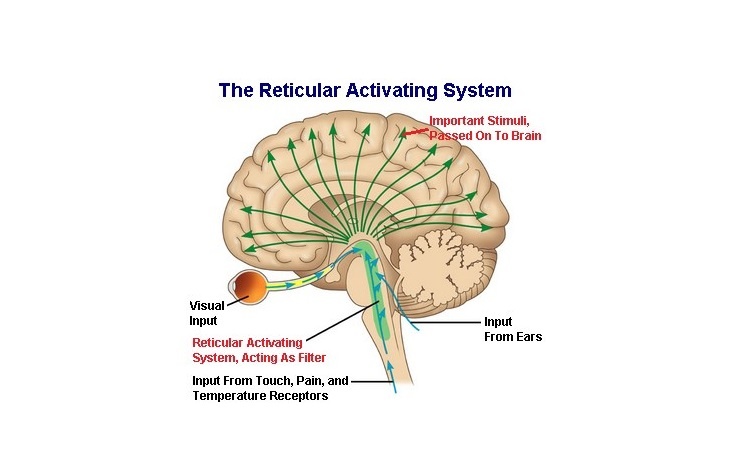
Reticular Formation Diagram. angelo. July 3, 2021. Pin By Jason Sun On Projets A Essayer Cholinergic Gene Therapy Hypothesis. Reticular Activating System Cholinergic Slow Wave Sleep. Reticular Formation The Reticular Formation Extends Through The Central Core Of The Medulla O Reticular Formation Brain Anatomy And Function Brain Anatomy ... Q: What part of the brain helps you sleep and awaken? Mnemonic: a calm, dreamy pond A: the pons Q: What part of the brain helps you become alert very quickly? Mnemonic: a feather tickling you on the foot while you sleep A: the reticular formation Q: What part of the brain maintains the autonomic activity of your heart and lung? 30.09.2021 · Reticular tissue is a special type of connective tissue that predominates in various locations that have a high cellular content. It has a branched and mesh-like pattern, often called reticulum, due to the arrangement of reticular fibers (reticulin).These fibers are actually type III collagen fibrils.In comparison to the predominant type I collagen, type III fibrils are narrower, do not form ...
Brain diagram reticular formation. Brain Diagram Reticular Formation. Like the spinal cord, the brain is made of mainly gray matter and white matter and hypothalamus); limbic system; reticular activating system. The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the The human reticular formation is composed of almost brain nuclei and contains ... The sulcus limitans is found in the fourth ventricle of the brain.It separates the cranial nerve motor nuclei (medial) from the sensory nuclei (lateral). It can also be located by searching laterally from the medial eminence.It is parallel to the median sulcus.. References. This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 799 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918) Diagram of brain stem showing the nuclei of the cranial nerves. Details; Part of: Medulla oblongata: Artery: AICA: Vein: Anterior medullary: Identifiers; Latin: Nucleus nervi facialis: MeSH: D065828: NeuroNames: 586: NeuroLex ID: birnlex_903: TA98: A14.1.05.412: TA2: 5939: FMA: 54572: Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy [edit on Wikidata] The facial motor nucleus is a collection of neurons in the ... 12.09.2020 · 54 Likes, 13 Comments - UCLA VA Physiatry Residency (@uclava_pmrresidency) on Instagram: “Resident’s Corner: Name: David Huy Blumeyer, MD …
The limbic system includes the hippocampal formation, amygdala, septal nuclei, cingulate cortex, entorhinal cortex, perirhinal cortex, and parahippocampal cortex. These last three cortical areas comprise different portions of the temporal lobe. (Some experts would also include parts of the hypothalamus, thalamus, midbrain reticular formation, and olfactory areas in the limbic system.) 5.2 ... 25 Jul 2015 — The reticular formation is found in the brainstem, at the center of ... Nolte J. The Human Brain: An Introduction to its Functional Anatomy. The reticular formation is the powerhouse portion of the brain, mostly found in the brain stem. There are multiple clusters of nuclei, each responsible for different things. The reticular formation is the primary regulator of arousal and consciousness. During sleep, the center normally suppresses the individual’s level of consciousness. The Brain Stem contains three subdivisions: the Midbrain, the ... Anatomy of the Reticular Formation. The reticular formation can be divided into three ...9 pages
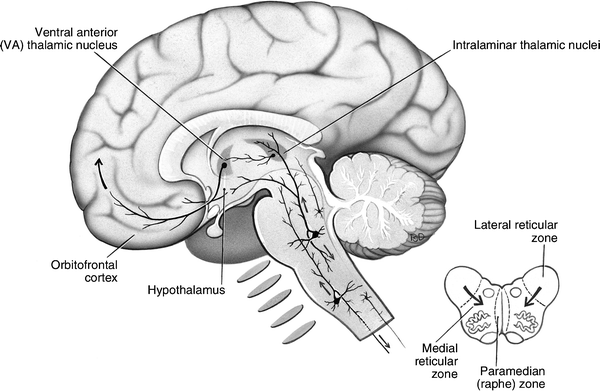
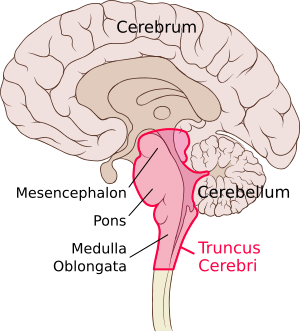
"Chapter 14 - The Brain and Cranial Nerves". Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function (8th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. The Reticular Formation, ...Location: BrainstemMeSH: D012154Latin: formatio reticularisNeuroLex ID: nlx_143558Medial and lateral reticular... · Major subsystems · Ascending reticular activating... Figure 12.16a Cross sections through different regions of the brain stem. Dorsal Cerebral aqueduct Superior colliculus Reticular formation Crus cerebri ofVentral cerebral peduncle Fibers of pyramidal tract Substantia nigra (a) Midbrain Red nucleus Medial lemniscus Oculomotor nucleus (III) Periaqueductal gray matter Tectum by MA Fernández-Gil · 2010 · Cited by 74 — Anatomy of the brainstem: a gaze into the stem of life ... the brainstem to form the cranial nerve nuclei, the reticular formation, and pontine nuclei. The reticular formation controls muscle tone in the body and acts as the switch between consciousness and sleep in the brain. The medulla oblongata is a roughly cylindrical mass of nervous tissue that connects to the spinal cord on its inferior border and to the pons on its superior border.
The reticular formation comprises a phylogenetically ancient network of small neurons throughout the brainstem, extending to the thalamus cranially and blending ...
Brainstem Thalamus Reticular Formation Cerebellum The Old Brain Simply Behaviour Applied Behaviour Analysis
Reticular formation, as the name suggests, is a network of neurons and nerve fibers, present in the brain. Earlier, no particular function was known to be associated with the reticular formation. Today, the reticular formation is considered to play a very important role in different activities of the brain and the nervous system.
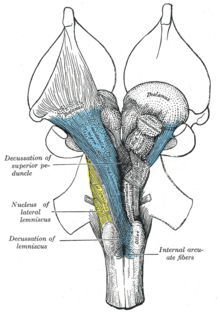
28.10.2021 · The reticular formation occupies a substantial amount of space in the dorsal half of the medulla. It is surrounded by the midline (medially), dorsomedial, dorsolateral, and lateral groups of nuclei and tracts mentioned above. The medial lemniscus occupies the ventral midline of the medulla. It is dorsally related to the pyramids and medial to the inferior and medial accessory olivary nuclei ...
Other articles where reticular formation is discussed: activation: …brain, but primarily from the reticular formation, the nerve network in the midbrain ...
23.07.2020 · Diagram showing the lobes of the brain. Image Source: Wikimedia Commons . The parietal lobe is located at the top of the brain, between the frontal and occipital lobe. It consists of the somatosensory cortex and is responsible for integrating sensory information from different parts of the body, especially visual information related to navigation and spatial orientation. The somatosensory ...
The reticular formation is a complex network of brainstem nuclei and neurons that serve as a major integration and relay center for many vital brain systems to coordinate functions necessary for survival. The structure of the reticular formation forms a net-like connection of nuclei and neurons, hence its name “reticular,” which correlates to its function of integrating, coordinating, and ...
B.L. Walter, A.G. Shaikh, in Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences (Second Edition), 2014 Reticular Activating System. The reticular activating system spans an extensive portion of the brainstem. Most of the neurons comprising the midbrain reticular formation lie dorsal and lateral to the red nuclei. Complex interactions between multiple neurotransmitters modulate the action of the ...
30.09.2021 · Reticular tissue is a special type of connective tissue that predominates in various locations that have a high cellular content. It has a branched and mesh-like pattern, often called reticulum, due to the arrangement of reticular fibers (reticulin).These fibers are actually type III collagen fibrils.In comparison to the predominant type I collagen, type III fibrils are narrower, do not form ...
Q: What part of the brain helps you sleep and awaken? Mnemonic: a calm, dreamy pond A: the pons Q: What part of the brain helps you become alert very quickly? Mnemonic: a feather tickling you on the foot while you sleep A: the reticular formation Q: What part of the brain maintains the autonomic activity of your heart and lung?
Reticular Formation Diagram. angelo. July 3, 2021. Pin By Jason Sun On Projets A Essayer Cholinergic Gene Therapy Hypothesis. Reticular Activating System Cholinergic Slow Wave Sleep. Reticular Formation The Reticular Formation Extends Through The Central Core Of The Medulla O Reticular Formation Brain Anatomy And Function Brain Anatomy ...
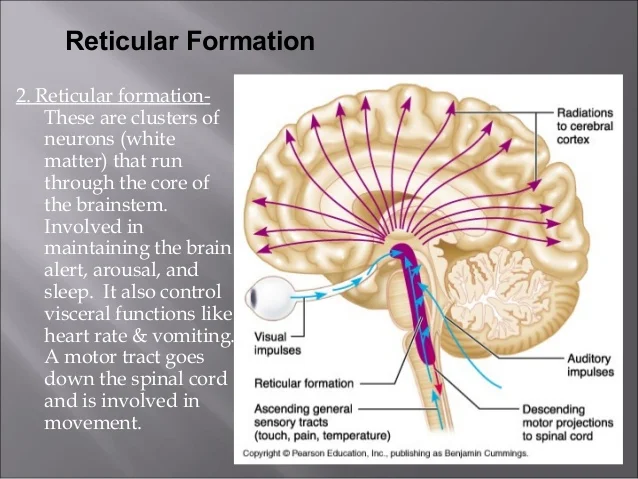

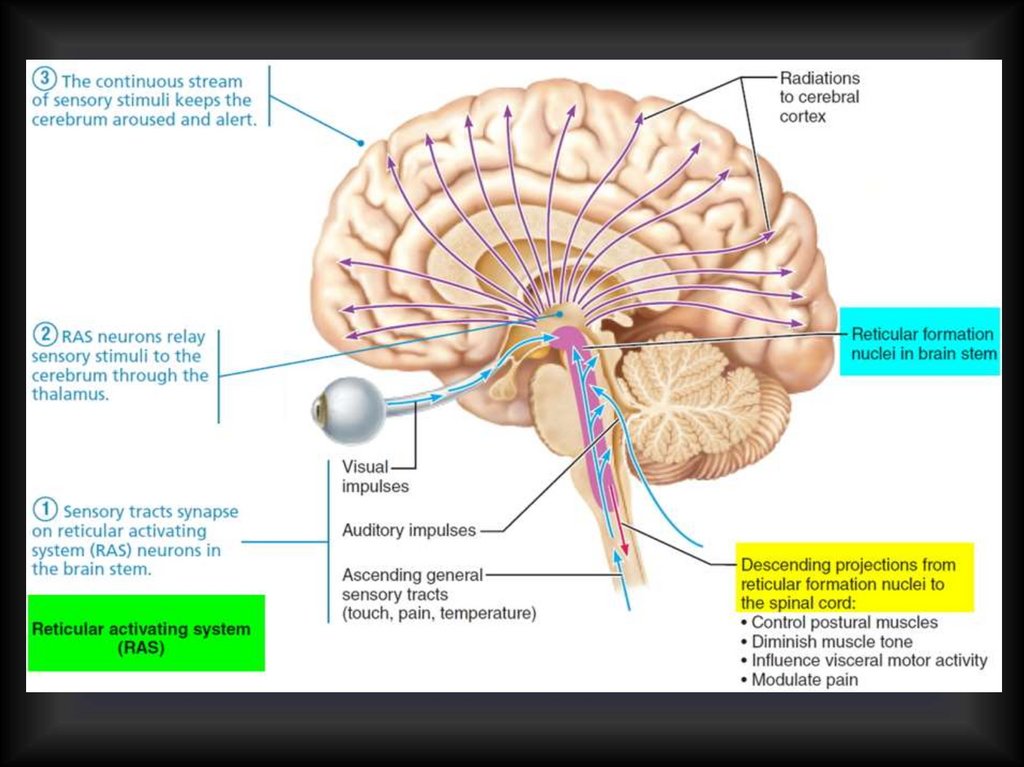


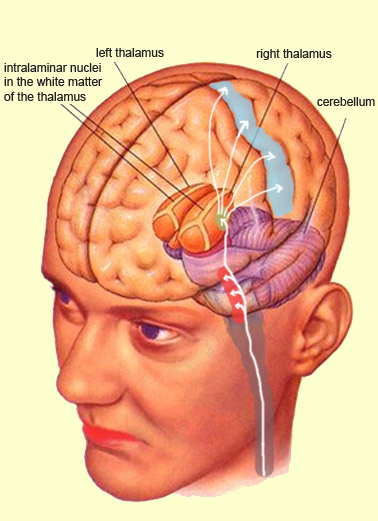


:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11464/image5.png)


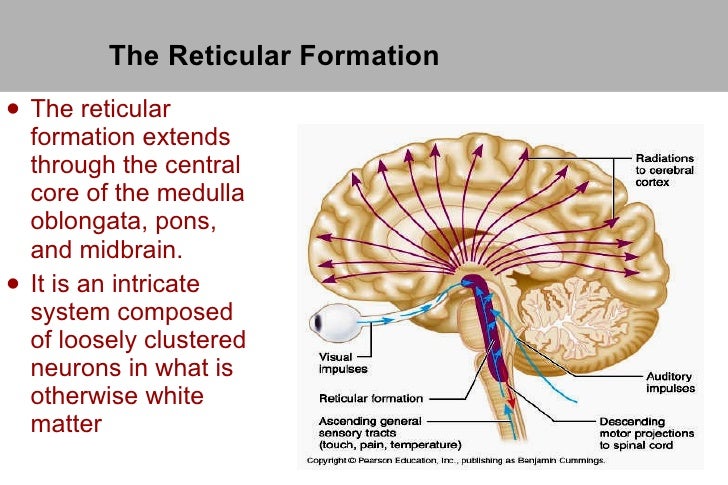









0 Response to "37 brain diagram reticular formation"
Post a Comment